diff --git a/solution/3500-3599/3528.Unit Conversion I/README.md b/solution/3500-3599/3528.Unit Conversion I/README.md
index dd0c34397aa00..4b9c7e712213b 100644
--- a/solution/3500-3599/3528.Unit Conversion I/README.md
+++ b/solution/3500-3599/3528.Unit Conversion I/README.md
@@ -34,8 +34,8 @@ tags:
解释:
- - 使用
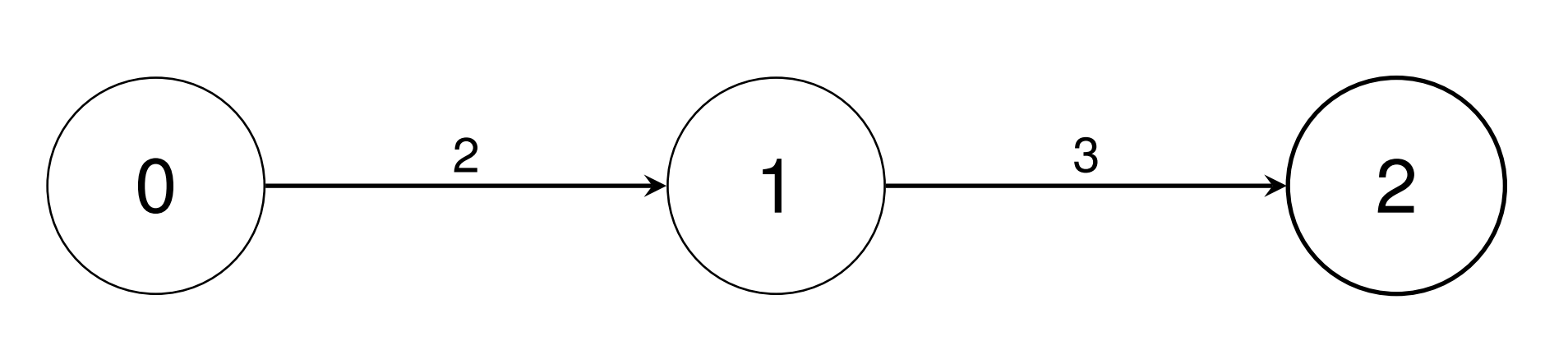
conversions[0]:将一个 0 类型单位转换为 2 个 1 类型单位。
- - 使用
conversions[0] 和 conversions[1] 将一个 0 类型单位转换为 6 个 2 类型单位。
+ - 使用
conversions[0]:将一个 0 类型单位转换为 2 个 1 类型单位。
+ - 使用
conversions[0] 和 conversions[1] 将一个 0 类型单位转换为 6 个 2 类型单位。
 @@ -49,13 +49,13 @@ tags:
@@ -49,13 +49,13 @@ tags:
解释:
- - 使用
conversions[0] 将一个 0 类型单位转换为 2 个 1 类型单位。
- - 使用
conversions[1] 将一个 0 类型单位转换为 3 个 2 类型单位。
- - 使用
conversions[0] 和 conversions[2] 将一个 0 类型单位转换为 8 个 3 类型单位。
- - 使用
conversions[0] 和 conversions[3] 将一个 0 类型单位转换为 10 个 4 类型单位。
- - 使用
conversions[1] 和 conversions[4] 将一个 0 类型单位转换为 6 个 5 类型单位。
- - 使用
conversions[0]、conversions[3] 和 conversions[5] 将一个 0 类型单位转换为 30 个 6 类型单位。
- - 使用
conversions[1]、conversions[4] 和 conversions[6] 将一个 0 类型单位转换为 24 个 7 类型单位。
+ - 使用
conversions[0] 将一个 0 类型单位转换为 2 个 1 类型单位。
+ - 使用
conversions[1] 将一个 0 类型单位转换为 3 个 2 类型单位。
+ - 使用
conversions[0] 和 conversions[2] 将一个 0 类型单位转换为 8 个 3 类型单位。
+ - 使用
conversions[0] 和 conversions[3] 将一个 0 类型单位转换为 10 个 4 类型单位。
+ - 使用
conversions[1] 和 conversions[4] 将一个 0 类型单位转换为 6 个 5 类型单位。
+ - 使用
conversions[0]、conversions[3] 和 conversions[5] 将一个 0 类型单位转换为 30 个 6 类型单位。
+ - 使用
conversions[1]、conversions[4] 和 conversions[6] 将一个 0 类型单位转换为 24 个 7 类型单位。
@@ -64,11 +64,11 @@ tags:
提示:
- 2 <= n <= 105conversions.length == n - 10 <= sourceUniti, targetUniti < n1 <= conversionFactori <= 109- 保证单位 0 可以通过 唯一 的转换路径(不需要反向转换)转换为任何其他单位。
+ 2 <= n <= 105conversions.length == n - 10 <= sourceUniti, targetUniti < n1 <= conversionFactori <= 109- 保证单位 0 可以通过 唯一 的转换路径(不需要反向转换)转换为任何其他单位。
@@ -77,32 +77,143 @@ tags:
-### 方法一
+### 方法一:DFS
+
+由于题目保证了单位 0 可以通过唯一的转换路径转换为其他单位,因此我们可以使用深度优先搜索(DFS)来遍历所有单位的转换关系。另外,由于 $\textit{conversions}$ 数组的长度为 $n - 1$,表示有 $n - 1$ 条转换关系,因此我们可以将单位转换关系看作一棵树,根节点为单位 0,其他节点为其他单位。
+
+我们可以用一个邻接表 $g$ 来表示单位转换关系,其中 $g[i]$ 表示单位 $i$ 可以转换到的单位和对应的转换因子。
+
+然后,我们从根节点 $0$ 开始进行深度优先搜索,即调函数 $\textit{dfs}(s, \textit{mul})$,其中 $s$ 表示当前单位,$\textit{mul}$ 表示从单位 $0$ 转换到单位 $s$ 的转换因子。初始时 $s = 0$, $\textit{mul} = 1$。在每次递归中,我们将当前单位 $s$ 的转换因子 $\textit{mul}$ 存储到答案数组中,然后遍历当前单位 $s$ 的所有邻接单位 $t$,递归调用 $\textit{dfs}(t, \textit{mul} \times w \mod (10^9 + 7))$,其中 $w$ 为单位 $s$ 转换到单位 $t$ 的转换因子。
+
+最后,我们返回答案数组即可。
+
+时间复杂度 $O(n)$,空间复杂度 $O(n)$。其中 $n$ 为单位的数量。
#### Python3
```python
-
+class Solution:
+ def baseUnitConversions(self, conversions: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
+ def dfs(s: int, mul: int) -> None:
+ ans[s] = mul
+ for t, w in g[s]:
+ dfs(t, mul * w % mod)
+
+ mod = 10**9 + 7
+ n = len(conversions) + 1
+ g = [[] for _ in range(n)]
+ for s, t, w in conversions:
+ g[s].append((t, w))
+ ans = [0] * n
+ dfs(0, 1)
+ return ans
```
#### Java
```java
-
+class Solution {
+ private final int mod = (int) 1e9 + 7;
+ private List[] g;
+ private int[] ans;
+ private int n;
+
+ public int[] baseUnitConversions(int[][] conversions) {
+ n = conversions.length + 1;
+ g = new List[n];
+ Arrays.setAll(g, k -> new ArrayList<>());
+ ans = new int[n];
+ for (var e : conversions) {
+ g[e[0]].add(new int[] {e[1], e[2]});
+ }
+ dfs(0, 1);
+ return ans;
+ }
+
+ private void dfs(int s, long mul) {
+ ans[s] = (int) mul;
+ for (var e : g[s]) {
+ dfs(e[0], mul * e[1] % mod);
+ }
+ }
+}
```
#### C++
```cpp
-
+class Solution {
+public:
+ vector baseUnitConversions(vector>& conversions) {
+ const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
+ int n = conversions.size() + 1;
+ vector>> g(n);
+ vector ans(n);
+ for (const auto& e : conversions) {
+ g[e[0]].push_back({e[1], e[2]});
+ }
+ auto dfs = [&](this auto&& dfs, int s, long long mul) -> void {
+ ans[s] = mul;
+ for (auto [t, w] : g[s]) {
+ dfs(t, mul * w % mod);
+ }
+ };
+ dfs(0, 1);
+ return ans;
+ }
+};
```
#### Go
```go
+func baseUnitConversions(conversions [][]int) []int {
+ const mod = int(1e9 + 7)
+ n := len(conversions) + 1
+
+ g := make([][]struct{ t, w int }, n)
+ for _, e := range conversions {
+ s, t, w := e[0], e[1], e[2]
+ g[s] = append(g[s], struct{ t, w int }{t, w})
+ }
+
+ ans := make([]int, n)
+
+ var dfs func(s int, mul int)
+ dfs = func(s int, mul int) {
+ ans[s] = mul
+ for _, e := range g[s] {
+ dfs(e.t, mul*e.w%mod)
+ }
+ }
+
+ dfs(0, 1)
+ return ans
+}
+```
+#### TypeScript
+
+```ts
+function baseUnitConversions(conversions: number[][]): number[] {
+ const mod = BigInt(1e9 + 7);
+ const n = conversions.length + 1;
+ const g: { t: number; w: number }[][] = Array.from({ length: n }, () => []);
+ for (const [s, t, w] of conversions) {
+ g[s].push({ t, w });
+ }
+ const ans: number[] = Array(n).fill(0);
+ const dfs = (s: number, mul: number) => {
+ ans[s] = mul;
+ for (const { t, w } of g[s]) {
+ dfs(t, Number((BigInt(mul) * BigInt(w)) % mod));
+ }
+ };
+ dfs(0, 1);
+ return ans;
+}
```
diff --git a/solution/3500-3599/3528.Unit Conversion I/README_EN.md b/solution/3500-3599/3528.Unit Conversion I/README_EN.md
index bdcd4ab35d682..01b370e3cedcf 100644
--- a/solution/3500-3599/3528.Unit Conversion I/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/3500-3599/3528.Unit Conversion I/README_EN.md
@@ -33,8 +33,8 @@ tags:
Explanation:
- - Convert a single unit of type 0 into 2 units of type 1 using
conversions[0].
- - Convert a single unit of type 0 into 6 units of type 2 using
conversions[0], then conversions[1].
+ - Convert a single unit of type 0 into 2 units of type 1 using
conversions[0].
+ - Convert a single unit of type 0 into 6 units of type 2 using
conversions[0], then conversions[1].
 @@ -48,13 +48,13 @@ tags:
@@ -48,13 +48,13 @@ tags:
Explanation:
- - Convert a single unit of type 0 into 2 units of type 1 using
conversions[0].
- - Convert a single unit of type 0 into 3 units of type 2 using
conversions[1].
- - Convert a single unit of type 0 into 8 units of type 3 using
conversions[0], then conversions[2].
- - Convert a single unit of type 0 into 10 units of type 4 using
conversions[0], then conversions[3].
- - Convert a single unit of type 0 into 6 units of type 5 using
conversions[1], then conversions[4].
- - Convert a single unit of type 0 into 30 units of type 6 using
conversions[0], conversions[3], then conversions[5].
- - Convert a single unit of type 0 into 24 units of type 7 using
conversions[1], conversions[4], then conversions[6].
+ - Convert a single unit of type 0 into 2 units of type 1 using
conversions[0].
+ - Convert a single unit of type 0 into 3 units of type 2 using
conversions[1].
+ - Convert a single unit of type 0 into 8 units of type 3 using
conversions[0], then conversions[2].
+ - Convert a single unit of type 0 into 10 units of type 4 using
conversions[0], then conversions[3].
+ - Convert a single unit of type 0 into 6 units of type 5 using
conversions[1], then conversions[4].
+ - Convert a single unit of type 0 into 30 units of type 6 using
conversions[0], conversions[3], then conversions[5].
+ - Convert a single unit of type 0 into 24 units of type 7 using
conversions[1], conversions[4], then conversions[6].
@@ -62,11 +62,11 @@ tags:
Constraints:
- 2 <= n <= 105conversions.length == n - 10 <= sourceUniti, targetUniti < n1 <= conversionFactori <= 109- It is guaranteed that unit 0 can be converted into any other unit through a unique combination of conversions without using any conversions in the opposite direction.
+ 2 <= n <= 105conversions.length == n - 10 <= sourceUniti, targetUniti < n1 <= conversionFactori <= 109- It is guaranteed that unit 0 can be converted into any other unit through a unique combination of conversions without using any conversions in the opposite direction.
@@ -75,32 +75,143 @@ tags:
-### Solution 1
+### Solution 1: DFS
+
+Since the problem guarantees that unit 0 can be converted to any other unit through a unique conversion path, we can use Depth-First Search (DFS) to traverse all unit conversion relationships. Additionally, since the length of the $\textit{conversions}$ array is $n - 1$, representing $n - 1$ conversion relationships, we can treat the unit conversion relationships as a tree, where the root node is unit 0, and the other nodes are the other units.
+
+We can use an adjacency list $g$ to represent the unit conversion relationships, where $g[i]$ represents the units that unit $i$ can convert to and the corresponding conversion factors.
+
+Then, we start the DFS from the root node $0$, i.e., call the function $\textit{dfs}(s, \textit{mul})$, where $s$ represents the current unit, and $\textit{mul}$ represents the conversion factor from unit $0$ to unit $s$. Initially, $s = 0$, $\textit{mul} = 1$. In each recursion, we store the conversion factor $\textit{mul}$ of the current unit $s$ into the answer array, then traverse all adjacent units $t$ of the current unit $s$, and recursively call $\textit{dfs}(t, \textit{mul} \times w \mod (10^9 + 7))$, where $w$ is the conversion factor from unit $s$ to unit $t$.
+
+Finally, we return the answer array.
+
+The complexity is $O(n)$, and the space complexity is $O(n)$, where $n$ is the number of units.
#### Python3
```python
-
+class Solution:
+ def baseUnitConversions(self, conversions: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
+ def dfs(s: int, mul: int) -> None:
+ ans[s] = mul
+ for t, w in g[s]:
+ dfs(t, mul * w % mod)
+
+ mod = 10**9 + 7
+ n = len(conversions) + 1
+ g = [[] for _ in range(n)]
+ for s, t, w in conversions:
+ g[s].append((t, w))
+ ans = [0] * n
+ dfs(0, 1)
+ return ans
```
#### Java
```java
-
+class Solution {
+ private final int mod = (int) 1e9 + 7;
+ private List[] g;
+ private int[] ans;
+ private int n;
+
+ public int[] baseUnitConversions(int[][] conversions) {
+ n = conversions.length + 1;
+ g = new List[n];
+ Arrays.setAll(g, k -> new ArrayList<>());
+ ans = new int[n];
+ for (var e : conversions) {
+ g[e[0]].add(new int[] {e[1], e[2]});
+ }
+ dfs(0, 1);
+ return ans;
+ }
+
+ private void dfs(int s, long mul) {
+ ans[s] = (int) mul;
+ for (var e : g[s]) {
+ dfs(e[0], mul * e[1] % mod);
+ }
+ }
+}
```
#### C++
```cpp
-
+class Solution {
+public:
+ vector baseUnitConversions(vector>& conversions) {
+ const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
+ int n = conversions.size() + 1;
+ vector>> g(n);
+ vector ans(n);
+ for (const auto& e : conversions) {
+ g[e[0]].push_back({e[1], e[2]});
+ }
+ auto dfs = [&](this auto&& dfs, int s, long long mul) -> void {
+ ans[s] = mul;
+ for (auto [t, w] : g[s]) {
+ dfs(t, mul * w % mod);
+ }
+ };
+ dfs(0, 1);
+ return ans;
+ }
+};
```
#### Go
```go
+func baseUnitConversions(conversions [][]int) []int {
+ const mod = int(1e9 + 7)
+ n := len(conversions) + 1
+
+ g := make([][]struct{ t, w int }, n)
+ for _, e := range conversions {
+ s, t, w := e[0], e[1], e[2]
+ g[s] = append(g[s], struct{ t, w int }{t, w})
+ }
+
+ ans := make([]int, n)
+
+ var dfs func(s int, mul int)
+ dfs = func(s int, mul int) {
+ ans[s] = mul
+ for _, e := range g[s] {
+ dfs(e.t, mul*e.w%mod)
+ }
+ }
+
+ dfs(0, 1)
+ return ans
+}
+```
+#### TypeScript
+
+```ts
+function baseUnitConversions(conversions: number[][]): number[] {
+ const mod = BigInt(1e9 + 7);
+ const n = conversions.length + 1;
+ const g: { t: number; w: number }[][] = Array.from({ length: n }, () => []);
+ for (const [s, t, w] of conversions) {
+ g[s].push({ t, w });
+ }
+ const ans: number[] = Array(n).fill(0);
+ const dfs = (s: number, mul: number) => {
+ ans[s] = mul;
+ for (const { t, w } of g[s]) {
+ dfs(t, Number((BigInt(mul) * BigInt(w)) % mod));
+ }
+ };
+ dfs(0, 1);
+ return ans;
+}
```
diff --git a/solution/3500-3599/3528.Unit Conversion I/Solution.cpp b/solution/3500-3599/3528.Unit Conversion I/Solution.cpp
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..1c5c52272b45f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/3500-3599/3528.Unit Conversion I/Solution.cpp
@@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
+class Solution {
+public:
+ vector baseUnitConversions(vector>& conversions) {
+ const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
+ int n = conversions.size() + 1;
+ vector>> g(n);
+ vector ans(n);
+ for (const auto& e : conversions) {
+ g[e[0]].push_back({e[1], e[2]});
+ }
+ auto dfs = [&](this auto&& dfs, int s, long long mul) -> void {
+ ans[s] = mul;
+ for (auto [t, w] : g[s]) {
+ dfs(t, mul * w % mod);
+ }
+ };
+ dfs(0, 1);
+ return ans;
+ }
+};
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/3500-3599/3528.Unit Conversion I/Solution.go b/solution/3500-3599/3528.Unit Conversion I/Solution.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..5b69c70470577
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/3500-3599/3528.Unit Conversion I/Solution.go
@@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
+func baseUnitConversions(conversions [][]int) []int {
+ const mod = int(1e9 + 7)
+ n := len(conversions) + 1
+
+ g := make([][]struct{ t, w int }, n)
+ for _, e := range conversions {
+ s, t, w := e[0], e[1], e[2]
+ g[s] = append(g[s], struct{ t, w int }{t, w})
+ }
+
+ ans := make([]int, n)
+
+ var dfs func(s int, mul int)
+ dfs = func(s int, mul int) {
+ ans[s] = mul
+ for _, e := range g[s] {
+ dfs(e.t, mul*e.w%mod)
+ }
+ }
+
+ dfs(0, 1)
+ return ans
+}
diff --git a/solution/3500-3599/3528.Unit Conversion I/Solution.java b/solution/3500-3599/3528.Unit Conversion I/Solution.java
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..7d44b96aefc6f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/3500-3599/3528.Unit Conversion I/Solution.java
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+class Solution {
+ private final int mod = (int) 1e9 + 7;
+ private List[] g;
+ private int[] ans;
+ private int n;
+
+ public int[] baseUnitConversions(int[][] conversions) {
+ n = conversions.length + 1;
+ g = new List[n];
+ Arrays.setAll(g, k -> new ArrayList<>());
+ ans = new int[n];
+ for (var e : conversions) {
+ g[e[0]].add(new int[] {e[1], e[2]});
+ }
+ dfs(0, 1);
+ return ans;
+ }
+
+ private void dfs(int s, long mul) {
+ ans[s] = (int) mul;
+ for (var e : g[s]) {
+ dfs(e[0], mul * e[1] % mod);
+ }
+ }
+}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/3500-3599/3528.Unit Conversion I/Solution.py b/solution/3500-3599/3528.Unit Conversion I/Solution.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..2b5a94c132eb9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/3500-3599/3528.Unit Conversion I/Solution.py
@@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
+class Solution:
+ def baseUnitConversions(self, conversions: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
+ def dfs(s: int, mul: int) -> None:
+ ans[s] = mul
+ for t, w in g[s]:
+ dfs(t, mul * w % mod)
+
+ mod = 10**9 + 7
+ n = len(conversions) + 1
+ g = [[] for _ in range(n)]
+ for s, t, w in conversions:
+ g[s].append((t, w))
+ ans = [0] * n
+ dfs(0, 1)
+ return ans
diff --git a/solution/3500-3599/3528.Unit Conversion I/Solution.ts b/solution/3500-3599/3528.Unit Conversion I/Solution.ts
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..c87af0f665d60
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/3500-3599/3528.Unit Conversion I/Solution.ts
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+function baseUnitConversions(conversions: number[][]): number[] {
+ const mod = BigInt(1e9 + 7);
+ const n = conversions.length + 1;
+ const g: { t: number; w: number }[][] = Array.from({ length: n }, () => []);
+ for (const [s, t, w] of conversions) {
+ g[s].push({ t, w });
+ }
+ const ans: number[] = Array(n).fill(0);
+ const dfs = (s: number, mul: number) => {
+ ans[s] = mul;
+ for (const { t, w } of g[s]) {
+ dfs(t, Number((BigInt(mul) * BigInt(w)) % mod));
+ }
+ };
+ dfs(0, 1);
+ return ans;
+}
 @@ -48,13 +48,13 @@ tags:
@@ -48,13 +48,13 @@ tags:
 @@ -49,13 +49,13 @@ tags:
@@ -49,13 +49,13 @@ tags: