diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3536_maximum_product_of_two_digits/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3536_maximum_product_of_two_digits/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..ca91a3beb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3536_maximum_product_of_two_digits/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3536_maximum_product_of_two_digits
+
+// #Easy #Math #Sorting #2025_05_04_Time_1_ms_(100.00%)_Space_40.93_MB_(100.00%)
+
+class Solution {
+ fun maxProduct(n: Int): Int {
+ var n = n
+ var m1 = n % 10
+ n /= 10
+ var m2 = n % 10
+ n /= 10
+ while (n > 0) {
+ val a = n % 10
+ if (a > m1) {
+ if (m1 > m2) {
+ m2 = m1
+ }
+ m1 = a
+ } else {
+ if (a > m2) {
+ m2 = a
+ }
+ }
+ n /= 10
+ }
+ return m1 * m2
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3536_maximum_product_of_two_digits/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3536_maximum_product_of_two_digits/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..11f945253
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3536_maximum_product_of_two_digits/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
+3536\. Maximum Product of Two Digits
+
+Easy
+
+You are given a positive integer `n`.
+
+Return the **maximum** product of any two digits in `n`.
+
+**Note:** You may use the **same** digit twice if it appears more than once in `n`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 31
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* The digits of `n` are `[3, 1]`.
+* The possible products of any two digits are: `3 * 1 = 3`.
+* The maximum product is 3.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 22
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* The digits of `n` are `[2, 2]`.
+* The possible products of any two digits are: `2 * 2 = 4`.
+* The maximum product is 4.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** n = 124
+
+**Output:** 8
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* The digits of `n` are `[1, 2, 4]`.
+* The possible products of any two digits are: `1 * 2 = 2`, `1 * 4 = 4`, `2 * 4 = 8`.
+* The maximum product is 8.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 10 <= n <= 109
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3537_fill_a_special_grid/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3537_fill_a_special_grid/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..a2612ba3c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3537_fill_a_special_grid/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3537_fill_a_special_grid
+
+// #Medium #Array #Matrix #Divide_and_Conquer
+// #2025_05_04_Time_2_ms_(100.00%)_Space_88.71_MB_(61.54%)
+
+import kotlin.math.pow
+
+class Solution {
+ fun specialGrid(n: Int): Array {
+ if (n == 0) {
+ return arrayOf(intArrayOf(0))
+ }
+ val len = 2.0.pow(n.toDouble()).toInt()
+ val ans = Array(len) { IntArray(len) }
+ val num = intArrayOf(2.0.pow(2.0 * n).toInt() - 1)
+ backtrack(ans, len, len, 0, 0, num)
+ return ans
+ }
+
+ private fun backtrack(ans: Array, m: Int, n: Int, x: Int, y: Int, num: IntArray) {
+ if (m == 2 && n == 2) {
+ ans[x][y] = num[0]
+ ans[x + 1][y] = num[0] - 1
+ ans[x + 1][y + 1] = num[0] - 2
+ ans[x][y + 1] = num[0] - 3
+ num[0] -= 4
+ return
+ }
+ backtrack(ans, m / 2, n / 2, x, y, num)
+ backtrack(ans, m / 2, n / 2, x + m / 2, y, num)
+ backtrack(ans, m / 2, n / 2, x + m / 2, y + n / 2, num)
+ backtrack(ans, m / 2, n / 2, x, y + n / 2, num)
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3537_fill_a_special_grid/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3537_fill_a_special_grid/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..e0ee432a9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3537_fill_a_special_grid/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
+3537\. Fill a Special Grid
+
+Medium
+
+You are given a non-negative integer `n` representing a 2n x 2n grid. You must fill the grid with integers from 0 to 22n - 1 to make it **special**. A grid is **special** if it satisfies **all** the following conditions:
+
+* All numbers in the top-right quadrant are smaller than those in the bottom-right quadrant.
+* All numbers in the bottom-right quadrant are smaller than those in the bottom-left quadrant.
+* All numbers in the bottom-left quadrant are smaller than those in the top-left quadrant.
+* Each of its quadrants is also a special grid.
+
+Return the **special** 2n x 2n grid.
+
+**Note**: Any 1x1 grid is special.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 0
+
+**Output:** [[0]]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The only number that can be placed is 0, and there is only one possible position in the grid.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 1
+
+**Output:** [[3,0],[2,1]]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The numbers in each quadrant are:
+
+* Top-right: 0
+* Bottom-right: 1
+* Bottom-left: 2
+* Top-left: 3
+
+Since `0 < 1 < 2 < 3`, this satisfies the given constraints.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** n = 2
+
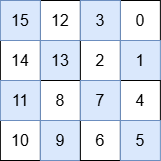
+**Output:** [[15,12,3,0],[14,13,2,1],[11,8,7,4],[10,9,6,5]]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+The numbers in each quadrant are:
+
+* Top-right: 3, 0, 2, 1
+* Bottom-right: 7, 4, 6, 5
+* Bottom-left: 11, 8, 10, 9
+* Top-left: 15, 12, 14, 13
+* `max(3, 0, 2, 1) < min(7, 4, 6, 5)`
+* `max(7, 4, 6, 5) < min(11, 8, 10, 9)`
+* `max(11, 8, 10, 9) < min(15, 12, 14, 13)`
+
+This satisfies the first three requirements. Additionally, each quadrant is also a special grid. Thus, this is a special grid.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `0 <= n <= 10`
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3538_merge_operations_for_minimum_travel_time/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3538_merge_operations_for_minimum_travel_time/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..8d84a2522
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3538_merge_operations_for_minimum_travel_time/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3538_merge_operations_for_minimum_travel_time
+
+// #Hard #Array #Dynamic_Programming #Prefix_Sum
+// #2025_05_04_Time_10_ms_(100.00%)_Space_46.96_MB_(100.00%)
+
+import kotlin.math.min
+
+@Suppress("unused")
+class Solution {
+ fun minTravelTime(l: Int, n: Int, k: Int, position: IntArray, time: IntArray): Int {
+ val dp = Array>(n) { Array(k + 1) { IntArray(k + 1) } }
+ for (i in 0.. 0` and `i + 1 < n`) and:
+
+* Update the sign at index `i + 1` so that its time becomes `time[i] + time[i + 1]`.
+* Remove the sign at index `i`.
+
+Return the **minimum** **total** **travel time** (in minutes) to travel from 0 to `l` after **exactly** `k` merges.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** l = 10, n = 4, k = 1, position = [0,3,8,10], time = [5,8,3,6]
+
+**Output:** 62
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* Merge the signs at indices 1 and 2. Remove the sign at index 1, and change the time at index 2 to `8 + 3 = 11`.
+
+* After the merge:
+ * `position` array: `[0, 8, 10]`
+ * `time` array: `[5, 11, 6]`
+
+| Segment | Distance (km) | Time per km (min) | Segment Travel Time (min) |
+|-----------|---------------|-------------------|----------------------------|
+| 0 → 8 | 8 | 5 | 8 × 5 = 40 |
+| 8 → 10 | 2 | 11 | 2 × 11 = 22 |
+
+
+* Total Travel Time: `40 + 22 = 62`, which is the minimum possible time after exactly 1 merge.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** l = 5, n = 5, k = 1, position = [0,1,2,3,5], time = [8,3,9,3,3]
+
+**Output:** 34
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* Merge the signs at indices 1 and 2. Remove the sign at index 1, and change the time at index 2 to `3 + 9 = 12`.
+* After the merge:
+ * `position` array: `[0, 2, 3, 5]`
+ * `time` array: `[8, 12, 3, 3]`
+
+| Segment | Distance (km) | Time per km (min) | Segment Travel Time (min) |
+|-----------|---------------|-------------------|----------------------------|
+| 0 → 2 | 2 | 8 | 2 × 8 = 16 |
+| 2 → 3 | 1 | 12 | 1 × 12 = 12 |
+| 3 → 5 | 2 | 3 | 2 × 3 = 6 |
+
+* Total Travel Time: `16 + 12 + 6 = 34`**,** which is the minimum possible time after exactly 1 merge.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= l <= 105
+* `2 <= n <= min(l + 1, 50)`
+* `0 <= k <= min(n - 2, 10)`
+* `position.length == n`
+* `position[0] = 0` and `position[n - 1] = l`
+* `position` is sorted in strictly increasing order.
+* `time.length == n`
+* `1 <= time[i] <= 100`
+* `1 <= sum(time) <= 100`
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3539_find_sum_of_array_product_of_magical_sequences/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3539_find_sum_of_array_product_of_magical_sequences/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..255af8e89
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3539_find_sum_of_array_product_of_magical_sequences/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3539_find_sum_of_array_product_of_magical_sequences
+
+// #Hard #Array #Dynamic_Programming #Math #Bit_Manipulation #Bitmask #Combinatorics
+// #2025_05_06_Time_60_ms_(100.00%)_Space_48.98_MB_(100.00%)
+
+class Solution {
+ fun magicalSum(m: Int, k: Int, nums: IntArray): Int {
+ val n = nums.size
+ val pow = Array(n) { LongArray(m + 1) }
+ for (j in 0..>(m + 1) { Array(k + 1) { LongArray(m + 1) } }
+ var next = Array>(m + 1) { Array(k + 1) { LongArray(m + 1) } }
+ dp[0][0][0] = 1L
+ for (i in 0.. k) {
+ continue
+ }
+ next[t + cc][o + (total and 1)][total ushr 1] =
+ (
+ (
+ next[t + cc][o + (total and 1)][total ushr 1] +
+ dp[t][o][c] *
+ C[m - t][cc] %
+ MOD
+ * pow[i][cc] %
+ MOD
+ ) %
+ MOD
+ )
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ val tmp = dp
+ dp = next
+ next = tmp
+ }
+ var res: Long = 0
+ for (o in 0..k) {
+ for (c in 0..m) {
+ if (o + P[c] == k) {
+ res = (res + dp[m][o][c]) % MOD
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return res.toInt()
+ }
+
+ companion object {
+ private const val MOD = 1000000007
+ private val C: Array = precomputeBinom(31)
+ private val P: IntArray = precomputePop(31)
+
+ private fun precomputeBinom(max: Int): Array {
+ val res = Array(max) { IntArray(max) }
+ for (i in 0..2seq[0] + 2seq[1] + ... + 2seq[m - 1] has `k` **set bits**.
+
+The **array product** of this sequence is defined as `prod(seq) = (nums[seq[0]] * nums[seq[1]] * ... * nums[seq[m - 1]])`.
+
+Return the **sum** of the **array products** for all valid **magical** sequences.
+
+Since the answer may be large, return it **modulo** 109 + 7.
+
+A **set bit** refers to a bit in the binary representation of a number that has a value of 1.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** m = 5, k = 5, nums = [1,10,100,10000,1000000]
+
+**Output:** 991600007
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+All permutations of `[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]` are magical sequences, each with an array product of 1013.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** m = 2, k = 2, nums = [5,4,3,2,1]
+
+**Output:** 170
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The magical sequences are `[0, 1]`, `[0, 2]`, `[0, 3]`, `[0, 4]`, `[1, 0]`, `[1, 2]`, `[1, 3]`, `[1, 4]`, `[2, 0]`, `[2, 1]`, `[2, 3]`, `[2, 4]`, `[3, 0]`, `[3, 1]`, `[3, 2]`, `[3, 4]`, `[4, 0]`, `[4, 1]`, `[4, 2]`, and `[4, 3]`.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** m = 1, k = 1, nums = [28]
+
+**Output:** 28
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The only magical sequence is `[0]`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `1 <= k <= m <= 30`
+* `1 <= nums.length <= 50`
+* 1 <= nums[i] <= 108
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3536_maximum_product_of_two_digits/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3536_maximum_product_of_two_digits/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..561984792
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3536_maximum_product_of_two_digits/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3536_maximum_product_of_two_digits
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun maxProduct() {
+ assertThat(Solution().maxProduct(31), equalTo(3))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun maxProduct2() {
+ assertThat(Solution().maxProduct(22), equalTo(4))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun maxProduct3() {
+ assertThat(Solution().maxProduct(124), equalTo(8))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun maxProduct4() {
+ assertThat(Solution().maxProduct(453), equalTo(20))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun maxProduct5() {
+ assertThat(Solution().maxProduct(437), equalTo(28))
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun maxProduct6() {
+ assertThat(Solution().maxProduct(724), equalTo(28))
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3537_fill_a_special_grid/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3537_fill_a_special_grid/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..61faf1519
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3537_fill_a_special_grid/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3537_fill_a_special_grid
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun specialGrid() {
+ assertThat>(
+ Solution().specialGrid(0),
+ equalTo>(arrayOf(intArrayOf(0))),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun specialGrid2() {
+ assertThat>(
+ Solution().specialGrid(1),
+ equalTo>(arrayOf(intArrayOf(3, 0), intArrayOf(2, 1))),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun specialGrid3() {
+ assertThat>(
+ Solution().specialGrid(2),
+ equalTo>(
+ arrayOf(
+ intArrayOf(15, 12, 3, 0),
+ intArrayOf(14, 13, 2, 1),
+ intArrayOf(11, 8, 7, 4),
+ intArrayOf(10, 9, 6, 5),
+ ),
+ ),
+ )
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3538_merge_operations_for_minimum_travel_time/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3538_merge_operations_for_minimum_travel_time/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..00be368ff
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3538_merge_operations_for_minimum_travel_time/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3538_merge_operations_for_minimum_travel_time
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun minTravelTime() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution()
+ .minTravelTime(10, 4, 1, intArrayOf(0, 3, 8, 10), intArrayOf(5, 8, 3, 6)),
+ equalTo(62),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun minTravelTime2() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution()
+ .minTravelTime(
+ 5,
+ 5,
+ 1,
+ intArrayOf(0, 1, 2, 3, 5),
+ intArrayOf(8, 3, 9, 3, 3),
+ ),
+ equalTo(34),
+ )
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3539_find_sum_of_array_product_of_magical_sequences/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3539_find_sum_of_array_product_of_magical_sequences/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..dd57b7af2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3501_3600/s3539_find_sum_of_array_product_of_magical_sequences/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
+package g3501_3600.s3539_find_sum_of_array_product_of_magical_sequences
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun magicalSum() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().magicalSum(5, 5, intArrayOf(1, 10, 100, 10000, 1000000)),
+ equalTo(991600007),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun magicalSum2() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().magicalSum(2, 2, intArrayOf(5, 4, 3, 2, 1)),
+ equalTo(170),
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun magicalSum3() {
+ assertThat(Solution().magicalSum(1, 1, intArrayOf(28)), equalTo(28))
+ }
+}