diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3280_convert_date_to_binary/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3280_convert_date_to_binary/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..d52fc350c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3280_convert_date_to_binary/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3280_convert_date_to_binary
+
+// #Easy #String #Math #2024_09_11_Time_174_ms_(79.31%)_Space_36.2_MB_(82.76%)
+
+class Solution {
+ fun convertDateToBinary(dat: String): String {
+ val str = StringBuilder()
+ val res = StringBuilder()
+ for (c in dat.toCharArray()) {
+ if (c.isDigit()) {
+ str.append(c)
+ } else if (c == '-') {
+ res.append(str.toString().toInt().toString(2))
+ res.append('-')
+ str.setLength(0)
+ }
+ }
+ if (str.isNotEmpty()) {
+ res.append(str.toString().toInt().toString(2))
+ }
+ return res.toString()
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3280_convert_date_to_binary/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3280_convert_date_to_binary/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..64ba96f9a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3280_convert_date_to_binary/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
+3280\. Convert Date to Binary
+
+Easy
+
+You are given a string `date` representing a Gregorian calendar date in the `yyyy-mm-dd` format.
+
+`date` can be written in its binary representation obtained by converting year, month, and day to their binary representations without any leading zeroes and writing them down in `year-month-day` format.
+
+Return the **binary** representation of `date`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** date = "2080-02-29"
+
+**Output:** "100000100000-10-11101"
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+100000100000, 10, and 11101 are the binary representations of 2080, 02, and 29 respectively.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** date = "1900-01-01"
+
+**Output:** "11101101100-1-1"
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+11101101100, 1, and 1 are the binary representations of 1900, 1, and 1 respectively.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `date.length == 10`
+* `date[4] == date[7] == '-'`, and all other `date[i]`'s are digits.
+* The input is generated such that `date` represents a valid Gregorian calendar date between Jan 1st, 1900 and Dec 31st, 2100 (both inclusive).
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3281_maximize_score_of_numbers_in_ranges/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3281_maximize_score_of_numbers_in_ranges/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..b39f092c7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3281_maximize_score_of_numbers_in_ranges/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3281_maximize_score_of_numbers_in_ranges
+
+// #Medium #Array #Sorting #Greedy #Binary_Search
+// #2024_09_11_Time_710_ms_(88.24%)_Space_80.7_MB_(5.88%)
+
+import kotlin.math.max
+
+class Solution {
+ fun maxPossibleScore(start: IntArray, d: Int): Int {
+ start.sort()
+ val n = start.size
+ var l = 0
+ var r = start[n - 1] - start[0] + d + 1
+ while (l < r) {
+ val m = l + (r - l) / 2
+ if (isPossible(start, d, m)) {
+ l = m + 1
+ } else {
+ r = m
+ }
+ }
+ return l - 1
+ }
+
+ private fun isPossible(start: IntArray, d: Int, score: Int): Boolean {
+ var pre = start[0]
+ for (i in 1 until start.size) {
+ if (start[i] + d - pre < score) {
+ return false
+ }
+ pre = max(start[i], (pre + score))
+ }
+ return true
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3281_maximize_score_of_numbers_in_ranges/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3281_maximize_score_of_numbers_in_ranges/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..547db6de9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3281_maximize_score_of_numbers_in_ranges/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
+3281\. Maximize Score of Numbers in Ranges
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an array of integers `start` and an integer `d`, representing `n` intervals `[start[i], start[i] + d]`.
+
+You are asked to choose `n` integers where the ith integer must belong to the ith interval. The **score** of the chosen integers is defined as the **minimum** absolute difference between any two integers that have been chosen.
+
+Return the **maximum** _possible score_ of the chosen integers.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** start = [6,0,3], d = 2
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The maximum possible score can be obtained by choosing integers: 8, 0, and 4. The score of these chosen integers is `min(|8 - 0|, |8 - 4|, |0 - 4|)` which equals 4.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** start = [2,6,13,13], d = 5
+
+**Output:** 5
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+The maximum possible score can be obtained by choosing integers: 2, 7, 13, and 18. The score of these chosen integers is `min(|2 - 7|, |2 - 13|, |2 - 18|, |7 - 13|, |7 - 18|, |13 - 18|)` which equals 5.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 2 <= start.length <= 105
+* 0 <= start[i] <= 109
+* 0 <= d <= 109
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3282_reach_end_of_array_with_max_score/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3282_reach_end_of_array_with_max_score/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..5f109b452
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3282_reach_end_of_array_with_max_score/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3282_reach_end_of_array_with_max_score
+
+// #Medium #Array #Greedy #2024_09_11_Time_789_ms_(90.91%)_Space_77.1_MB_(36.36%)
+
+import kotlin.math.max
+
+class Solution {
+ fun findMaximumScore(nums: List): Long {
+ var res: Long = 0
+ var ma: Long = 0
+ for (num in nums) {
+ res += ma
+ ma = max(ma, num.toLong())
+ }
+ return res
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3282_reach_end_of_array_with_max_score/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3282_reach_end_of_array_with_max_score/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..c20c31408
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3282_reach_end_of_array_with_max_score/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
+3282\. Reach End of Array With Max Score
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an integer array `nums` of length `n`.
+
+Your goal is to start at index `0` and reach index `n - 1`. You can only jump to indices **greater** than your current index.
+
+The score for a jump from index `i` to index `j` is calculated as `(j - i) * nums[i]`.
+
+Return the **maximum** possible **total score** by the time you reach the last index.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [1,3,1,5]
+
+**Output:** 7
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+First, jump to index 1 and then jump to the last index. The final score is `1 * 1 + 2 * 3 = 7`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** nums = [4,3,1,3,2]
+
+**Output:** 16
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Jump directly to the last index. The final score is `4 * 4 = 16`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 1 <= nums.length <= 105
+* 1 <= nums[i] <= 105
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3283_maximum_number_of_moves_to_kill_all_pawns/Solution.kt b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3283_maximum_number_of_moves_to_kill_all_pawns/Solution.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..cab8d7856
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3283_maximum_number_of_moves_to_kill_all_pawns/Solution.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3283_maximum_number_of_moves_to_kill_all_pawns
+
+// #Hard #Array #Math #Breadth_First_Search #Bit_Manipulation #Bitmask #Game_Theory
+// #2024_09_11_Time_638_ms_(100.00%)_Space_62.2_MB_(87.50%)
+
+import java.util.LinkedList
+import java.util.Queue
+import kotlin.math.max
+import kotlin.math.min
+
+class Solution {
+ private lateinit var distances: Array
+ private lateinit var memo: Array?>
+
+ fun maxMoves(kx: Int, ky: Int, positions: Array): Int {
+ val n = positions.size
+ distances = Array(n + 1) { IntArray(n + 1) { 0 } }
+ memo = Array?>(n + 1) { arrayOfNulls(1 shl n) }
+ // Calculate distances between all pairs of positions (including knight's initial position)
+ for (i in 0 until n) {
+ distances[n][i] = calculateMoves(kx, ky, positions[i][0], positions[i][1])
+ for (j in i + 1 until n) {
+ val dist =
+ calculateMoves(
+ positions[i][0], positions[i][1], positions[j][0], positions[j][1]
+ )
+ distances[j][i] = dist
+ distances[i][j] = distances[j][i]
+ }
+ }
+ return minimax(n, (1 shl n) - 1, true)
+ }
+
+ private fun minimax(lastPos: Int, remainingPawns: Int, isAlice: Boolean): Int {
+ if (remainingPawns == 0) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ if (memo[lastPos]!![remainingPawns] != null) {
+ return memo[lastPos]!![remainingPawns]!!
+ }
+ var result = if (isAlice) 0 else Int.Companion.MAX_VALUE
+ for (i in 0 until distances.size - 1) {
+ if ((remainingPawns and (1 shl i)) != 0) {
+ val newRemainingPawns = remainingPawns and (1 shl i).inv()
+ val moveValue = distances[lastPos][i] + minimax(i, newRemainingPawns, !isAlice)
+ result = if (isAlice) {
+ max(result, moveValue)
+ } else {
+ min(result, moveValue)
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ memo[lastPos]!![remainingPawns] = result
+ return result
+ }
+
+ private fun calculateMoves(x1: Int, y1: Int, x2: Int, y2: Int): Int {
+ if (x1 == x2 && y1 == y2) {
+ return 0
+ }
+ val visited = Array(50) { BooleanArray(50) }
+ val queue: Queue = LinkedList()
+ queue.offer(intArrayOf(x1, y1, 0))
+ visited[x1]!![y1] = true
+ while (queue.isNotEmpty()) {
+ val current = queue.poll()
+ val x = current[0]
+ val y = current[1]
+ val moves = current[2]
+ for (move in KNIGHT_MOVES) {
+ val nx = x + move[0]
+ val ny = y + move[1]
+ if (nx == x2 && ny == y2) {
+ return moves + 1
+ }
+ if (nx >= 0 && nx < 50 && ny >= 0 && ny < 50 && !visited[nx]!![ny]) {
+ queue.offer(intArrayOf(nx, ny, moves + 1))
+ visited[nx]!![ny] = true
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ // Should never reach here if input is valid
+ return -1
+ }
+
+ companion object {
+ private val KNIGHT_MOVES = arrayOf(
+ intArrayOf(-2, -1), intArrayOf(-2, 1), intArrayOf(-1, -2), intArrayOf(-1, 2),
+ intArrayOf(1, -2), intArrayOf(1, 2), intArrayOf(2, -1), intArrayOf(2, 1)
+ )
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3283_maximum_number_of_moves_to_kill_all_pawns/readme.md b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3283_maximum_number_of_moves_to_kill_all_pawns/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..67ab70621
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3283_maximum_number_of_moves_to_kill_all_pawns/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
+3283\. Maximum Number of Moves to Kill All Pawns
+
+Hard
+
+There is a `50 x 50` chessboard with **one** knight and some pawns on it. You are given two integers `kx` and `ky` where `(kx, ky)` denotes the position of the knight, and a 2D array `positions` where positions[i] = [xi, yi] denotes the position of the pawns on the chessboard.
+
+Alice and Bob play a _turn-based_ game, where Alice goes first. In each player's turn:
+
+* The player _selects_ a pawn that still exists on the board and captures it with the knight in the **fewest** possible **moves**. **Note** that the player can select **any** pawn, it **might not** be one that can be captured in the **least** number of moves.
+* In the process of capturing the _selected_ pawn, the knight **may** pass other pawns **without** capturing them. **Only** the _selected_ pawn can be captured in _this_ turn.
+
+Alice is trying to **maximize** the **sum** of the number of moves made by _both_ players until there are no more pawns on the board, whereas Bob tries to **minimize** them.
+
+Return the **maximum** _total_ number of moves made during the game that Alice can achieve, assuming both players play **optimally**.
+
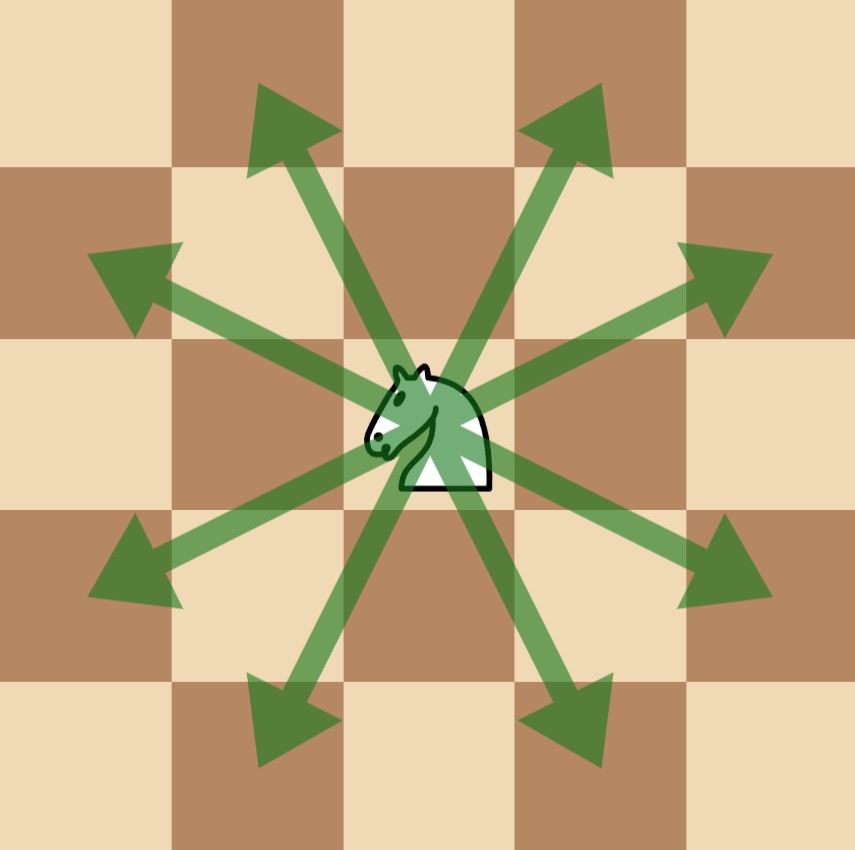
+Note that in one **move,** a chess knight has eight possible positions it can move to, as illustrated below. Each move is two cells in a cardinal direction, then one cell in an orthogonal direction.
+
+
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** kx = 1, ky = 1, positions = [[0,0]]
+
+**Output:** 4
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+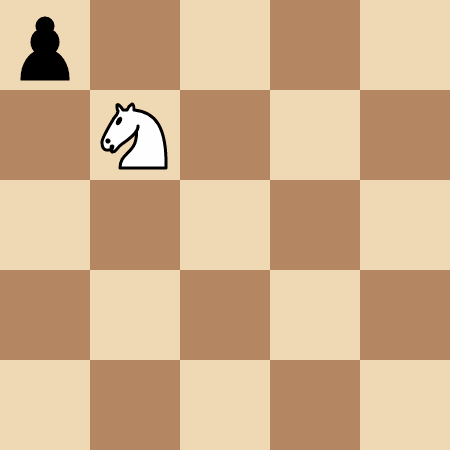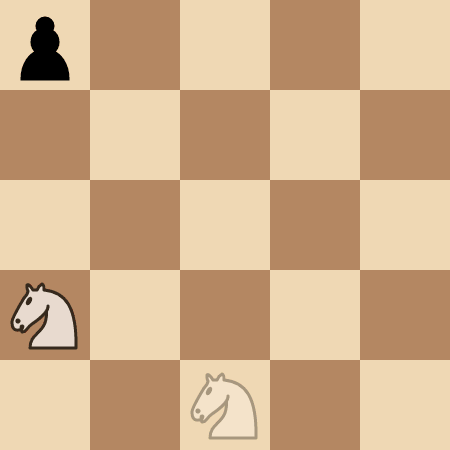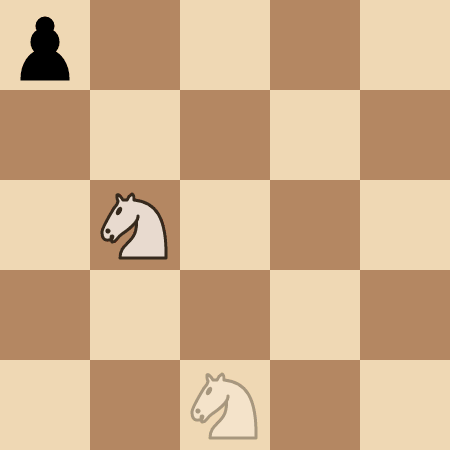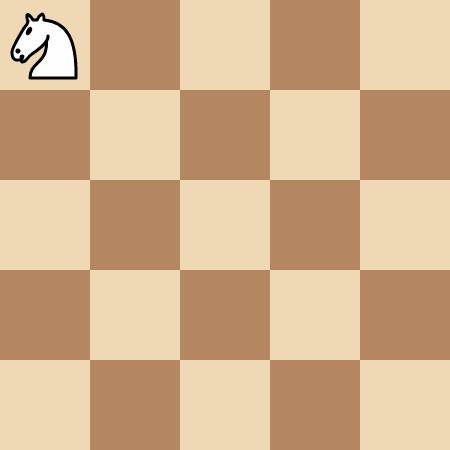
+
+The knight takes 4 moves to reach the pawn at `(0, 0)`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** kx = 0, ky = 2, positions = [[1,1],[2,2],[3,3]]
+
+**Output:** 8
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+**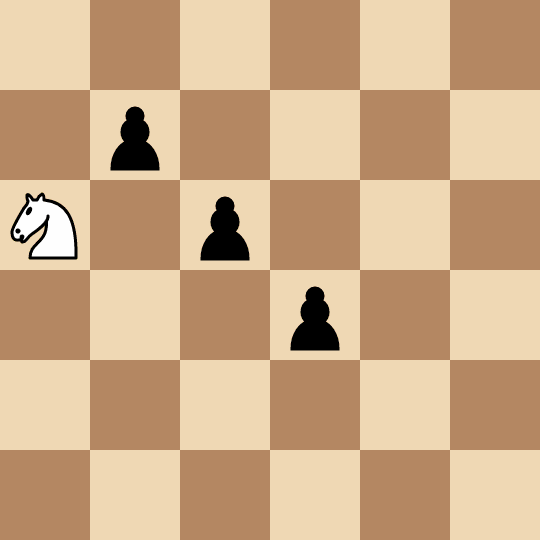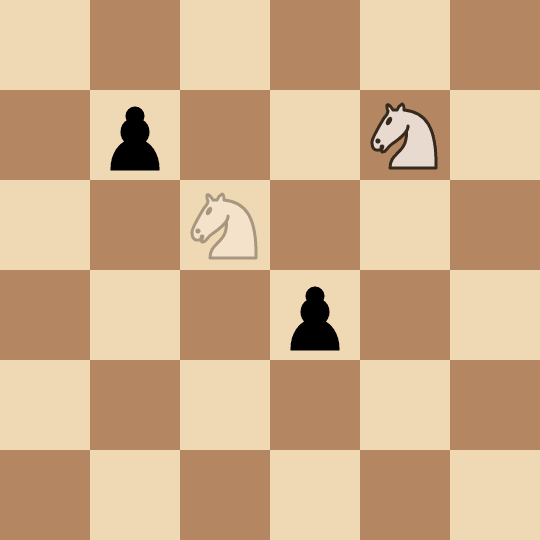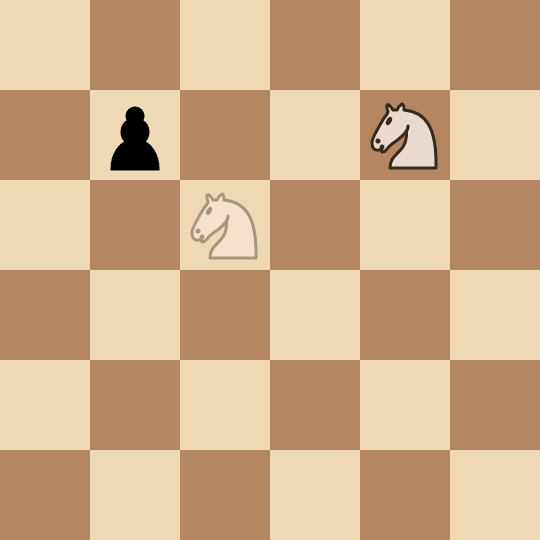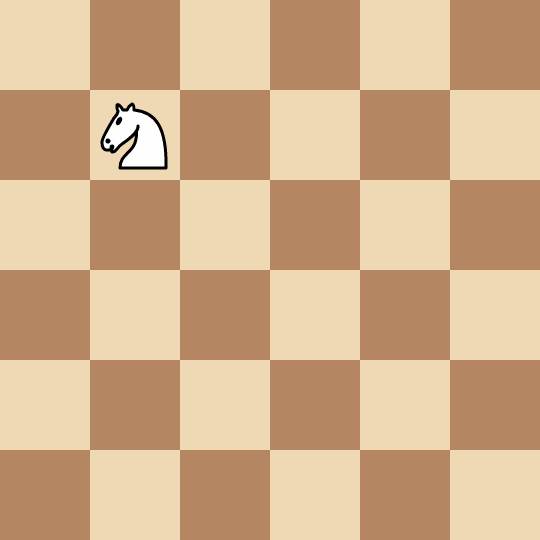**
+
+* Alice picks the pawn at `(2, 2)` and captures it in two moves: `(0, 2) -> (1, 4) -> (2, 2)`.
+* Bob picks the pawn at `(3, 3)` and captures it in two moves: `(2, 2) -> (4, 1) -> (3, 3)`.
+* Alice picks the pawn at `(1, 1)` and captures it in four moves: `(3, 3) -> (4, 1) -> (2, 2) -> (0, 3) -> (1, 1)`.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** kx = 0, ky = 0, positions = [[1,2],[2,4]]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+* Alice picks the pawn at `(2, 4)` and captures it in two moves: `(0, 0) -> (1, 2) -> (2, 4)`. Note that the pawn at `(1, 2)` is not captured.
+* Bob picks the pawn at `(1, 2)` and captures it in one move: `(2, 4) -> (1, 2)`.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `0 <= kx, ky <= 49`
+* `1 <= positions.length <= 15`
+* `positions[i].length == 2`
+* `0 <= positions[i][0], positions[i][1] <= 49`
+* All `positions[i]` are unique.
+* The input is generated such that `positions[i] != [kx, ky]` for all `0 <= i < positions.length`.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3280_convert_date_to_binary/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3280_convert_date_to_binary/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..0ad03638b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3280_convert_date_to_binary/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3280_convert_date_to_binary
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun convertDateToBinary() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().convertDateToBinary("2080-02-29"), equalTo("100000100000-10-11101")
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun convertDateToBinary2() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().convertDateToBinary("1900-01-01"),
+ equalTo("11101101100-1-1")
+ )
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3281_maximize_score_of_numbers_in_ranges/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3281_maximize_score_of_numbers_in_ranges/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..2c02c8112
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3281_maximize_score_of_numbers_in_ranges/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3281_maximize_score_of_numbers_in_ranges
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun maxPossibleScore() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().maxPossibleScore(intArrayOf(6, 0, 3), 2),
+ equalTo(4)
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun maxPossibleScore2() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().maxPossibleScore(intArrayOf(2, 6, 13, 13), 5),
+ equalTo(5)
+ )
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3282_reach_end_of_array_with_max_score/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3282_reach_end_of_array_with_max_score/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..a66b0515e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3282_reach_end_of_array_with_max_score/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3282_reach_end_of_array_with_max_score
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun findMaximumScore() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().findMaximumScore(mutableListOf(1, 3, 1, 5)),
+ equalTo(7L)
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun findMaximumScore2() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().findMaximumScore(mutableListOf(4, 3, 1, 3, 2)),
+ equalTo(16L)
+ )
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3283_maximum_number_of_moves_to_kill_all_pawns/SolutionTest.kt b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3283_maximum_number_of_moves_to_kill_all_pawns/SolutionTest.kt
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..856e51a2d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/kotlin/g3201_3300/s3283_maximum_number_of_moves_to_kill_all_pawns/SolutionTest.kt
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3283_maximum_number_of_moves_to_kill_all_pawns
+
+import org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo
+import org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test
+
+internal class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ fun maxMoves() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().maxMoves(1, 1, arrayOf(intArrayOf(0, 0))),
+ equalTo(4)
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun maxMoves2() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().maxMoves(
+ 0,
+ 2,
+ arrayOf(intArrayOf(1, 1), intArrayOf(2, 2), intArrayOf(3, 3))
+ ),
+ equalTo(8)
+ )
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ fun maxMoves3() {
+ assertThat(
+ Solution().maxMoves(
+ 0,
+ 0,
+ arrayOf(intArrayOf(1, 2), intArrayOf(2, 4))
+ ),
+ equalTo(3)
+ )
+ }
+}