diff --git a/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3238_find_the_number_of_winning_players/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3238_find_the_number_of_winning_players/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..f491f618a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3238_find_the_number_of_winning_players/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3238_find_the_number_of_winning_players;
+
+// #Easy #Array #Hash_Table #Counting #2024_08_06_Time_1_ms_(100.00%)_Space_44.5_MB_(99.46%)
+
+@SuppressWarnings({"unused", "java:S1172"})
+public class Solution {
+ public int winningPlayerCount(int n, int[][] pick) {
+ int[][] dp = new int[11][11];
+ for (int[] ints : pick) {
+ int p = ints[0];
+ int pi = ints[1];
+ dp[p][pi] += 1;
+ }
+ int count = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < 11; i++) {
+ boolean win = false;
+ for (int j = 0; j < 11; j++) {
+ if (dp[i][j] >= i + 1) {
+ win = true;
+ break;
+ }
+ }
+ if (win) {
+ count += 1;
+ }
+ }
+ return count;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3238_find_the_number_of_winning_players/readme.md b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3238_find_the_number_of_winning_players/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..a42ca5743
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3238_find_the_number_of_winning_players/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
+3238\. Find the Number of Winning Players
+
+Easy
+
+You are given an integer `n` representing the number of players in a game and a 2D array `pick` where pick[i] = [xi, yi] represents that the player xi picked a ball of color yi.
+
+Player `i` **wins** the game if they pick **strictly more** than `i` balls of the **same** color. In other words,
+
+* Player 0 wins if they pick any ball.
+* Player 1 wins if they pick at least two balls of the _same_ color.
+* ...
+* Player `i` wins if they pick at least`i + 1` balls of the _same_ color.
+
+Return the number of players who **win** the game.
+
+**Note** that _multiple_ players can win the game.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 4, pick = [[0,0],[1,0],[1,0],[2,1],[2,1],[2,0]]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Player 0 and player 1 win the game, while players 2 and 3 do not win.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 5, pick = [[1,1],[1,2],[1,3],[1,4]]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+No player wins the game.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** n = 5, pick = [[1,1],[2,4],[2,4],[2,4]]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+Player 2 wins the game by picking 3 balls with color 4.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `2 <= n <= 10`
+* `1 <= pick.length <= 100`
+* `pick[i].length == 2`
+* 0 <= xi <= n - 1
+* 0 <= yi <= 10
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3239_minimum_number_of_flips_to_make_binary_grid_palindromic_i/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3239_minimum_number_of_flips_to_make_binary_grid_palindromic_i/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..1ef760ae0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3239_minimum_number_of_flips_to_make_binary_grid_palindromic_i/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3239_minimum_number_of_flips_to_make_binary_grid_palindromic_i;
+
+// #Medium #Array #Matrix #Two_Pointers #2024_08_06_Time_3_ms_(100.00%)_Space_111.4_MB_(41.81%)
+
+public class Solution {
+ public int minFlips(int[][] grid) {
+ int m = grid.length;
+ int n = grid[0].length;
+ int rowFlips = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < m / 2; i++) {
+ for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
+ int sum = grid[i][j] + grid[m - 1 - i][j];
+ rowFlips += Math.min(sum, 2 - sum);
+ }
+ }
+ int columnFlips = 0;
+ for (int j = 0; j < n / 2; j++) {
+ for (int[] ints : grid) {
+ int sum = ints[j] + ints[n - 1 - j];
+ columnFlips += Math.min(sum, 2 - sum);
+ }
+ }
+ return Math.min(rowFlips, columnFlips);
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3239_minimum_number_of_flips_to_make_binary_grid_palindromic_i/readme.md b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3239_minimum_number_of_flips_to_make_binary_grid_palindromic_i/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..0e89c8faa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3239_minimum_number_of_flips_to_make_binary_grid_palindromic_i/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
+3239\. Minimum Number of Flips to Make Binary Grid Palindromic I
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an `m x n` binary matrix `grid`.
+
+A row or column is considered **palindromic** if its values read the same forward and backward.
+
+You can **flip** any number of cells in `grid` from `0` to `1`, or from `1` to `0`.
+
+Return the **minimum** number of cells that need to be flipped to make **either** all rows **palindromic** or all columns **palindromic**.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
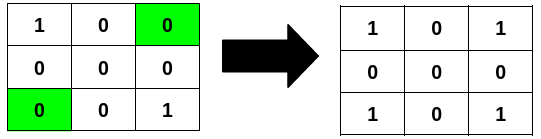
+**Input:** grid = [[1,0,0],[0,0,0],[0,0,1]]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+Flipping the highlighted cells makes all the rows palindromic.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
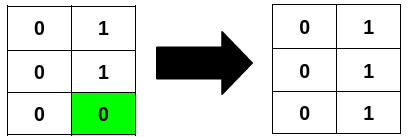
+**Input:** grid = [[0,1],[0,1],[0,0]]
+
+**Output:** 1
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+Flipping the highlighted cell makes all the columns palindromic.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** grid = [[1],[0]]
+
+**Output:** 0
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+All rows are already palindromic.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `m == grid.length`
+* `n == grid[i].length`
+* 1 <= m * n <= 2 * 105
+* `0 <= grid[i][j] <= 1`
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3240_minimum_number_of_flips_to_make_binary_grid_palindromic_ii/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3240_minimum_number_of_flips_to_make_binary_grid_palindromic_ii/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..f683e79cd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3240_minimum_number_of_flips_to_make_binary_grid_palindromic_ii/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3240_minimum_number_of_flips_to_make_binary_grid_palindromic_ii;
+
+// #Medium #Array #Matrix #Two_Pointers #2024_08_06_Time_3_ms_(96.90%)_Space_93.8_MB_(76.14%)
+
+public class Solution {
+ public int minFlips(int[][] grid) {
+ int res = 0;
+ int one = 0;
+ int diff = 0;
+ int m = grid.length;
+ int n = grid[0].length;
+ // Handle quadrants
+ for (int i = 0; i < m / 2; ++i) {
+ for (int j = 0; j < n / 2; ++j) {
+ int v =
+ grid[i][j]
+ + grid[i][n - 1 - j]
+ + grid[m - 1 - i][j]
+ + grid[m - 1 - i][n - 1 - j];
+ res += Math.min(v, 4 - v);
+ }
+ }
+ // Handle middle column
+ if (n % 2 > 0) {
+ for (int i = 0; i < m / 2; ++i) {
+ diff += grid[i][n / 2] ^ grid[m - 1 - i][n / 2];
+ one += grid[i][n / 2] + grid[m - 1 - i][n / 2];
+ }
+ }
+ // Handle middle row
+ if (m % 2 > 0) {
+ for (int j = 0; j < n / 2; ++j) {
+ diff += grid[m / 2][j] ^ grid[m / 2][n - 1 - j];
+ one += grid[m / 2][j] + grid[m / 2][n - 1 - j];
+ }
+ }
+ // Handle center point
+ if (n % 2 > 0 && m % 2 > 0) {
+ res += grid[m / 2][n / 2];
+ }
+ // Divisible by 4
+ if (diff == 0 && one % 4 > 0) {
+ res += 2;
+ }
+ return res + diff;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3240_minimum_number_of_flips_to_make_binary_grid_palindromic_ii/readme.md b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3240_minimum_number_of_flips_to_make_binary_grid_palindromic_ii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..1d1a9765c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3240_minimum_number_of_flips_to_make_binary_grid_palindromic_ii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
+3240\. Minimum Number of Flips to Make Binary Grid Palindromic II
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an `m x n` binary matrix `grid`.
+
+A row or column is considered **palindromic** if its values read the same forward and backward.
+
+You can **flip** any number of cells in `grid` from `0` to `1`, or from `1` to `0`.
+
+Return the **minimum** number of cells that need to be flipped to make **all** rows and columns **palindromic**, and the total number of `1`'s in `grid` **divisible** by `4`.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
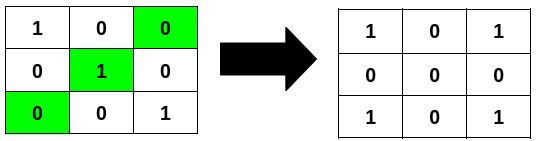
+**Input:** grid = [[1,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,1]]
+
+**Output:** 3
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+**Example 2:**
+
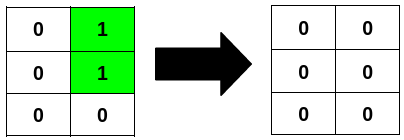
+**Input:** grid = [[0,1],[0,1],[0,0]]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+**Example 3:**
+
+**Input:** grid = [[1],[1]]
+
+**Output:** 2
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `m == grid.length`
+* `n == grid[i].length`
+* 1 <= m * n <= 2 * 105
+* `0 <= grid[i][j] <= 1`
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3241_time_taken_to_mark_all_nodes/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3241_time_taken_to_mark_all_nodes/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..dc8325572
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3241_time_taken_to_mark_all_nodes/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3241_time_taken_to_mark_all_nodes;
+
+// #Hard #Dynamic_Programming #Tree #Graph #Depth_First_Search
+// #2024_08_06_Time_39_ms_(100.00%)_Space_115.8_MB_(83.90%)
+
+import java.util.Arrays;
+
+public class Solution {
+ private int[] head;
+ private int[] nxt;
+ private int[] to;
+ private int[] last;
+ private int[] lastNo;
+ private int[] second;
+ private int[] ans;
+
+ public int[] timeTaken(int[][] edges) {
+ int n = edges.length + 1;
+ head = new int[n];
+ nxt = new int[n << 1];
+ to = new int[n << 1];
+ Arrays.fill(head, -1);
+ int i = 0;
+ int j = 2;
+ while (i < edges.length) {
+ int u = edges[i][0];
+ int v = edges[i][1];
+ nxt[j] = head[u];
+ head[u] = j;
+ to[j] = v;
+ j++;
+ nxt[j] = head[v];
+ head[v] = j;
+ to[j] = u;
+ j++;
+ i++;
+ }
+ last = new int[n];
+ lastNo = new int[n];
+ second = new int[n];
+ ans = new int[n];
+ dfs(-1, 0);
+ System.arraycopy(last, 0, ans, 0, n);
+ dfs2(-1, 0, 0);
+ return ans;
+ }
+
+ private void dfs2(int f, int u, int preLast) {
+ int e = head[u];
+ int v;
+ while (e != -1) {
+ v = to[e];
+ if (f != v) {
+ int pl;
+ if (v == lastNo[u]) {
+ pl = Math.max(preLast, second[u]) + ((u & 1) == 0 ? 2 : 1);
+ } else {
+ pl = Math.max(preLast, last[u]) + ((u & 1) == 0 ? 2 : 1);
+ }
+ ans[v] = Math.max(ans[v], pl);
+ dfs2(u, v, pl);
+ }
+ e = nxt[e];
+ }
+ }
+
+ private void dfs(int f, int u) {
+ int e = head[u];
+ int v;
+ while (e != -1) {
+ v = to[e];
+ if (f != v) {
+ dfs(u, v);
+ int t = last[v] + ((v & 1) == 0 ? 2 : 1);
+ if (last[u] < t) {
+ second[u] = last[u];
+ last[u] = t;
+ lastNo[u] = v;
+ } else if (second[u] < t) {
+ second[u] = t;
+ }
+ }
+ e = nxt[e];
+ }
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3241_time_taken_to_mark_all_nodes/readme.md b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3241_time_taken_to_mark_all_nodes/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..a64e0c6eb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3241_time_taken_to_mark_all_nodes/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
+3241\. Time Taken to Mark All Nodes
+
+Hard
+
+There exists an **undirected** tree with `n` nodes numbered `0` to `n - 1`. You are given a 2D integer array `edges` of length `n - 1`, where edges[i] = [ui, vi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ui and vi in the tree.
+
+Initially, **all** nodes are **unmarked**. For each node `i`:
+
+* If `i` is odd, the node will get marked at time `x` if there is **at least** one node _adjacent_ to it which was marked at time `x - 1`.
+* If `i` is even, the node will get marked at time `x` if there is **at least** one node _adjacent_ to it which was marked at time `x - 2`.
+
+Return an array `times` where `times[i]` is the time when all nodes get marked in the tree, if you mark node `i` at time `t = 0`.
+
+**Note** that the answer for each `times[i]` is **independent**, i.e. when you mark node `i` all other nodes are _unmarked_.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** edges = [[0,1],[0,2]]
+
+**Output:** [2,4,3]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+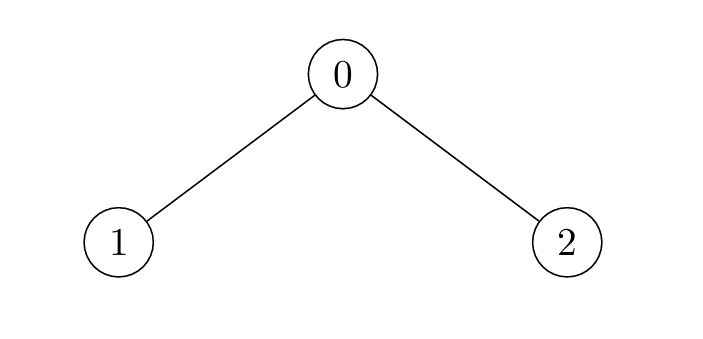
+
+* For `i = 0`:
+ * Node 1 is marked at `t = 1`, and Node 2 at `t = 2`.
+* For `i = 1`:
+ * Node 0 is marked at `t = 2`, and Node 2 at `t = 4`.
+* For `i = 2`:
+ * Node 0 is marked at `t = 2`, and Node 1 at `t = 3`.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** edges = [[0,1]]
+
+**Output:** [1,2]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+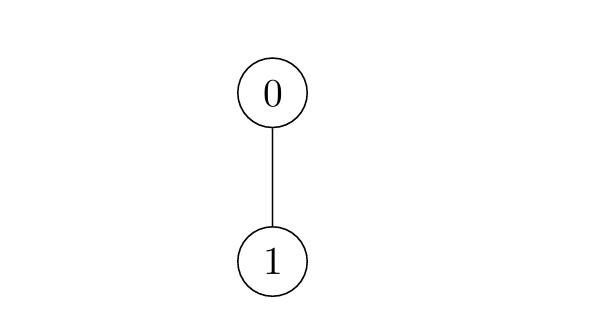
+
+* For `i = 0`:
+ * Node 1 is marked at `t = 1`.
+* For `i = 1`:
+ * Node 0 is marked at `t = 2`.
+
+**Example 3:**
+
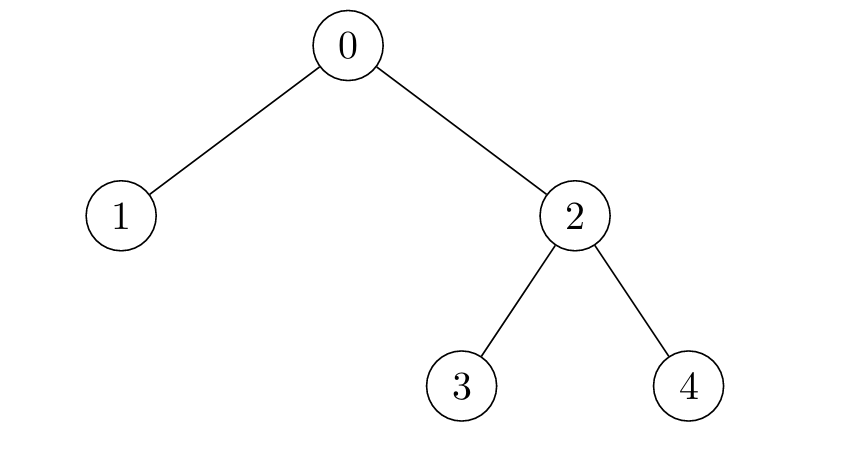
+**Input:** edges = [[2,4],[0,1],[2,3],[0,2]]
+
+**Output:** [4,6,3,5,5]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 2 <= n <= 105
+* `edges.length == n - 1`
+* `edges[i].length == 2`
+* `0 <= edges[i][0], edges[i][1] <= n - 1`
+* The input is generated such that `edges` represents a valid tree.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3242_design_neighbor_sum_service/NeighborSum.java b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3242_design_neighbor_sum_service/NeighborSum.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..8a08d2995
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3242_design_neighbor_sum_service/NeighborSum.java
@@ -0,0 +1,78 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3242_design_neighbor_sum_service;
+
+// #Easy #Array #Hash_Table #Matrix #Design #Simulation
+// #2024_08_06_Time_14_ms_(100.00%)_Space_45.6_MB_(26.72%)
+
+public class NeighborSum {
+ private final int[][] grid;
+ private final int n;
+ private final int[] rowIndex;
+ private final int[] colIndex;
+
+ public NeighborSum(int[][] grid) {
+ this.grid = grid;
+ this.n = grid.length;
+ this.rowIndex = new int[n * n];
+ this.colIndex = new int[n * n];
+ // Precompute the positions of each value in the grid for quick access
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
+ for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
+ rowIndex[grid[i][j]] = i;
+ colIndex[grid[i][j]] = j;
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ public int adjacentSum(int value) {
+ int sum = 0;
+ int i = rowIndex[value];
+ int j = colIndex[value];
+ // Check up
+ if (i > 0) {
+ sum += grid[i - 1][j];
+ }
+ // Check down
+ if (i < n - 1) {
+ sum += grid[i + 1][j];
+ }
+ // Check left
+ if (j > 0) {
+ sum += grid[i][j - 1];
+ }
+ // Check right
+ if (j < n - 1) {
+ sum += grid[i][j + 1];
+ }
+ return sum;
+ }
+
+ public int diagonalSum(int value) {
+ int sum = 0;
+ int i = rowIndex[value];
+ int j = colIndex[value];
+ // Check top-left
+ if (i > 0 && j > 0) {
+ sum += grid[i - 1][j - 1];
+ }
+ // Check top-right
+ if (i > 0 && j < n - 1) {
+ sum += grid[i - 1][j + 1];
+ }
+ // Check bottom-left
+ if (i < n - 1 && j > 0) {
+ sum += grid[i + 1][j - 1];
+ }
+ // Check bottom-right
+ if (i < n - 1 && j < n - 1) {
+ sum += grid[i + 1][j + 1];
+ }
+ return sum;
+ }
+}
+
+/*
+ * Your neighborSum object will be instantiated and called as such:
+ * neighborSum obj = new neighborSum(grid);
+ * int param_1 = obj.adjacentSum(value);
+ * int param_2 = obj.diagonalSum(value);
+ */
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3242_design_neighbor_sum_service/readme.md b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3242_design_neighbor_sum_service/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..e84038b26
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3242_design_neighbor_sum_service/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
+3242\. Design Neighbor Sum Service
+
+Easy
+
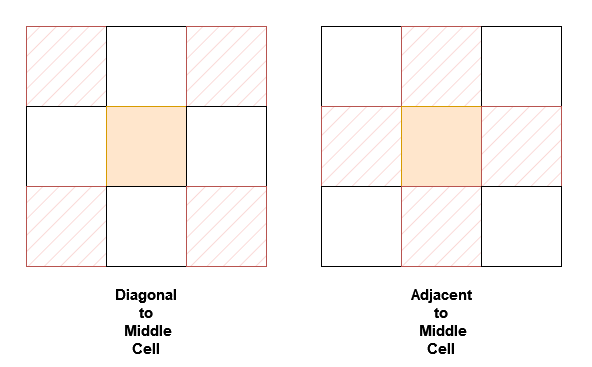
+You are given a `n x n` 2D array `grid` containing **distinct** elements in the range [0, n2 - 1].
+
+Implement the `neighborSum` class:
+
+* `neighborSum(int [][]grid)` initializes the object.
+* `int adjacentSum(int value)` returns the **sum** of elements which are adjacent neighbors of `value`, that is either to the top, left, right, or bottom of `value` in `grid`.
+* `int diagonalSum(int value)` returns the **sum** of elements which are diagonal neighbors of `value`, that is either to the top-left, top-right, bottom-left, or bottom-right of `value` in `grid`.
+
+
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:**
+
+["neighborSum", "adjacentSum", "adjacentSum", "diagonalSum", "diagonalSum"]
+
+[[[[0, 1, 2], [3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8]]], [1], [4], [4], [8]]
+
+**Output:** [null, 6, 16, 16, 4]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+**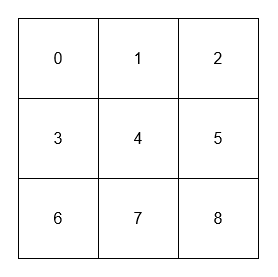**
+
+* The adjacent neighbors of 1 are 0, 2, and 4.
+* The adjacent neighbors of 4 are 1, 3, 5, and 7.
+* The diagonal neighbors of 4 are 0, 2, 6, and 8.
+* The diagonal neighbor of 8 is 4.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:**
+
+["neighborSum", "adjacentSum", "diagonalSum"]
+
+[[[[1, 2, 0, 3], [4, 7, 15, 6], [8, 9, 10, 11], [12, 13, 14, 5]]], [15], [9]]
+
+**Output:** [null, 23, 45]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+**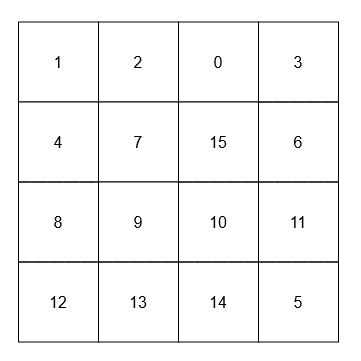**
+
+* The adjacent neighbors of 15 are 0, 10, 7, and 6.
+* The diagonal neighbors of 9 are 4, 12, 14, and 15.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `3 <= n == grid.length == grid[0].length <= 10`
+* 0 <= grid[i][j] <= n2 - 1
+* All `grid[i][j]` are distinct.
+* `value` in `adjacentSum` and `diagonalSum` will be in the range [0, n2 - 1].
+* At most 2 * n2 calls will be made to `adjacentSum` and `diagonalSum`.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3243_shortest_distance_after_road_addition_queries_i/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3243_shortest_distance_after_road_addition_queries_i/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..4a67c4aed
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3243_shortest_distance_after_road_addition_queries_i/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3243_shortest_distance_after_road_addition_queries_i;
+
+// #Medium #Array #Graph #Breadth_First_Search
+// #2024_08_06_Time_6_ms_(100.00%)_Space_45.6_MB_(67.96%)
+
+import java.util.ArrayList;
+
+@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
+public class Solution {
+ public int[] shortestDistanceAfterQueries(int n, int[][] queries) {
+ int[] dist = new int[n];
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
+ dist[i] = i;
+ }
+ ArrayList[] parent = new ArrayList[n];
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
+ parent[i] = new ArrayList<>();
+ if (i != n - 1) {
+ parent[i].add(i + 1);
+ }
+ }
+ int[] ans = new int[queries.length];
+ for (int i = 0; i < queries.length; i++) {
+ int u = queries[i][0];
+ int v = queries[i][1];
+ if (dist[v] > dist[u] + 1) {
+ dist[v] = dist[u] + 1;
+ parent[u].add(v);
+ updateDistance(v, dist, parent);
+ } else {
+ parent[u].add(v);
+ }
+ ans[i] = dist[n - 1];
+ }
+ return ans;
+ }
+
+ public void updateDistance(int par, int[] dist, ArrayList[] parent) {
+ for (int i = 0; i < parent[par].size(); i++) {
+ int child = parent[par].get(i);
+ if (dist[child] > dist[par] + 1) {
+ dist[child] = dist[par] + 1;
+ updateDistance(child, dist, parent);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3243_shortest_distance_after_road_addition_queries_i/readme.md b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3243_shortest_distance_after_road_addition_queries_i/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..c1eab87a2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3243_shortest_distance_after_road_addition_queries_i/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
+3243\. Shortest Distance After Road Addition Queries I
+
+Medium
+
+You are given an integer `n` and a 2D integer array `queries`.
+
+There are `n` cities numbered from `0` to `n - 1`. Initially, there is a **unidirectional** road from city `i` to city `i + 1` for all `0 <= i < n - 1`.
+
+queries[i] = [ui, vi] represents the addition of a new **unidirectional** road from city ui to city vi. After each query, you need to find the **length** of the **shortest path** from city `0` to city `n - 1`.
+
+Return an array `answer` where for each `i` in the range `[0, queries.length - 1]`, `answer[i]` is the _length of the shortest path_ from city `0` to city `n - 1` after processing the **first** `i + 1` queries.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 5, queries = [[2,4],[0,2],[0,4]]
+
+**Output:** [3,2,1]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+After the addition of the road from 2 to 4, the length of the shortest path from 0 to 4 is 3.
+
+
+
+After the addition of the road from 0 to 2, the length of the shortest path from 0 to 4 is 2.
+
+
+
+After the addition of the road from 0 to 4, the length of the shortest path from 0 to 4 is 1.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 4, queries = [[0,3],[0,2]]
+
+**Output:** [1,1]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+After the addition of the road from 0 to 3, the length of the shortest path from 0 to 3 is 1.
+
+
+
+After the addition of the road from 0 to 2, the length of the shortest path remains 1.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* `3 <= n <= 500`
+* `1 <= queries.length <= 500`
+* `queries[i].length == 2`
+* `0 <= queries[i][0] < queries[i][1] < n`
+* `1 < queries[i][1] - queries[i][0]`
+* There are no repeated roads among the queries.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3244_shortest_distance_after_road_addition_queries_ii/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3244_shortest_distance_after_road_addition_queries_ii/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..aaef59d22
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3244_shortest_distance_after_road_addition_queries_ii/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3244_shortest_distance_after_road_addition_queries_ii;
+
+// #Hard #Array #Greedy #Graph #Ordered_Set #2024_08_06_Time_5_ms_(97.43%)_Space_78.1_MB_(80.21%)
+
+public class Solution {
+ public int[] shortestDistanceAfterQueries(int n, int[][] queries) {
+ int[] flag = new int[n];
+ int[] res = new int[queries.length];
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
+ flag[i] = i + 1;
+ }
+ for (int k = 0; k < queries.length; k++) {
+ int[] query = queries[k];
+ int preRes = k == 0 ? (n - 1) : res[k - 1];
+ if (flag[query[0]] >= query[1]) {
+ res[k] = preRes;
+ continue;
+ }
+ int subDis = 0;
+ int curr = query[0];
+ while (curr < query[1]) {
+ int next = flag[curr];
+ subDis += 1;
+ flag[curr] = query[1];
+ curr = next;
+ }
+ res[k] = preRes + 1 - subDis;
+ }
+ return res;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3244_shortest_distance_after_road_addition_queries_ii/readme.md b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3244_shortest_distance_after_road_addition_queries_ii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..4d6f354f9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3244_shortest_distance_after_road_addition_queries_ii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
+3244\. Shortest Distance After Road Addition Queries II
+
+Hard
+
+You are given an integer `n` and a 2D integer array `queries`.
+
+There are `n` cities numbered from `0` to `n - 1`. Initially, there is a **unidirectional** road from city `i` to city `i + 1` for all `0 <= i < n - 1`.
+
+queries[i] = [ui, vi] represents the addition of a new **unidirectional** road from city ui to city vi. After each query, you need to find the **length** of the **shortest path** from city `0` to city `n - 1`.
+
+There are no two queries such that `queries[i][0] < queries[j][0] < queries[i][1] < queries[j][1]`.
+
+Return an array `answer` where for each `i` in the range `[0, queries.length - 1]`, `answer[i]` is the _length of the shortest path_ from city `0` to city `n - 1` after processing the **first** `i + 1` queries.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** n = 5, queries = [[2,4],[0,2],[0,4]]
+
+**Output:** [3,2,1]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+After the addition of the road from 2 to 4, the length of the shortest path from 0 to 4 is 3.
+
+
+
+After the addition of the road from 0 to 2, the length of the shortest path from 0 to 4 is 2.
+
+
+
+After the addition of the road from 0 to 4, the length of the shortest path from 0 to 4 is 1.
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** n = 4, queries = [[0,3],[0,2]]
+
+**Output:** [1,1]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+After the addition of the road from 0 to 3, the length of the shortest path from 0 to 3 is 1.
+
+
+
+After the addition of the road from 0 to 2, the length of the shortest path remains 1.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 3 <= n <= 105
+* 1 <= queries.length <= 105
+* `queries[i].length == 2`
+* `0 <= queries[i][0] < queries[i][1] < n`
+* `1 < queries[i][1] - queries[i][0]`
+* There are no repeated roads among the queries.
+* There are no two queries such that `i != j` and `queries[i][0] < queries[j][0] < queries[i][1] < queries[j][1]`.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3245_alternating_groups_iii/Solution.java b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3245_alternating_groups_iii/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..2fe889966
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3245_alternating_groups_iii/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,245 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3245_alternating_groups_iii;
+
+// #Hard #Array #Binary_Indexed_Tree #2024_08_06_Time_36_ms_(82.22%)_Space_70.3_MB_(97.78%)
+
+import java.util.ArrayList;
+import java.util.List;
+
+public class Solution {
+ private void go(int ind, LST lst, int[] fs, int n, LST ff, int[] c) {
+ if (ind > 0) {
+ int pre = lst.prev(ind - 1);
+ int nex = lst.next(pre + 1);
+ if (nex == -1) {
+ nex = 2 * n;
+ }
+ if (pre != -1 && pre < n && --fs[nex - pre] == 0) {
+ ff.unsetPos(nex - pre);
+ }
+ }
+ if (lst.get(ind)) {
+ int pre = ind;
+ int nex = lst.next(ind + 1);
+ if (nex == -1) {
+ nex = 2 * n;
+ }
+ if (pre != -1 && pre < n && --fs[nex - pre] == 0) {
+ ff.unsetPos(nex - pre);
+ }
+ }
+ if (lst.get(ind + 1)) {
+ int pre = ind + 1;
+ int nex = lst.next(ind + 2);
+ if (nex == -1) {
+ nex = 2 * n;
+ }
+ if (pre != -1 && pre < n && --fs[nex - pre] == 0) {
+ ff.unsetPos(nex - pre);
+ }
+ }
+ lst.unsetPos(ind);
+ lst.unsetPos(ind + 1);
+ c[ind] ^= 1;
+ if (ind > 0 && c[ind] != c[ind - 1]) {
+ lst.setPos(ind);
+ }
+ if (ind + 1 < c.length && c[ind + 1] != c[ind]) {
+ lst.setPos(ind + 1);
+ }
+ if (ind > 0) {
+ int pre = lst.prev(ind - 1);
+ int nex = lst.next(pre + 1);
+ if (nex == -1) {
+ nex = 2 * n;
+ }
+ if (pre != -1 && pre < n && ++fs[nex - pre] == 1) {
+ ff.setPos(nex - pre);
+ }
+ }
+ if (lst.get(ind)) {
+ int pre = ind;
+ int nex = lst.next(ind + 1);
+ if (nex == -1) {
+ nex = 2 * n;
+ }
+ if (pre < n && ++fs[nex - pre] == 1) {
+ ff.setPos(nex - pre);
+ }
+ }
+ if (lst.get(ind + 1)) {
+ int pre = ind + 1;
+ int nex = lst.next(ind + 2);
+ if (nex == -1) {
+ nex = 2 * n;
+ }
+ if (pre < n && ++fs[nex - pre] == 1) {
+ ff.setPos(nex - pre);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ public List numberOfAlternatingGroups(int[] colors, int[][] queries) {
+ int n = colors.length;
+ int[] c = new int[2 * n];
+ for (int i = 0; i < 2 * n; i++) {
+ c[i] = colors[i % n] ^ (i % 2 == 0 ? 0 : 1);
+ }
+ LST lst = new LST(2 * n + 3);
+ for (int i = 1; i < 2 * n; i++) {
+ if (c[i] != c[i - 1]) {
+ lst.setPos(i);
+ }
+ }
+ int[] fs = new int[2 * n + 1];
+ LST ff = new LST(2 * n + 1);
+ for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
+ if (lst.get(i)) {
+ int ne = lst.next(i + 1);
+ if (ne == -1) {
+ ne = 2 * n;
+ }
+ fs[ne - i]++;
+ ff.setPos(ne - i);
+ }
+ }
+ List ans = new ArrayList<>();
+ for (int[] q : queries) {
+ if (q[0] == 1) {
+ if (lst.next(0) == -1) {
+ ans.add(n);
+ } else {
+ int lans = 0;
+ for (int i = ff.next(q[1]); i != -1; i = ff.next(i + 1)) {
+ lans += (i - q[1] + 1) * fs[i];
+ }
+ if (c[2 * n - 1] != c[0]) {
+ int f = lst.next(0);
+ if (f >= q[1]) {
+ lans += (f - q[1] + 1);
+ }
+ }
+ ans.add(lans);
+ }
+ } else {
+ int ind = q[1];
+ int val = q[2];
+ if (colors[ind] == val) {
+ continue;
+ }
+ colors[ind] ^= 1;
+ go(ind, lst, fs, n, ff, c);
+ go(ind + n, lst, fs, n, ff, c);
+ }
+ }
+ return ans;
+ }
+
+ private static class LST {
+ private long[][] set;
+ private int n;
+
+ public LST(int n) {
+ this.n = n;
+ int d = 1;
+ d = getD(n, d);
+ set = new long[d][];
+ for (int i = 0, m = n >>> 6; i < d; i++, m >>>= 6) {
+ set[i] = new long[m + 1];
+ }
+ }
+
+ private int getD(int n, int d) {
+ int m = n;
+ while (m > 1) {
+ m >>>= 6;
+ d++;
+ }
+ return d;
+ }
+
+ public LST setPos(int pos) {
+ if (pos >= 0 && pos < n) {
+ for (int i = 0; i < set.length; i++, pos >>>= 6) {
+ set[i][pos >>> 6] |= 1L << pos;
+ }
+ }
+ return this;
+ }
+
+ public LST unsetPos(int pos) {
+ if (pos >= 0 && pos < n) {
+ for (int i = 0;
+ i < set.length && (i == 0 || set[i - 1][pos] == 0L);
+ i++, pos >>>= 6) {
+ set[i][pos >>> 6] &= ~(1L << pos);
+ }
+ }
+ return this;
+ }
+
+ public boolean get(int pos) {
+ return pos >= 0 && pos < n && set[0][pos >>> 6] << ~pos < 0;
+ }
+
+ public int prev(int pos) {
+ int i = 0;
+ while (i < set.length && pos >= 0) {
+ int pre = prev(set[i][pos >>> 6], pos & 63);
+ if (pre != -1) {
+ pos = pos >>> 6 << 6 | pre;
+ while (i > 0) {
+ pos = pos << 6 | 63 - Long.numberOfLeadingZeros(set[--i][pos]);
+ }
+ return pos;
+ }
+ i++;
+ pos >>>= 6;
+ pos--;
+ }
+ return -1;
+ }
+
+ private int prev(long set, int n) {
+ long h = set << ~n;
+ if (h == 0L) {
+ return -1;
+ }
+ return -Long.numberOfLeadingZeros(h) + n;
+ }
+
+ public int next(int pos) {
+ int i = 0;
+ while (i < set.length && pos >>> 6 < set[i].length) {
+ int nex = next(set[i][pos >>> 6], pos & 63);
+ if (nex != -1) {
+ pos = pos >>> 6 << 6 | nex;
+ while (i > 0) {
+ pos = pos << 6 | Long.numberOfTrailingZeros(set[--i][pos]);
+ }
+ return pos;
+ }
+ i++;
+ pos >>>= 6;
+ pos++;
+ }
+ return -1;
+ }
+
+ private static int next(long set, int n) {
+ long h = set >>> n;
+ if (h == 0L) {
+ return -1;
+ }
+ return Long.numberOfTrailingZeros(h) + n;
+ }
+
+ @Override
+ public String toString() {
+ List list = new ArrayList<>();
+ for (int pos = next(0); pos != -1; pos = next(pos + 1)) {
+ list.add(pos);
+ }
+ return list.toString();
+ }
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3245_alternating_groups_iii/readme.md b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3245_alternating_groups_iii/readme.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..5e869ed84
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/main/java/g3201_3300/s3245_alternating_groups_iii/readme.md
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
+3245\. Alternating Groups III
+
+Hard
+
+There are some red and blue tiles arranged circularly. You are given an array of integers `colors` and a 2D integers array `queries`.
+
+The color of tile `i` is represented by `colors[i]`:
+
+* `colors[i] == 0` means that tile `i` is **red**.
+* `colors[i] == 1` means that tile `i` is **blue**.
+
+An **alternating** group is a contiguous subset of tiles in the circle with **alternating** colors (each tile in the group except the first and last one has a different color from its **adjacent** tiles in the group).
+
+You have to process queries of two types:
+
+* queries[i] = [1, sizei], determine the count of **alternating** groups with size sizei.
+* queries[i] = [2, indexi, colori], change colors[indexi] to colori.
+
+Return an array `answer` containing the results of the queries of the first type _in order_.
+
+**Note** that since `colors` represents a **circle**, the **first** and the **last** tiles are considered to be next to each other.
+
+**Example 1:**
+
+**Input:** colors = [0,1,1,0,1], queries = [[2,1,0],[1,4]]
+
+**Output:** [2]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+****
+
+First query:
+
+Change `colors[1]` to 0.
+
+
+
+Second query:
+
+Count of the alternating groups with size 4:
+
+
+
+**Example 2:**
+
+**Input:** colors = [0,0,1,0,1,1], queries = [[1,3],[2,3,0],[1,5]]
+
+**Output:** [2,0]
+
+**Explanation:**
+
+
+
+First query:
+
+Count of the alternating groups with size 3:
+
+
+
+Second query: `colors` will not change.
+
+Third query: There is no alternating group with size 5.
+
+**Constraints:**
+
+* 4 <= colors.length <= 5 * 104
+* `0 <= colors[i] <= 1`
+* 1 <= queries.length <= 5 * 104
+* `queries[i][0] == 1` or `queries[i][0] == 2`
+* For all `i` that:
+ * `queries[i][0] == 1`: `queries[i].length == 2`, `3 <= queries[i][1] <= colors.length - 1`
+ * `queries[i][0] == 2`: `queries[i].length == 3`, `0 <= queries[i][1] <= colors.length - 1`, `0 <= queries[i][2] <= 1`
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3238_find_the_number_of_winning_players/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3238_find_the_number_of_winning_players/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..bcf3d923e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3238_find_the_number_of_winning_players/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3238_find_the_number_of_winning_players;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void winningPlayerCount() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution()
+ .winningPlayerCount(
+ 4, new int[][] {{0, 0}, {1, 0}, {1, 0}, {2, 1}, {2, 1}, {2, 0}}),
+ equalTo(2));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void winningPlayerCount2() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution().winningPlayerCount(5, new int[][] {{1, 1}, {1, 2}, {1, 3}, {1, 4}}),
+ equalTo(0));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void winningPlayerCount3() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution().winningPlayerCount(5, new int[][] {{1, 1}, {2, 4}, {2, 4}, {2, 4}}),
+ equalTo(1));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3239_minimum_number_of_flips_to_make_binary_grid_palindromic_i/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3239_minimum_number_of_flips_to_make_binary_grid_palindromic_i/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..04aa04d0a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3239_minimum_number_of_flips_to_make_binary_grid_palindromic_i/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3239_minimum_number_of_flips_to_make_binary_grid_palindromic_i;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void minFlips() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution().minFlips(new int[][] {{1, 0, 0}, {0, 0, 0}, {0, 0, 1}}), equalTo(2));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void minFlips2() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().minFlips(new int[][] {{0, 1}, {0, 1}, {0, 0}}), equalTo(1));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void minFlips3() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().minFlips(new int[][] {{1}, {0}}), equalTo(0));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3240_minimum_number_of_flips_to_make_binary_grid_palindromic_ii/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3240_minimum_number_of_flips_to_make_binary_grid_palindromic_ii/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..faa2f3524
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3240_minimum_number_of_flips_to_make_binary_grid_palindromic_ii/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3240_minimum_number_of_flips_to_make_binary_grid_palindromic_ii;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void minFlips() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution().minFlips(new int[][] {{1, 0, 0}, {0, 1, 0}, {0, 0, 1}}), equalTo(3));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void minFlips2() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().minFlips(new int[][] {{0, 1}, {0, 1}, {0, 0}}), equalTo(2));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void minFlips3() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().minFlips(new int[][] {{1}, {1}}), equalTo(2));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3241_time_taken_to_mark_all_nodes/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3241_time_taken_to_mark_all_nodes/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..af6326361
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3241_time_taken_to_mark_all_nodes/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3241_time_taken_to_mark_all_nodes;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void timeTaken() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution().timeTaken(new int[][] {{0, 1}, {0, 2}}),
+ equalTo(new int[] {2, 4, 3}));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void timeTaken2() {
+ assertThat(new Solution().timeTaken(new int[][] {{0, 1}}), equalTo(new int[] {1, 2}));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void timeTaken3() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution().timeTaken(new int[][] {{2, 4}, {0, 1}, {2, 3}, {0, 2}}),
+ equalTo(new int[] {4, 6, 3, 5, 5}));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3242_design_neighbor_sum_service/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3242_design_neighbor_sum_service/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..964d71c4f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3242_design_neighbor_sum_service/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3242_design_neighbor_sum_service;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void neighborSum() {
+ NeighborSum neighborSum = new NeighborSum(new int[][] {{0, 1, 2}, {3, 4, 5}, {6, 7, 8}});
+ assertThat(neighborSum.adjacentSum(1), equalTo(6));
+ assertThat(neighborSum.adjacentSum(4), equalTo(16));
+ assertThat(neighborSum.diagonalSum(4), equalTo(16));
+ assertThat(neighborSum.diagonalSum(8), equalTo(4));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void neighborSum2() {
+ NeighborSum neighborSum =
+ new NeighborSum(
+ new int[][] {{1, 2, 0, 3}, {4, 7, 15, 6}, {8, 9, 10, 11}, {12, 13, 14, 5}});
+ assertThat(neighborSum.adjacentSum(15), equalTo(23));
+ assertThat(neighborSum.diagonalSum(9), equalTo(45));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3243_shortest_distance_after_road_addition_queries_i/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3243_shortest_distance_after_road_addition_queries_i/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..1800af188
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3243_shortest_distance_after_road_addition_queries_i/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3243_shortest_distance_after_road_addition_queries_i;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void shortestDistanceAfterQueries() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution()
+ .shortestDistanceAfterQueries(5, new int[][] {{2, 4}, {0, 2}, {0, 4}}),
+ equalTo(new int[] {3, 2, 1}));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void shortestDistanceAfterQueries2() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution().shortestDistanceAfterQueries(4, new int[][] {{0, 3}, {0, 2}}),
+ equalTo(new int[] {1, 1}));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3244_shortest_distance_after_road_addition_queries_ii/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3244_shortest_distance_after_road_addition_queries_ii/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..f715152c1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3244_shortest_distance_after_road_addition_queries_ii/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3244_shortest_distance_after_road_addition_queries_ii;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void shortestDistanceAfterQueries() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution()
+ .shortestDistanceAfterQueries(5, new int[][] {{2, 4}, {0, 2}, {0, 4}}),
+ equalTo(new int[] {3, 2, 1}));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void shortestDistanceAfterQueries2() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution().shortestDistanceAfterQueries(4, new int[][] {{0, 3}, {0, 2}}),
+ equalTo(new int[] {1, 1}));
+ }
+}
diff --git a/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3245_alternating_groups_iii/SolutionTest.java b/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3245_alternating_groups_iii/SolutionTest.java
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..8ba2fe7f6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/test/java/g3201_3300/s3245_alternating_groups_iii/SolutionTest.java
@@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
+package g3201_3300.s3245_alternating_groups_iii;
+
+import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.equalTo;
+import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
+
+import java.util.List;
+import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
+
+class SolutionTest {
+ @Test
+ void numberOfAlternatingGroups() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution()
+ .numberOfAlternatingGroups(
+ new int[] {0, 1, 1, 0, 1}, new int[][] {{2, 1, 0}, {1, 4}}),
+ equalTo(List.of(2)));
+ }
+
+ @Test
+ void numberOfAlternatingGroups2() {
+ assertThat(
+ new Solution()
+ .numberOfAlternatingGroups(
+ new int[] {0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1},
+ new int[][] {{1, 3}, {2, 3, 0}, {1, 5}}),
+ equalTo(List.of(2, 0)));
+ }
+}