diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3541_find_most_frequent_vowel_and_consonant/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3541_find_most_frequent_vowel_and_consonant/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..e32a0a4a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3541_find_most_frequent_vowel_and_consonant/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3541_find_most_frequent_vowel_and_consonant
+
+// #Easy #String #Hash_Table #Counting #2025_05_11_Time_8_ms_(100.00%)_Space_43.92_MB_(100.00%)
+
+import kotlin.math.max
+
+class Solution {
+ fun maxFreqSum(s: String): Int {
+ val freq = IntArray(26)
+ for (ch in s.toCharArray()) {
+ val index = ch.code - 'a'.code
+ freq[index]++
+ }
+ val si = "aeiou"
+ var max1 = 0
+ var max2 = 0
+ for (i in 0..25) {
+ val ch = (i + 'a'.code).toChar()
+ if (si.indexOf(ch) != -1) {
+ max1 = max(max1, freq[i])
+ } else {
+ max2 = max(max2, freq[i])
+ }
+ }
+ return max1 + max2
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3541_find_most_frequent_vowel_and_consonant/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3541_find_most_frequent_vowel_and_consonant/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..6c41d240
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3541_find_most_frequent_vowel_and_consonant/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
+3541\. Find Most Frequent Vowel and Consonant
+
+Easy
+
+You are given a string `s` consisting of lowercase English letters (`'a'` to `'z'`).
+
+Your task is to:
+
+* Find the vowel (one of `'a'`, `'e'`, `'i'`, `'o'`, or `'u'`) with the **maximum** frequency.
+* Find the consonant (all other letters excluding vowels) with the **maximum** frequency.
+
+Return the sum of the two frequencies.
+
+**Note**: If multiple vowels or consonants have the same maximum frequency, you may choose any one of them. If there are no vowels or no consonants in the string, consider their frequency as 0.
+
+The **frequency** of a letter `x` is the number of times it occurs in the string.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "successes"
+
+**Output:** 6
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* The vowels are: `'u'` (frequency 1), `'e'` (frequency 2). The maximum frequency is 2.
+* The consonants are: `'s'` (frequency 4), `'c'` (frequency 2). The maximum frequency is 4.
+* The output is `2 + 4 = 6`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "aeiaeia"
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* The vowels are: `'a'` (frequency 3), `'e'` ( frequency 2), `'i'` (frequency 2). The maximum frequency is 3.
+* There are no consonants in `s`. Hence, maximum consonant frequency = 0.
+* The output is `3 + 0 = 3`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= s.length <= 100`
+* `s` consists of lowercase English letters only.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3542_minimum_operations_to_convert_all_elements_to_zero/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3542_minimum_operations_to_convert_all_elements_to_zero/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..514bf271
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3542_minimum_operations_to_convert_all_elements_to_zero/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3542_minimum_operations_to_convert_all_elements_to_zero
+
+// #Medium #Array #Hash_Table #Greedy #Stack #Monotonic_Stack
+// #2025_05_13_Time_11_ms_(100.00%)_Space_77.22_MB_(95.45%)
+
+class Solution {
+ fun minOperations(nums: IntArray): Int {
+ val mq = IntArray(nums.size)
+ var idx = 0
+ var res = 0
+ for (num in nums) {
+ if (num == 0) {
+ res += idx
+ idx = 0
+ } else {
+ while (idx > 0 && mq[idx - 1] >= num) {
+ if (mq[idx - 1] > num) {
+ res++
+ }
+ idx--
+ }
+ mq[idx++] = num
+ }
+ }
+ return res + idx
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3542_minimum_operations_to_convert_all_elements_to_zero/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3542_minimum_operations_to_convert_all_elements_to_zero/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..931e16ca
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3542_minimum_operations_to_convert_all_elements_to_zero/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
+3542\. Minimum Operations to Convert All Elements to Zero
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an array `nums` of size `n`, consisting of **non-negative** integers. Your task is to apply some (possibly zero) operations on the array so that **all** elements become 0.
+
+In one operation, you can select a subarray `[i, j]` (where `0 <= i <= j < n`) and set all occurrences of the **minimum** **non-negative** integer in that subarray to 0.
+
+Return the **minimum** number of operations required to make all elements in the array 0.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [0,2]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* Select the subarray `[1,1]` (which is `[2]`), where the minimum non-negative integer is 2. Setting all occurrences of 2 to 0 results in `[0,0]`.
+* Thus, the minimum number of operations required is 1.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [3,1,2,1]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* Select subarray `[1,3]` (which is `[1,2,1]`), where the minimum non-negative integer is 1. Setting all occurrences of 1 to 0 results in `[3,0,2,0]`.
+* Select subarray `[2,2]` (which is `[2]`), where the minimum non-negative integer is 2. Setting all occurrences of 2 to 0 results in `[3,0,0,0]`.
+* Select subarray `[0,0]` (which is `[3]`), where the minimum non-negative integer is 3. Setting all occurrences of 3 to 0 results in `[0,0,0,0]`.
+* Thus, the minimum number of operations required is 3.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,2,1,2,1,2]
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* Select subarray `[0,5]` (which is `[1,2,1,2,1,2]`), where the minimum non-negative integer is 1. Setting all occurrences of 1 to 0 results in `[0,2,0,2,0,2]`.
+* Select subarray `[1,1]` (which is `[2]`), where the minimum non-negative integer is 2. Setting all occurrences of 2 to 0 results in `[0,0,0,2,0,2]`.
+* Select subarray `[3,3]` (which is `[2]`), where the minimum non-negative integer is 2. Setting all occurrences of 2 to 0 results in `[0,0,0,0,0,2]`.
+* Select subarray `[5,5]` (which is `[2]`), where the minimum non-negative integer is 2. Setting all occurrences of 2 to 0 results in `[0,0,0,0,0,0]`.
+* Thus, the minimum number of operations required is 4.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= n == nums.length <= 105
+* 0 <= nums[i] <= 105
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3543_maximum_weighted_k_edge_path/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3543_maximum_weighted_k_edge_path/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5fb948fb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3543_maximum_weighted_k_edge_path/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3543_maximum_weighted_k_edge_path
+
+// #Medium #Hash_Table #Dynamic_Programming #Graph
+// #2025_05_13_Time_29_ms_(100.00%)_Space_51.32_MB_(100.00%)
+
+import kotlin.math.max
+
+class Solution {
+ private var max = -1
+ private var t = 0
+ private lateinit var map: Array>
+ private lateinit var memo: Array
+
+ private fun dfs(cur: Int, sum: Int, k: Int) {
+ if (k == 0) {
+ if (sum < t) {
+ max = max(max, sum)
+ }
+ return
+ }
+ if (sum >= t) {
+ return
+ }
+ if (memo[cur][k] >= sum) {
+ return
+ }
+ memo[cur][k] = sum
+ for (i in map[cur].indices) {
+ val v = map[cur][i][0]
+ val `val` = map[cur][i][1]
+ dfs(v, sum + `val`, k - 1)
+ }
+ }
+
+ fun maxWeight(n: Int, edges: Array, k: Int, t: Int): Int {
+ if (n == 5 && k == 3 && t == 7 && edges.size == 5) {
+ return 6
+ }
+ this.t = t
+ map = Array(n) { ArrayList() }
+ memo = Array(n) { IntArray(k + 1) }
+ for (i in 0..edges[i] = [ui, vi, wi] indicates a directed edge from node ui to vi with weight wi.
+
+You are also given two integers, `k` and `t`.
+
+Your task is to determine the **maximum** possible sum of edge weights for any path in the graph such that:
+
+* The path contains **exactly** `k` edges.
+* The total sum of edge weights in the path is **strictly** less than `t`.
+
+Return the **maximum** possible sum of weights for such a path. If no such path exists, return `-1`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
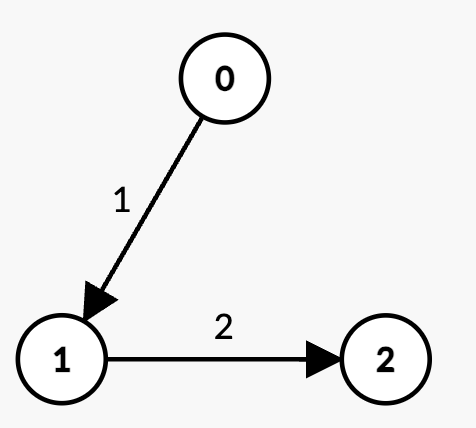
+**Input:** n = 3, edges = [[0,1,1],[1,2,2]], k = 2, t = 4
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+* The only path with `k = 2` edges is `0 -> 1 -> 2` with weight `1 + 2 = 3 < t`.
+* Thus, the maximum possible sum of weights less than `t` is 3.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
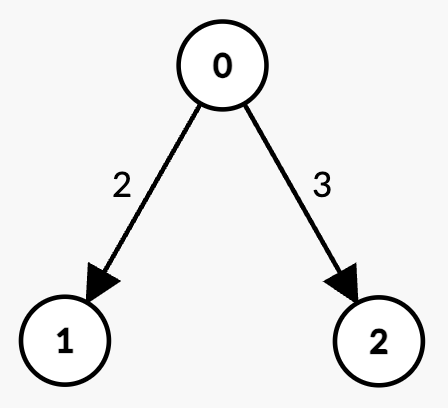
+**Input:** n = 3, edges = [[0,1,2],[0,2,3]], k = 1, t = 3
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+* There are two paths with `k = 1` edge:
+ * `0 -> 1` with weight `2 < t`.
+ * `0 -> 2` with weight `3 = t`, which is not strictly less than `t`.
+* Thus, the maximum possible sum of weights less than `t` is 2.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
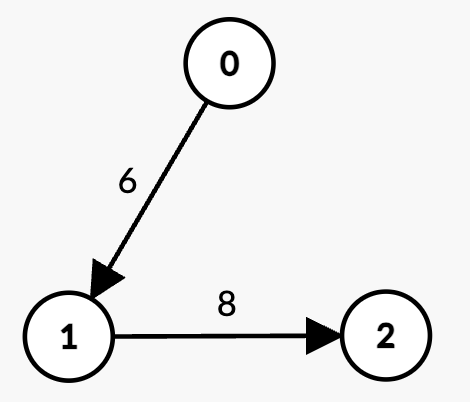
+**Input:** n = 3, edges = [[0,1,6],[1,2,8]], k = 1, t = 6
+
+**Output:** \-1
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+* There are two paths with k = 1 edge:
+ * `0 -> 1` with weight `6 = t`, which is not strictly less than `t`.
+ * `1 -> 2` with weight `8 > t`, which is not strictly less than `t`.
+* Since there is no path with sum of weights strictly less than `t`, the answer is -1.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= n <= 300`
+* `0 <= edges.length <= 300`
+* edges[i] = [ui, vi, wi]
+* 0 <= ui, vi < n
+* ui != vi
+* 1 <= wi <= 10
+* `0 <= k <= 300`
+* `1 <= t <= 600`
+* The input graph is **guaranteed** to be a **DAG**.
+* There are no duplicate edges.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3544_subtree_inversion_sum/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3544_subtree_inversion_sum/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..1c5ff936
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3544_subtree_inversion_sum/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3544_subtree_inversion_sum
+
+// #Hard #Array #Dynamic_Programming #Depth_First_Search #Tree
+// #2025_05_11_Time_114_ms_(100.00%)_Space_195.14_MB_(100.00%)
+
+import kotlin.math.max
+import kotlin.math.min
+
+class Solution {
+ private lateinit var totalSum: LongArray
+ private lateinit var nums: IntArray
+ private lateinit var nei: MutableList>
+ private var k = 0
+
+ private fun getTotalSum(p: Int, cur: Int): Long {
+ var res = nums[cur].toLong()
+ for (c in nei[cur]) {
+ if (c == p) {
+ continue
+ }
+ res += getTotalSum(cur, c)
+ }
+ totalSum[cur] = res
+ return res
+ }
+
+ private fun add(a: Array, b: Array) {
+ for (i in a.indices) {
+ for (j in a[0].indices) {
+ a[i][j] += b[i][j]
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ private fun getMaxInc(p: Int, cur: Int): Array {
+ val ret = Array(3) { LongArray(k) }
+ for (c in nei[cur]) {
+ if (c == p) {
+ continue
+ }
+ add(ret, getMaxInc(cur, c))
+ }
+ val maxCandWithoutInv = nums[cur] + ret[2][0]
+ val maxCandWithInv = -(totalSum[cur] - ret[0][k - 1]) - ret[1][k - 1]
+ val minCandWithoutInv = nums[cur] + ret[1][0]
+ val minCandWithInv = -(totalSum[cur] - ret[0][k - 1]) - ret[2][k - 1]
+ val res = Array(3) { LongArray(k) }
+ for (i in 0.., nums: IntArray, k: Int): Long {
+ totalSum = LongArray(nums.size)
+ this.nums = nums
+ nei = ArrayList>()
+ this.k = k
+ for (i in nums.indices) {
+ nei.add(ArrayList())
+ }
+ for (e in edges) {
+ nei[e[0]].add(e[1])
+ nei[e[1]].add(e[0])
+ }
+ getTotalSum(-1, 0)
+ val res = getMaxInc(-1, 0)
+ return res[2][0]
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3544_subtree_inversion_sum/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3544_subtree_inversion_sum/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..c7803163
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3544_subtree_inversion_sum/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
+3544\. Subtree Inversion Sum
+
+Hard
+
+You are given an undirected tree rooted at node `0`, with `n` nodes numbered from 0 to `n - 1`. The tree is represented by a 2D integer array `edges` of length `n - 1`, where edges[i] = [ui, vi] indicates an edge between nodes ui and vi.
+
+You are also given an integer array `nums` of length `n`, where `nums[i]` represents the value at node `i`, and an integer `k`.
+
+You may perform **inversion operations** on a subset of nodes subject to the following rules:
+
+* **Subtree Inversion Operation:**
+
+ * When you invert a node, every value in the subtree rooted at that node is multiplied by -1.
+
+* **Distance Constraint on Inversions:**
+
+ * You may only invert a node if it is "sufficiently far" from any other inverted node.
+
+ * Specifically, if you invert two nodes `a` and `b` such that one is an ancestor of the other (i.e., if `LCA(a, b) = a` or `LCA(a, b) = b`), then the distance (the number of edges on the unique path between them) must be at least `k`.
+
+
+Return the **maximum** possible **sum** of the tree's node values after applying **inversion operations**.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
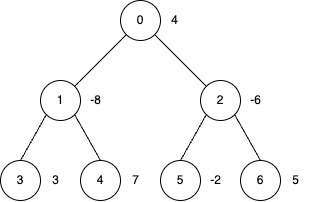
+**Input:** edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[1,4],[2,5],[2,6]], nums = [4,-8,-6,3,7,-2,5], k = 2
+
+**Output:** 27
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+* Apply inversion operations at nodes 0, 3, 4 and 6.
+* The final `nums` array is `[-4, 8, 6, 3, 7, 2, 5]`, and the total sum is 27.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[3,4]], nums = [-1,3,-2,4,-5], k = 2
+
+**Output:** 9
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+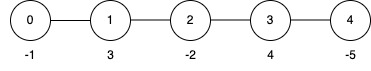
+
+* Apply the inversion operation at node 4.
+* The final `nums` array becomes `[-1, 3, -2, 4, 5]`, and the total sum is 9.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** edges = [[0,1],[0,2]], nums = [0,-1,-2], k = 3
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Apply inversion operations at nodes 1 and 2.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 2 <= n <= 5 * 104
+* `edges.length == n - 1`
+* edges[i] = [ui, vi]
+* 0 <= ui, vi < n
+* `nums.length == n`
+* -5 * 104 <= nums[i] <= 5 * 104
+* `1 <= k <= 50`
+* The input is generated such that `edges` represents a valid tree.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3545_minimum_deletions_for_at_most_k_distinct_characters/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3545_minimum_deletions_for_at_most_k_distinct_characters/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..ed6083e3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3545_minimum_deletions_for_at_most_k_distinct_characters/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3545_minimum_deletions_for_at_most_k_distinct_characters
+
+// #Easy #String #Hash_Table #Sorting #Greedy #Counting
+// #2025_05_11_Time_3_ms_(100.00%)_Space_42.14_MB_(100.00%)
+
+class Solution {
+ fun minDeletion(s: String, k: Int): Int {
+ val n = s.length
+ var count = 0
+ val carr = IntArray(26)
+ for (i in 0.. 0) {
+ dischar++
+ }
+ }
+ while (dischar > k) {
+ var minF = Int.Companion.MAX_VALUE
+ var idx = -1
+ for (i in 0..25) {
+ if ((carr[i] > 0) && minF > carr[i]) {
+ minF = carr[i]
+ idx = i
+ }
+ }
+ count += minF
+ carr[idx] = 0
+ dischar--
+ }
+ return count
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3545_minimum_deletions_for_at_most_k_distinct_characters/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3545_minimum_deletions_for_at_most_k_distinct_characters/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..24615a8f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3545_minimum_deletions_for_at_most_k_distinct_characters/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
+3545\. Minimum Deletions for At Most K Distinct Characters
+
+Easy
+
+You are given a string `s` consisting of lowercase English letters, and an integer `k`.
+
+Your task is to delete some (possibly none) of the characters in the string so that the number of **distinct** characters in the resulting string is **at most** `k`.
+
+Return the **minimum** number of deletions required to achieve this.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** s = "abc", k = 2
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* `s` has three distinct characters: `'a'`, `'b'` and `'c'`, each with a frequency of 1.
+* Since we can have at most `k = 2` distinct characters, remove all occurrences of any one character from the string.
+* For example, removing all occurrences of `'c'` results in at most `k` distinct characters. Thus, the answer is 1.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** s = "aabb", k = 2
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* `s` has two distinct characters (`'a'` and `'b'`) with frequencies of 2 and 2, respectively.
+* Since we can have at most `k = 2` distinct characters, no deletions are required. Thus, the answer is 0.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** s = "yyyzz", k = 1
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* `s` has two distinct characters (`'y'` and `'z'`) with frequencies of 3 and 2, respectively.
+* Since we can have at most `k = 1` distinct character, remove all occurrences of any one character from the string.
+* Removing all `'z'` results in at most `k` distinct characters. Thus, the answer is 2.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= s.length <= 16`
+* `1 <= k <= 16`
+* `s` consists only of lowercase English letters.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3546_equal_sum_grid_partition_i/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3546_equal_sum_grid_partition_i/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..5a8022b8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3546_equal_sum_grid_partition_i/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3546_equal_sum_grid_partition_i
+
+// #Medium #Array #Matrix #Prefix_Sum #Enumeration
+// #2025_05_13_Time_7_ms_(82.61%)_Space_90.22_MB_(17.39%)
+
+class Solution {
+ fun canPartitionGrid(grid: Array): Boolean {
+ val n = grid.size
+ val m = grid[0].size
+ var totalRowSum = 0L
+ val prefixRowWise = LongArray(n)
+ val prefixColWise = LongArray(m)
+ for (i in 0..1 <= m == grid.length <= 105
+* 1 <= n == grid[i].length <= 105
+* 2 <= m * n <= 105
+* 1 <= grid[i][j] <= 105
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3547_maximum_sum_of_edge_values_in_a_graph/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3547_maximum_sum_of_edge_values_in_a_graph/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..8f59c79b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3547_maximum_sum_of_edge_values_in_a_graph/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,154 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3547_maximum_sum_of_edge_values_in_a_graph
+
+// #Hard #Sorting #Depth_First_Search #Greedy #Graph
+// #2025_05_11_Time_61_ms_(100.00%)_Space_86.35_MB_(100.00%)
+
+class Solution {
+ private lateinit var p: IntArray
+ private lateinit var c: BooleanArray
+ private lateinit var s: IntArray
+
+ fun maxScore(n: Int, edges: Array): Long {
+ initializeArrays(n)
+ processEdges(edges)
+ val circles: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ val chains: MutableList = ArrayList()
+ findParentsAndUpdateCircles()
+ collectCirclesAndChains(circles, chains)
+ circles.sort()
+ chains.sortWith { a: Int, b: Int -> Integer.compare(b, a) }
+ return calculateScore(n, circles, chains)
+ }
+
+ private fun initializeArrays(n: Int) {
+ p = IntArray(n)
+ c = BooleanArray(n)
+ s = IntArray(n)
+ for (i in 0..) {
+ for (ele in edges) {
+ join(ele[0], ele[1])
+ }
+ }
+
+ private fun findParentsAndUpdateCircles() {
+ for (i in p.indices) {
+ p[i] = findParent(i)
+ if (c[i]) {
+ c[p[i]] = true
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ private fun collectCirclesAndChains(circles: MutableList, chains: MutableList) {
+ for (i in p.indices) {
+ if (p[i] == i) {
+ val size = s[i]
+ if (c[i]) {
+ circles.add(size)
+ } else {
+ chains.add(size)
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ private fun calculateScore(n: Int, circles: MutableList, chains: MutableList): Long {
+ var ret: Long = 0
+ var start = n
+ ret += processCircles(circles, start)
+ start = n - getTotalCircleSize(circles)
+ ret += processChains(chains, start)
+ return ret
+ }
+
+ private fun getTotalCircleSize(circles: MutableList): Int {
+ return circles.stream().mapToInt { obj: Int -> obj }.sum()
+ }
+
+ private fun processCircles(circles: MutableList, start: Int): Long {
+ var start = start
+ var ret: Long = 0
+ for (size in circles) {
+ if (size == 1) {
+ continue
+ }
+ val temp = createTempArray(size, start)
+ val pro = calculateProduct(temp, true)
+ ret += pro
+ start = start - size
+ }
+ return ret
+ }
+
+ private fun processChains(chains: MutableList, start: Int): Long {
+ var start = start
+ var ret: Long = 0
+ for (size in chains) {
+ if (size == 1) {
+ continue
+ }
+ val temp = createTempArray(size, start)
+ val pro = calculateProduct(temp, false)
+ ret += pro
+ start = start - size
+ }
+ return ret
+ }
+
+ private fun createTempArray(size: Int, start: Int): IntArray {
+ val temp = IntArray(size)
+ var ptr1 = 0
+ var ptr2 = size - 1
+ val curStart = start - size + 1
+ for (i in 0.. s2) {
+ p[bp] = ap
+ s[ap] += s[bp]
+ } else {
+ p[ap] = bp
+ s[bp] += s[ap]
+ }
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3547_maximum_sum_of_edge_values_in_a_graph/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3547_maximum_sum_of_edge_values_in_a_graph/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f182f4a8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3547_maximum_sum_of_edge_values_in_a_graph/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
+3547\. Maximum Sum of Edge Values in a Graph
+
+Hard
+
+You are given an **und****irected** graph of `n` nodes, numbered from `0` to `n - 1`. Each node is connected to **at most** 2 other nodes.
+
+The graph consists of `m` edges, represented by a 2D array `edges`, where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi.
+
+You have to assign a **unique** value from `1` to `n` to each node. The value of an edge will be the **product** of the values assigned to the two nodes it connects.
+
+Your score is the sum of the values of all edges in the graph.
+
+Return the **maximum** score you can achieve.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+
+
+**Input:** n = 7, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,0],[3,4],[4,5],[5,6]]
+
+**Output:** 130
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The diagram above illustrates an optimal assignment of values to nodes. The sum of the values of the edges is: `(7 * 6) + (7 * 5) + (6 * 5) + (1 * 3) + (3 * 4) + (4 * 2) = 130`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+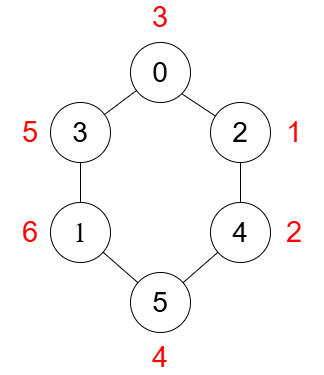
+
+**Input:** n = 6, edges = [[0,3],[4,5],[2,0],[1,3],[2,4],[1,5]]
+
+**Output:** 82
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The diagram above illustrates an optimal assignment of values to nodes. The sum of the values of the edges is: `(1 * 2) + (2 * 4) + (4 * 6) + (6 * 5) + (5 * 3) + (3 * 1) = 82`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= n <= 5 * 104
+* `m == edges.length`
+* `1 <= m <= n`
+* `edges[i].length == 2`
+* 0 <= ai, bi < n
+* ai != bi
+* There are no repeated edges.
+* Each node is connected to at most 2 other nodes.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3548_equal_sum_grid_partition_ii/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3548_equal_sum_grid_partition_ii/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..eaad1e93
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3548_equal_sum_grid_partition_ii/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,123 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3548_equal_sum_grid_partition_ii
+
+// #Hard #Array #Hash_Table #Matrix #Prefix_Sum #Enumeration
+// #2025_05_13_Time_61_ms_(100.00%)_Space_98.01_MB_(100.00%)
+
+class Solution {
+ private fun calculateSum(grid: Array, count: IntArray): Long {
+ var sum: Long = 0
+ for (line in grid) {
+ for (num in line) {
+ sum += num.toLong()
+ count[num]++
+ }
+ }
+ return sum
+ }
+
+ private fun checkHorizontalPartition(grid: Array, sum: Long, count: IntArray): Boolean {
+ val half = IntArray(MAX_SIZE)
+ var now: Long = 0
+ val m = grid.size
+ val n = grid[0].size
+ for (i in 0.. sum) {
+ val diff = now * 2 - sum
+ if (diff <= MAX_SIZE - 1 && half[diff.toInt()] > 0) {
+ if (n > 1) {
+ if (i > 0 || grid[0][0].toLong() == diff || grid[0][n - 1].toLong() == diff) {
+ return true
+ }
+ } else {
+ if (i > 0 && (grid[0][0].toLong() == diff || grid[i][0].toLong() == diff)) {
+ return true
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ } else {
+ val diff = sum - now * 2
+ if (diff <= MAX_SIZE - 1 && count[diff.toInt()] > 0) {
+ if (n > 1) {
+ if (i < m - 2 || grid[m - 1][0].toLong() == diff || grid[m - 1][n - 1].toLong() == diff) {
+ return true
+ }
+ } else {
+ if (i > 0 && (grid[m - 1][0].toLong() == diff || grid[i + 1][0].toLong() == diff)) {
+ return true
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return false
+ }
+
+ private fun checkVerticalPartition(grid: Array, sum: Long): Boolean {
+ val count = IntArray(MAX_SIZE)
+ val half = IntArray(MAX_SIZE)
+ for (line in grid) {
+ for (num in line) {
+ count[num]++
+ }
+ }
+ var now: Long = 0
+ val m = grid.size
+ val n = grid[0].size
+ for (i in 0.. sum) {
+ val diff = now * 2 - sum
+ if (diff <= MAX_SIZE - 1 && half[diff.toInt()] > 0) {
+ if (m > 1) {
+ if (i > 0 || grid[0][0].toLong() == diff || grid[m - 1][0].toLong() == diff) {
+ return true
+ }
+ } else {
+ if (i > 0 && (grid[0][0].toLong() == diff || grid[0][i].toLong() == diff)) {
+ return true
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ } else {
+ val diff = sum - now * 2
+ if (diff <= MAX_SIZE - 1 && count[diff.toInt()] > 0) {
+ if (m > 1) {
+ if (i < n - 2 || grid[0][n - 1].toLong() == diff || grid[m - 1][n - 1].toLong() == diff) {
+ return true
+ }
+ } else {
+ if (i > 0 && (grid[0][n - 1].toLong() == diff || grid[0][i + 1].toLong() == diff)) {
+ return true
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return false
+ }
+
+ fun canPartitionGrid(grid: Array): Boolean {
+ val count = IntArray(MAX_SIZE)
+ val sum = calculateSum(grid, count)
+ return checkHorizontalPartition(grid, sum, count) || checkVerticalPartition(grid, sum)
+ }
+
+ companion object {
+ private const val MAX_SIZE = 100001
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3548_equal_sum_grid_partition_ii/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3548_equal_sum_grid_partition_ii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..b8f30183
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3548_equal_sum_grid_partition_ii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
+3548\. Equal Sum Grid Partition II
+
+Hard
+
+You are given an `m x n` matrix `grid` of positive integers. Your task is to determine if it is possible to make **either one horizontal or one vertical cut** on the grid such that:
+
+* Each of the two resulting sections formed by the cut is **non-empty**.
+* The sum of elements in both sections is **equal**, or can be made equal by discounting **at most** one single cell in total (from either section).
+* If a cell is discounted, the rest of the section must **remain connected**.
+
+Return `true` if such a partition exists; otherwise, return `false`.
+
+**Note:** A section is **connected** if every cell in it can be reached from any other cell by moving up, down, left, or right through other cells in the section.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** grid = [[1,4],[2,3]]
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+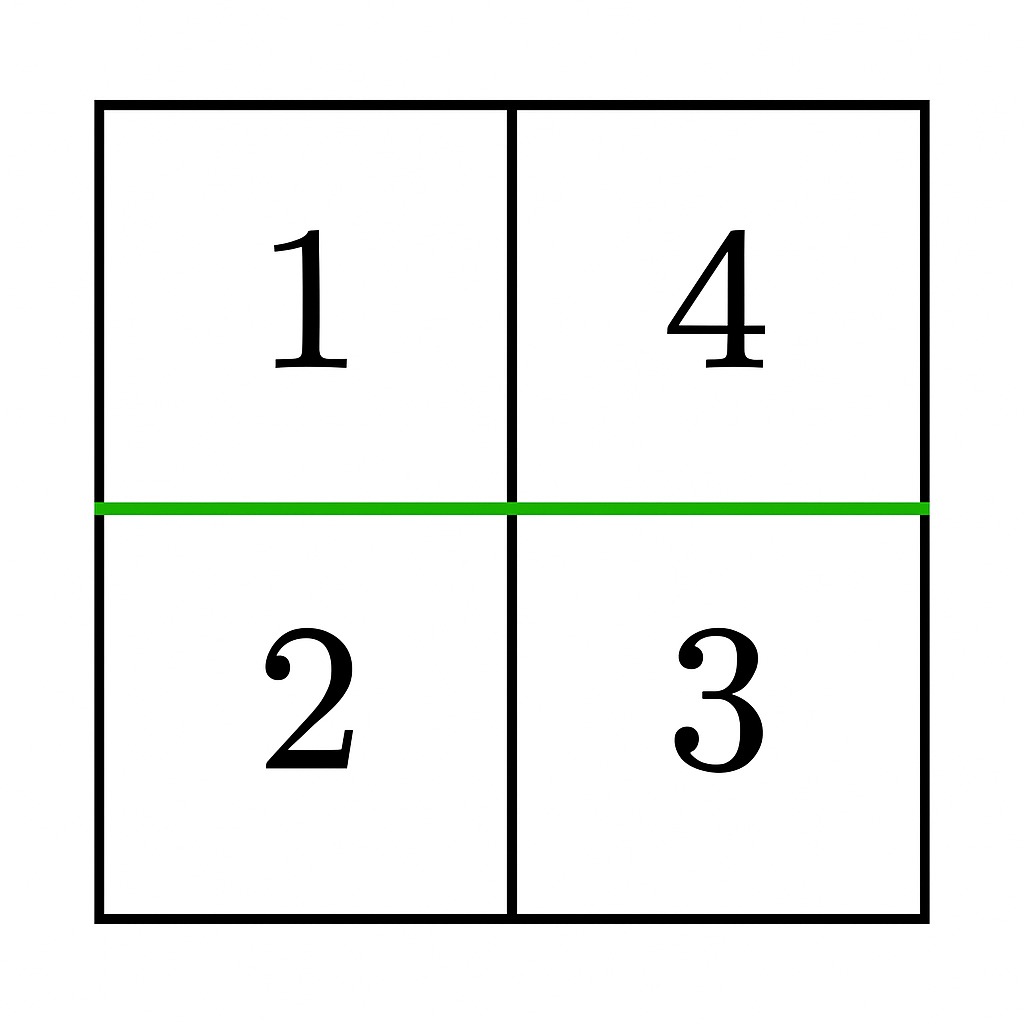
+
+* A horizontal cut after the first row gives sums `1 + 4 = 5` and `2 + 3 = 5`, which are equal. Thus, the answer is `true`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** grid = [[1,2],[3,4]]
+
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+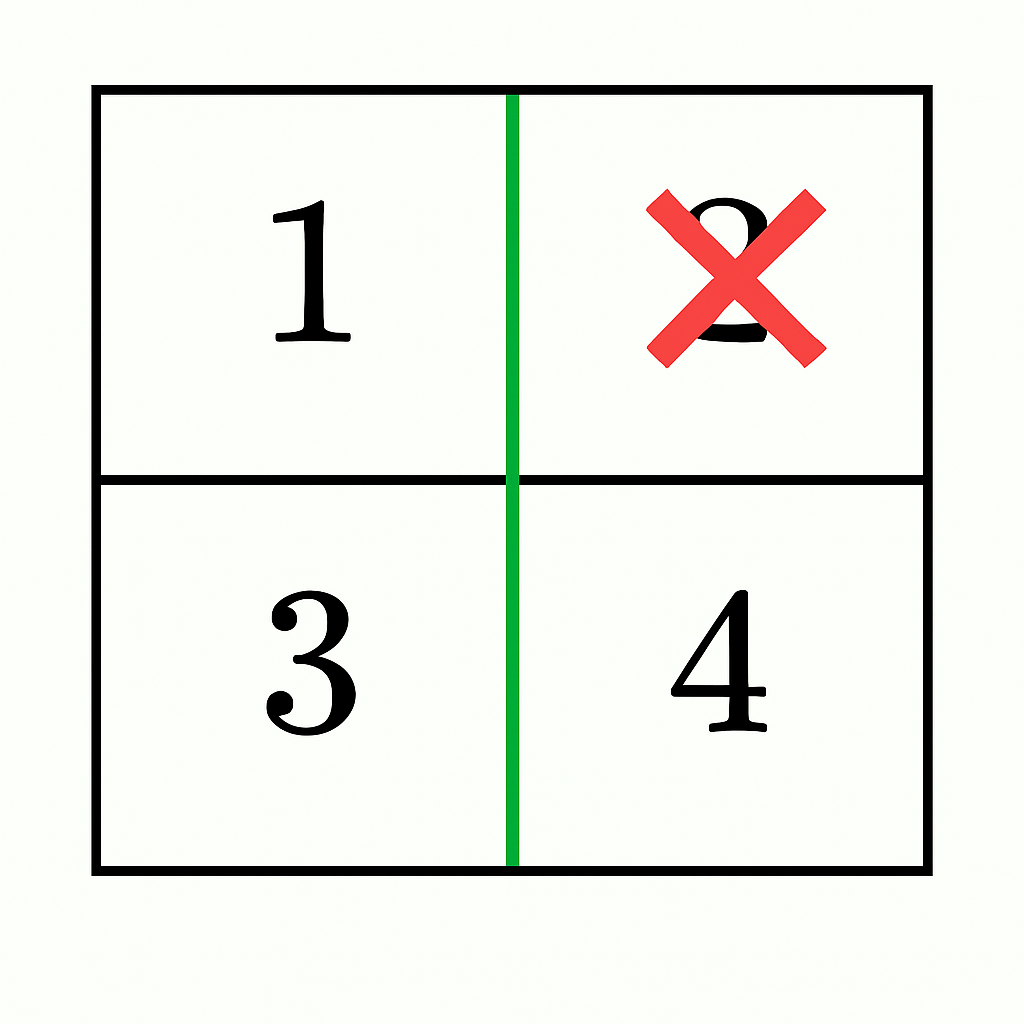
+
+* A vertical cut after the first column gives sums `1 + 3 = 4` and `2 + 4 = 6`.
+* By discounting 2 from the right section (`6 - 2 = 4`), both sections have equal sums and remain connected. Thus, the answer is `true`.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** grid = [[1,2,4],[2,3,5]]
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+**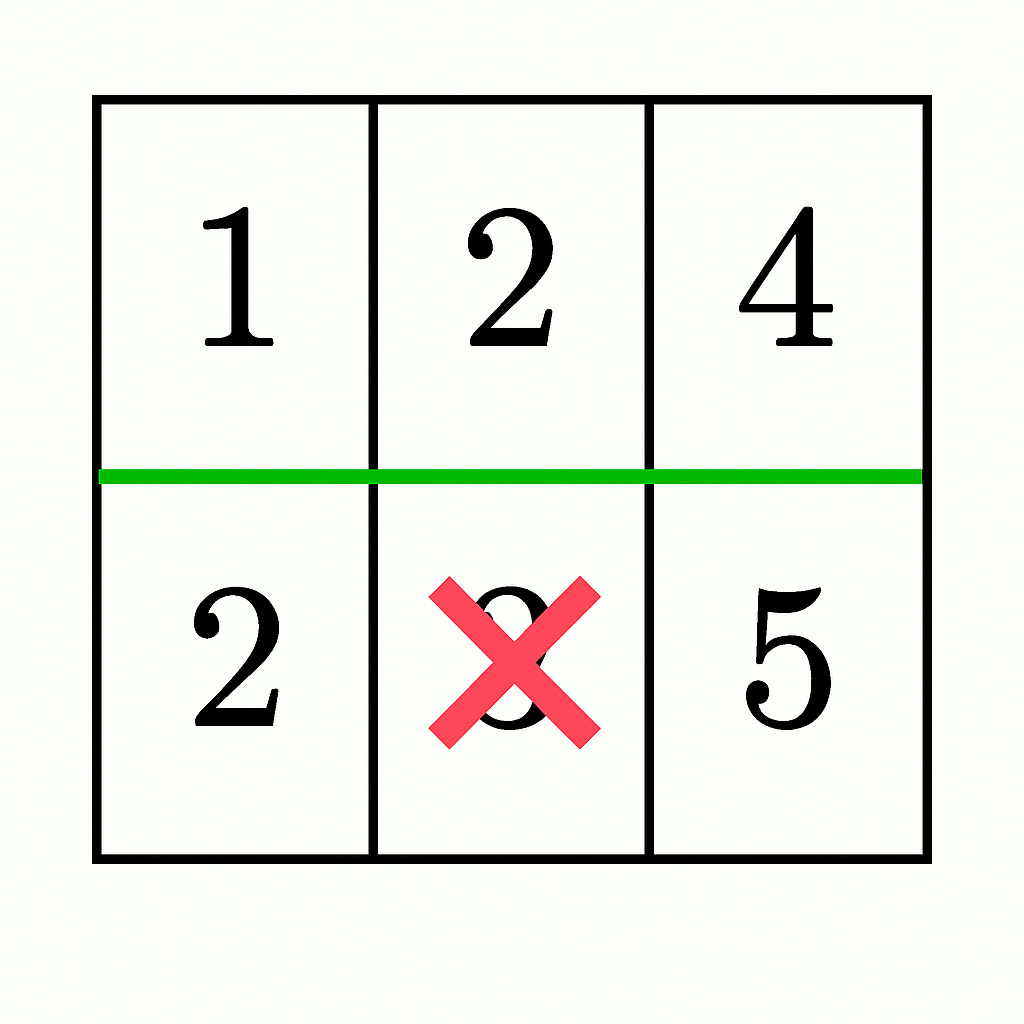**
+
+* A horizontal cut after the first row gives `1 + 2 + 4 = 7` and `2 + 3 + 5 = 10`.
+* By discounting 3 from the bottom section (`10 - 3 = 7`), both sections have equal sums, but they do not remain connected as it splits the bottom section into two parts (`[2]` and `[5]`). Thus, the answer is `false`.
+
+**Example 4:**
+
+**Input:** grid = [[4,1,8],[3,2,6]]
+
+**Output:** false
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+No valid cut exists, so the answer is `false`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= m == grid.length <= 105
+* 1 <= n == grid[i].length <= 105
+* 2 <= m * n <= 105
+* 1 <= grid[i][j] <= 105
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3541_find_most_frequent_vowel_and_consonant/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3541_find_most_frequent_vowel_and_consonant/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..9c3d4932
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3541_find_most_frequent_vowel_and_consonant/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3541_find_most_frequent_vowel_and_consonant
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun maxFreqSum() {
+ MatcherAssert.assertThat(Solution().maxFreqSum("successes"), CoreMatchers.equalTo(6))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun maxFreqSum2() {
+ MatcherAssert.assertThat(Solution().maxFreqSum("aeiaeia"), CoreMatchers.equalTo(3))
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3542_minimum_operations_to_convert_all_elements_to_zero/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3542_minimum_operations_to_convert_all_elements_to_zero/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..9ecd8e75
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3542_minimum_operations_to_convert_all_elements_to_zero/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3542_minimum_operations_to_convert_all_elements_to_zero
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun minOperations() {
+ MatcherAssert.assertThat(Solution().minOperations(intArrayOf(0, 2)), CoreMatchers.equalTo(1))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun minOperations2() {
+ MatcherAssert.assertThat(Solution().minOperations(intArrayOf(3, 1, 2, 1)), CoreMatchers.equalTo(3))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun minOperations3() {
+ MatcherAssert.assertThat(
+ Solution().minOperations(intArrayOf(1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 2)),
+ CoreMatchers.equalTo(4),
+ )
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3543_maximum_weighted_k_edge_path/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3543_maximum_weighted_k_edge_path/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..67b61ff2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3543_maximum_weighted_k_edge_path/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3543_maximum_weighted_k_edge_path
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun maxWeight() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().maxWeight(3, arrayOf(intArrayOf(0, 1, 1), intArrayOf(1, 2, 2)), 2, 4),
+ equalTo(3),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun maxWeight2() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().maxWeight(3, arrayOf(intArrayOf(0, 1, 2), intArrayOf(0, 2, 3)), 1, 3),
+ equalTo(2),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun maxWeight3() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().maxWeight(3, arrayOf(intArrayOf(0, 1, 6), intArrayOf(1, 2, 8)), 1, 6),
+ equalTo(-1),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun maxWeight4() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().maxWeight(3, arrayOf(intArrayOf(0, 1, 6), intArrayOf(1, 2, 8)), 0, 6),
+ equalTo(0),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun maxWeight5() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution()
+ .maxWeight(
+ 6,
+ arrayOf(
+ intArrayOf(0, 1, 10),
+ intArrayOf(0, 2, 1),
+ intArrayOf(1, 3, 2),
+ intArrayOf(2, 3, 5),
+ intArrayOf(3, 4, 5),
+ intArrayOf(3, 5, 3),
+ ),
+ 3,
+ 12,
+ ),
+ equalTo(11),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun maxWeight6() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution()
+ .maxWeight(
+ 5,
+ arrayOf(
+ intArrayOf(0, 1, 2),
+ intArrayOf(0, 2, 3),
+ intArrayOf(1, 3, 3),
+ intArrayOf(2, 3, 1),
+ intArrayOf(3, 4, 2),
+ ),
+ 3,
+ 7,
+ ),
+ equalTo(6),
+ )
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3544_subtree_inversion_sum/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3544_subtree_inversion_sum/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..2809da0f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3544_subtree_inversion_sum/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3544_subtree_inversion_sum
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun subtreeInversionSum() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution()
+ .subtreeInversionSum(
+ arrayOf(
+ intArrayOf(0, 1),
+ intArrayOf(0, 2),
+ intArrayOf(1, 3),
+ intArrayOf(1, 4),
+ intArrayOf(2, 5),
+ intArrayOf(2, 6),
+ ),
+ intArrayOf(4, -8, -6, 3, 7, -2, 5),
+ 2,
+ ),
+ equalTo(27L),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun subtreeInversionSum2() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution()
+ .subtreeInversionSum(
+ arrayOf(intArrayOf(0, 1), intArrayOf(1, 2), intArrayOf(2, 3), intArrayOf(3, 4)),
+ intArrayOf(-1, 3, -2, 4, -5),
+ 2,
+ ),
+ equalTo(9L),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun subtreeInversionSum3() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution()
+ .subtreeInversionSum(
+ arrayOf(intArrayOf(0, 1), intArrayOf(0, 2)),
+ intArrayOf(0, -1, -2),
+ 3,
+ ),
+ equalTo(3L),
+ )
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3545_minimum_deletions_for_at_most_k_distinct_characters/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3545_minimum_deletions_for_at_most_k_distinct_characters/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..50ee92a9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3545_minimum_deletions_for_at_most_k_distinct_characters/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3545_minimum_deletions_for_at_most_k_distinct_characters
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun minDeletion() {
+ assertThat(Solution().minDeletion("abc", 2), equalTo(1))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun minDeletion2() {
+ assertThat(Solution().minDeletion("aabb", 2), equalTo(0))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun minDeletion3() {
+ assertThat(Solution().minDeletion("yyyzz", 1), equalTo(2))
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3546_equal_sum_grid_partition_i/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3546_equal_sum_grid_partition_i/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..78b6e55f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3546_equal_sum_grid_partition_i/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3546_equal_sum_grid_partition_i
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun canPartitionGrid() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().canPartitionGrid(
+ arrayOf(
+ intArrayOf(1, 4),
+ intArrayOf(2, 3),
+ ),
+ ),
+ equalTo(true),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun canPartitionGrid2() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().canPartitionGrid(
+ arrayOf(
+ intArrayOf(1, 3),
+ intArrayOf(2, 4),
+ ),
+ ),
+ equalTo(false),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun canPartitionGrid3() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().canPartitionGrid(arrayOf(intArrayOf(1))),
+ equalTo(false),
+ )
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3547_maximum_sum_of_edge_values_in_a_graph/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3547_maximum_sum_of_edge_values_in_a_graph/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..7cd7407e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3547_maximum_sum_of_edge_values_in_a_graph/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3547_maximum_sum_of_edge_values_in_a_graph
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun maxScore() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution()
+ .maxScore(
+ 7,
+ arrayOf(
+ intArrayOf(0, 1),
+ intArrayOf(1, 2),
+ intArrayOf(2, 0),
+ intArrayOf(3, 4),
+ intArrayOf(4, 5),
+ intArrayOf(5, 6),
+ ),
+ ),
+ equalTo(130L),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun maxScore2() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution()
+ .maxScore(
+ 6,
+ arrayOf(
+ intArrayOf(0, 3),
+ intArrayOf(4, 5),
+ intArrayOf(2, 0),
+ intArrayOf(1, 3),
+ intArrayOf(2, 4),
+ intArrayOf(1, 5),
+ ),
+ ),
+ equalTo(82L),
+ )
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3548_equal_sum_grid_partition_ii/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3548_equal_sum_grid_partition_ii/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 00000000..f3eac317
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3548_equal_sum_grid_partition_ii/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,134 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3548_equal_sum_grid_partition_ii
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun canPartitionGrid() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().canPartitionGrid(
+ arrayOf(
+ intArrayOf(1, 4),
+ intArrayOf(2, 3),
+ ),
+ ),
+ equalTo(true),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun canPartitionGrid2() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().canPartitionGrid(
+ arrayOf(
+ intArrayOf(1, 2),
+ intArrayOf(3, 4),
+ ),
+ ),
+ equalTo(true),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun canPartitionGrid3() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().canPartitionGrid(arrayOf(intArrayOf(1, 2, 4), intArrayOf(2, 3, 5))),
+ equalTo(false),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun canPartitionGrid4() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().canPartitionGrid(arrayOf(intArrayOf(4, 1, 8), intArrayOf(3, 2, 6))),
+ equalTo(false),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun canPartitionGrid5() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().canPartitionGrid(arrayOf(intArrayOf(1))),
+ equalTo(false),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun canPartitionGrid6() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().canPartitionGrid(
+ arrayOf(
+ intArrayOf(25372, 100000, 100000),
+ ),
+ ),
+ equalTo(true),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun canPartitionGrid7() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().canPartitionGrid(
+ arrayOf(
+ intArrayOf(100000, 100000, 100000, 100000, 1),
+ ),
+ ),
+ equalTo(true),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun canPartitionGrid8() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().canPartitionGrid(
+ arrayOf(
+ intArrayOf(55753, 55753),
+ ),
+ ),
+ equalTo(true),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun canPartitionGrid9() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().canPartitionGrid(
+ arrayOf(
+ intArrayOf(253, 10, 10),
+ ),
+ ),
+ equalTo(true),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun canPartitionGrid10() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().canPartitionGrid(
+ arrayOf(
+ intArrayOf(4, 4, 4),
+ intArrayOf(2, 2, 1),
+ intArrayOf(1, 1, 1),
+ ),
+ ),
+ equalTo(true),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun canPartitionGrid11() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().canPartitionGrid(
+ arrayOf(
+ intArrayOf(2, 40, 2),
+ intArrayOf(4, 2, 3),
+ intArrayOf(5, 1, 6),
+ intArrayOf(7, 8, 9),
+ ),
+ ),
+ equalTo(true),
+ )
+ }
+}