list = template.loadAll(Employee.class);
+ return list;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+#### 5) `applicationContext.xml`:
+
+```xml title="applicationContext.xml"
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ employee.hbm.xml
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ org.hibernate.dialect.Oracle9Dialect
+ update
+ true
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+```
+
+#### 6) `InsertTest.java`:
+
+```java title="InsertTest.java"
+package com.codeharbourhub;
+
+import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
+import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory;
+import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
+import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
+
+public class InsertTest {
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ Resource r = new ClassPathResource("applicationContext.xml");
+ BeanFactory factory = new XmlBeanFactory(r);
+
+ EmployeeDao dao = (EmployeeDao) factory.getBean("d");
+
+ Employee e = new Employee();
+ e.setId(114);
+ e.setName("varun");
+ e.setSalary(50000);
+
+ dao.saveEmployee(e);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+Now, upon executing `InsertTest.java`, the record will be successfully inserted into the Oracle database.
+In this tutorial, we explored the integration of Hibernate with the Spring framework, leveraging Spring's powerful features to simplify the development process. Here's a summary of the key points covered:
+
+1. **Integration Overview**:
+ - Spring offers seamless integration with ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) frameworks like Hibernate, JPA, JDO, Oracle Toplink, and iBATIS.
+ - The integration provides advantages such as reduced boilerplate code, easier testing through IoC (Inversion of Control), improved exception handling, and integrated transaction management.
+
+2. **Hibernate and Spring Integration**:
+ - Hibernate applications typically require a `hibernate.cfg.xml` file to configure database information. However, when integrating with Spring, this configuration can be provided in the `applicationContext.xml` file.
+ - Spring simplifies Hibernate usage by providing classes like `HibernateTemplate`, reducing the need for manual configuration and session management.
+
+3. **Benefits of Spring with Hibernate**:
+ - With Spring, developers can utilize the `HibernateTemplate` class, significantly reducing the amount of code required compared to using Hibernate alone.
+ - The `HibernateTemplate` class provides methods for common operations like persisting, updating, and deleting objects, as well as fetching objects by ID or loading all objects of a particular type.
+
+4. **Steps for Integration**:
+ - The integration process involves several steps, including creating database tables, defining Hibernate mapping files (`employee.hbm.xml`), implementing the persistent class (`Employee.java`), creating a DAO (Data Access Object) class (`EmployeeDao.java`), and configuring the Spring application context (`applicationContext.xml`).
+ - Finally, a test class (`InsertTest.java`) is used to demonstrate the integration by saving an instance of the `Employee` class using the `EmployeeDao`.
+
+5. **Configuration**:
+ - The `applicationContext.xml` file contains configuration details such as DataSource setup, session factory configuration, Hibernate properties, and bean definitions for the `HibernateTemplate` and DAO classes.
+
+6. **Execution**:
+ - Upon executing the `InsertTest` class, the Spring context is initialized, and the `EmployeeDao` bean is obtained from the context. An instance of `Employee` is created and saved using the DAO's `saveEmployee` method, demonstrating successful integration and data persistence.
+
+By following these steps, developers can seamlessly integrate Hibernate with Spring, leveraging the powerful features of both frameworks to build robust and maintainable Java applications.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/docs/java/Spring-and-Spring-Boot/spring-environment-setup.md b/docs/java/Spring-and-Spring-Boot/spring-environment-setup.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..a38ae27bd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/java/Spring-and-Spring-Boot/spring-environment-setup.md
@@ -0,0 +1,172 @@
+---
+id: spring-environment-setup
+title: Spring Environment Setup
+sidebar_label: spring environment setup
+sidebar_position: 2
+tags: [java, spring,core-java, programming, java core, java spring, java web]
+description: in thi tutorial you will learn about how to install and use spring framework in you local computer environment. and make your first java spring project in ecllips
+---
+
+# Spring Environment Setup
+
+## Step 1 - Setup Java Development Kit (JDK)
+
+You can download the latest version of SDK from Oracle's Java site − [Java SE Downloads](https://www.oracle.com/java/technologies/javase-downloads.html). You will find instructions for installing JDK in the downloaded files, follow the given instructions to install and configure the setup. Finally, set PATH and JAVA_HOME environment variables to refer to the directory that contains `java` and `javac`, typically `java_install_dir/bin` and `java_install_dir` respectively.
+
+If you are running Windows and have installed the JDK in `C:\jdk1.6.0_15`, you would have to put the following line in your `C:\autoexec.bat` file.
+
+```shell
+set PATH=C:\jdk1.6.0_15\bin;%PATH%
+set JAVA_HOME=C:\jdk1.6.0_15
+```
+
+Alternatively, on Windows NT/2000/XP, you will have to right-click on My Computer, select Properties → Advanced → Environment Variables. Then, you will have to update the PATH value and click the OK button.
+
+On Unix (Solaris, Linux, etc.), if the SDK is installed in `/usr/local/jdk1.6.0_15` and you use the C shell, you will have to put the following into your `.cshrc` file.
+
+```shell
+setenv PATH /usr/local/jdk1.6.0_15/bin:$PATH
+setenv JAVA_HOME /usr/local/jdk1.6.0_15
+```
+
+Alternatively, if you use an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) like Borland JBuilder, Eclipse, IntelliJ IDEA, or Sun ONE Studio, you will have to compile and run a simple program to confirm that the IDE knows where you have installed Java. Otherwise, you will have to carry out a proper setup as given in the document of the IDE.
+
+## Step 2 - Install Apache Common Logging API
+
+You can download the latest version of the Apache Commons Logging API from [Apache Commons Logging](https://commons.apache.org/logging/). Once you download the installation, unpack the binary distribution into a convenient location. For example, in `C:\commons-logging-1.1.1` on Windows, or `/usr/local/commons-logging-1.1.1` on Linux/Unix. This directory will have the following jar files and other supporting documents, etc.
+
+Make sure you set your CLASSPATH variable on this directory properly otherwise you will face a problem while running your application.
+
+## Step 3 - Setup Eclipse IDE
+
+All the examples in this tutorial have been written using Eclipse IDE. So we would suggest you should have the latest version of Eclipse installed on your machine.
+
+To install Eclipse IDE, download the latest Eclipse binaries from [Eclipse Downloads](https://www.eclipse.org/downloads/). Once you download the installation, unpack the binary distribution into a convenient location. For example, in `C:\eclipse` on Windows, or `/usr/local/eclipse` on Linux/Unix and finally set the PATH variable appropriately.
+
+Eclipse can be started by executing the following commands on Windows machines, or you can simply double-click on `eclipse.exe`.
+
+```shell
+%C:\eclipse\eclipse.exe
+```
+
+Eclipse can be started by executing the following commands on Unix (Solaris, Linux, etc.) machines −
+
+```shell
+$/usr/local/eclipse/eclipse
+```
+
+After a successful startup, if everything is fine then it should display the following result −
+
+## Step 4 - Setup Spring Framework Libraries
+
+Now if everything is fine, then you can proceed to set up your Spring framework. Following are the simple steps to download and install the framework on your machine.
+
+1. Make a choice whether you want to install Spring on Windows or Unix, and then proceed to the next step to download the `.zip` file for Windows and `.tz` file for Unix.
+
+2. Download the latest version of Spring framework binaries from [Spring Releases](https://repo.spring.io/release/org/springframework/spring).
+
+At the time of developing this tutorial, `spring-framework-4.1.6.RELEASE-dist.zip` was downloaded on a Windows machine. After the downloaded file was unzipped, it gives the following directory structure inside `E:\spring`.
+
+
+
+You will find all the Spring libraries in the directory `E:\spring\libs`. Make sure you set your CLASSPATH variable on this directory properly otherwise you will face a problem while running your application. If you are using Eclipse, then it is not required to set CLASSPATH because all the settings will be done through Eclipse.
+
+Once you are done with this last step, you are ready to proceed to your first Spring example.
+
+## Steps to Create Spring Application in Eclipse IDE
+
+Let's see the 5 steps to create the first Spring application using Eclipse IDE.
+
+### 1. Create the Java Project
+
+Go to File menu → New → Project → Java Project. Write the project name e.g., `firstspring` and click Finish. Now the Java project is created.
+
+### 2. Add Spring Jar Files
+
+There are mainly three jar files required to run this application.
+
+- `org.springframework.core-3.0.1.RELEASE-A`
+- `com.springsource.org.apache.commons.logging-1.1.1`
+- `org.springframework.beans-3.0.1.RELEASE-A`
+
+To load the jar files in Eclipse IDE, right-click on your project → Build Path → Add external archives → select all the required jar files → Finish.
+
+### 3. Create Java Class
+
+In this case, we are simply creating the `Student` class with a `name` property. The name of the student will be provided by the XML file. It is just a simple example, not the actual use of Spring. We will see the actual use in the Dependency Injection chapter. To create the Java class, right-click on `src` → New → Class → Write the class name e.g., `Student` → Finish. Write the following code:
+
+```java
+package com.javatpoint;
+
+public class Student {
+ private String name;
+
+ public String getName() {
+ return name;
+ }
+
+ public void setName(String name) {
+ this.name = name;
+ }
+
+ public void displayInfo() {
+ System.out.println("Hello: " + name);
+ }
+}
+```
+
+This is a simple bean class, containing only one property `name` with its getter and setter methods. This class contains one extra method named `displayInfo()` that prints the student name with a hello message.
+
+### 4. Create the XML File
+
+To create the XML file click on `src` → New → File → Give the file name such as `applicationContext.xml` → Finish. Open the `applicationContext.xml` file, and write the following code:
+
+```xml
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+```
+
+The `bean` element is used to define the bean for the given class. The `property` sub-element of `bean` specifies the property of the `Student` class named `name`. The value specified in the `property` element will be set in the `Student` class object by the IOC container.
+
+### 5. Create the Test Class
+
+Create the Java class e.g., `Test`. Here we are getting the object of the `Student` class from the IOC container using the `getBean()` method of `BeanFactory`. Let's see the code of the test class.
+
+```java
+package com.javatpoint;
+
+import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
+import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory;
+import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
+import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
+
+public class Test {
+ public static void main(String[] args) {
+ Resource resource = new ClassPathResource("applicationContext.xml");
+ BeanFactory factory = new XmlBeanFactory(resource);
+
+ Student student = (Student) factory.getBean("studentbean");
+ student.displayInfo();
+ }
+}
+```
+
+---
+
+## Conclusion
+
+Setting up the Java Development Kit (JDK), Apache Commons Logging API, Eclipse IDE, and Spring Framework libraries are essential steps in preparing your development environment for building Java applications with the Spring Framework. By following these steps, you ensure that your environment is properly configured, enabling you to focus on writing and running your Spring applications efficiently.
+
+Once your setup is complete, creating your first Spring application becomes straightforward with the help of Eclipse IDE. This guide walked you through the steps to create a simple Spring application, demonstrating the power and flexibility of the Spring Framework.
+
+With your environment ready and your first application up and running, you're well on your way to exploring the many features and capabilities of Spring. Happy coding!
diff --git a/docs/java/Spring-and-Spring-Boot/spring-mvc.md b/docs/java/Spring-and-Spring-Boot/spring-mvc.md
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..1135b9f7d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/java/Spring-and-Spring-Boot/spring-mvc.md
@@ -0,0 +1,227 @@
+---
+id: spring-mvc
+title: introduction to spring mvc
+sidebar_label: Introduction to Spring mvc
+sidebar_position: 6
+tags: [java, spring,core-java, programming, java core, java spring, java web,java-mvc,model,view,controller,mvc in]
+description: in thi tutorial you will learn about what is MVC and how to sue it in java and it works with java with example
+---
+### Spring MVC Tutorial
+
+Spring MVC is a Java framework used for building web applications. It implements the Model-View-Controller (MVC) design pattern and provides features like Inversion of Control and Dependency Injection.
+
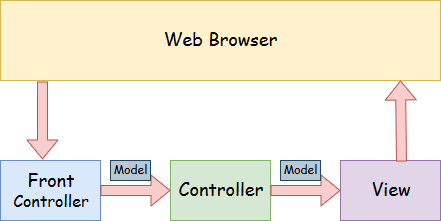
+#### Spring Web Model-View-Controller
+
+
+
+- **Model:** Contains the data of the application. It can be a single object or a collection of objects.
+- **Controller:** Contains the business logic of the application. Marked with the `@Controller` annotation.
+- **View:** Represents the provided information in a particular format. JSP+JSTL is commonly used for creating view pages.
+
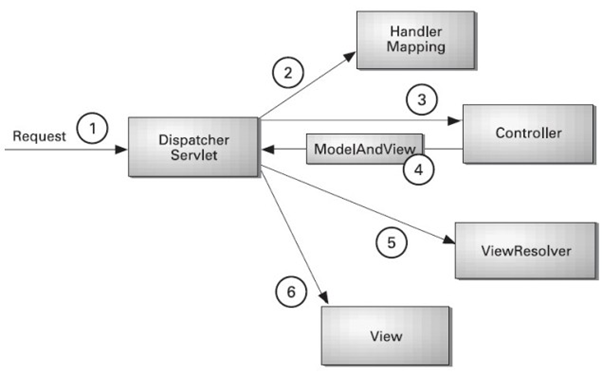
+#### Front Controller
+
+In Spring Web MVC, the `DispatcherServlet` class acts as the front controller, managing the flow of the Spring MVC application.
+
+
+
+- All incoming requests are intercepted by the `DispatcherServlet`.
+- The `DispatcherServlet` forwards the request to the appropriate controller.
+- The controller returns a `ModelAndView` object.
+- The `DispatcherServlet` invokes the specified view component.
+
+#### Advantages of Spring MVC Framework
+
+- **Separate roles:** Each role is fulfilled by a specialized object, promoting better code organization.
+- **Lightweight:** Utilizes a lightweight servlet container for application development and deployment.
+- **Powerful Configuration:** Provides robust configuration for both framework and application classes.
+- **Rapid Development:** Facilitates fast and parallel development.
+- **Reusable Business Code:** Allows the reuse of existing business objects.
+- **Easy to Test:** Supports the creation of JavaBeans classes for easy testing.
+
+#### Spring Web MVC Framework Example
+
+##### Required Jar files or Maven Dependency
+
+If using Maven, add the following dependencies to the `pom.xml` file:
+
+```xml title="pom.xml"
+
+
+ org.springframework
+ spring-webmvc
+ 5.1.1.RELEASE
+
+
+
+
+ javax.servlet
+ servlet-api
+ 3.0-alpha-1
+
+```
+
+##### Create the Controller Class
+
+```java title="controller.java"
+package com.javatpoint;
+
+import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
+import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
+
+@Controller
+public class HelloController {
+ @RequestMapping("/")
+ public String display() {
+ return "index";
+ }
+}
+```
+
+##### Provide the entry of controller in the `web.xml` file
+
+```xml title="web.xml"
+
+ spring
+ org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
+ 1
+
+
+ spring
+ /
+
+```
+
+##### Define the bean in the XML file (`spring-servlet.xml`)
+
+```xml
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+```
+
+##### Display the message in the JSP page (`index.jsp`)
+
+```jsp
+
+
+Welcome to Spring MVC Tutorial
+
+
+```
+
+In this tutorial, we've seen how to set up a basic Spring MVC application. With this setup, incoming requests are handled by the `DispatcherServlet`, which maps them to the appropriate controller. The controller then returns a view, which is rendered to the user.
+
+
+##### Create Multiple Controllers
+
+Let's extend our example to include multiple controllers, each handling different requests.
+
+1. **Add Dependencies to `pom.xml`**
+
+ Ensure that the Spring Web MVC dependency is included in the `pom.xml` file.
+
+2. **Create the Request Page (`index.jsp`)**
+
+ Create a simple JSP page containing links to different controllers.
+
+ ```jsp
+
+
+ Spring MVC ||
+ Spring Boot
+
+
+ ```
+
+3. **Create Controller Classes**
+
+ We'll create two controller classes, each handling a different request.
+
+
+
+ ```java title="HelloController.java"
+ package com.javatpoint;
+
+ import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
+ import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
+
+ @Controller
+ public class HelloController1 {
+ @RequestMapping("/hello1")
+ public String display() {
+ return "viewpage1";
+ }
+ }
+ ```
+
+
+ ```java title="hellocontroller2.java"
+ package com.javatpoint;
+
+ import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
+ import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
+
+ @Controller
+ public class HelloController2 {
+ @RequestMapping("/hello2")
+ public String display() {
+ return "viewpage2";
+ }
+ }
+ ```
+
+4. **Provide the Entry of Controllers in `web.xml`**
+
+ Ensure that the `DispatcherServlet` is configured to map requests correctly.
+
+5. **Define the Bean in the XML File (`spring-servlet.xml`)**
+
+ Define the view resolver to map logical view names to physical JSP files.
+
+6. **Create the View Pages**
+
+ Create JSP pages corresponding to each controller.
+
+ **viewpage1.jsp**
+
+ ```jsp
+
+
+ Welcome to Spring MVC Tutorial
+
+
+ ```
+
+ **viewpage2.jsp**
+
+ ```jsp
+
+
+ Welcome to Spring Boot Tutorial
+
+
+ ```
+
+By following these steps, you can create a Spring MVC application with multiple controllers, each handling specific requests and returning corresponding views.
+
+This concludes the extended example of a Spring MVC framework. You can now deploy the project and start the server to see the application in action.
\ No newline at end of file