|
| 1 | +--- |
| 2 | +id: dijkstra |
| 3 | +title: Dijkstra's Algorithm |
| 4 | +sidebar_label: Dijkstra's Algorithm |
| 5 | +tags: [python, java, c++, javascript, programming, algorithms, dijkstra, graph, shortest-path, data structures, tutorial, in-depth] |
| 6 | +description: In this tutorial, we will learn about Dijkstra's Algorithm and its implementation in Python, Java, C++, and JavaScript with detailed explanations and examples. |
| 7 | +--- |
| 8 | + |
| 9 | +# Dijkstra's Algorithm |
| 10 | + |
| 11 | +Dijkstra's Algorithm is a popular algorithm used for finding the shortest paths between nodes in a graph. This tutorial will cover the basics of Dijkstra's Algorithm, its applications, and how to implement it in Python, Java, C++, and JavaScript. We will also delve into various optimizations and advanced use cases. |
| 12 | + |
| 13 | +## Introduction to Dijkstra's Algorithm |
| 14 | + |
| 15 | +Dijkstra's Algorithm was conceived by computer scientist Edsger W. Dijkstra in 1956. It is used to find the shortest path from a starting node to all other nodes in a weighted graph, where the weights represent the cost to traverse from one node to another. |
| 16 | + |
| 17 | +## How Dijkstra's Algorithm Works |
| 18 | + |
| 19 | +- **Initialization**: Start with a set of nodes. Assign a tentative distance value to every node: set it to zero for the initial node and to infinity for all other nodes. Set the initial node as the current node. |
| 20 | +- **Visit Neighbors**: For the current node, consider all its unvisited neighbors and calculate their tentative distances. Compare the newly calculated tentative distance to the current assigned value and assign the smaller one. |
| 21 | +- **Mark Visited**: Once all neighbors are visited, mark the current node as visited. A visited node will not be checked again. |
| 22 | +- **Select Next Node**: Select the unvisited node that is marked with the smallest tentative distance and set it as the new current node. |
| 23 | +- **Repeat**: Continue the process until all nodes have been visited. |
| 24 | + |
| 25 | +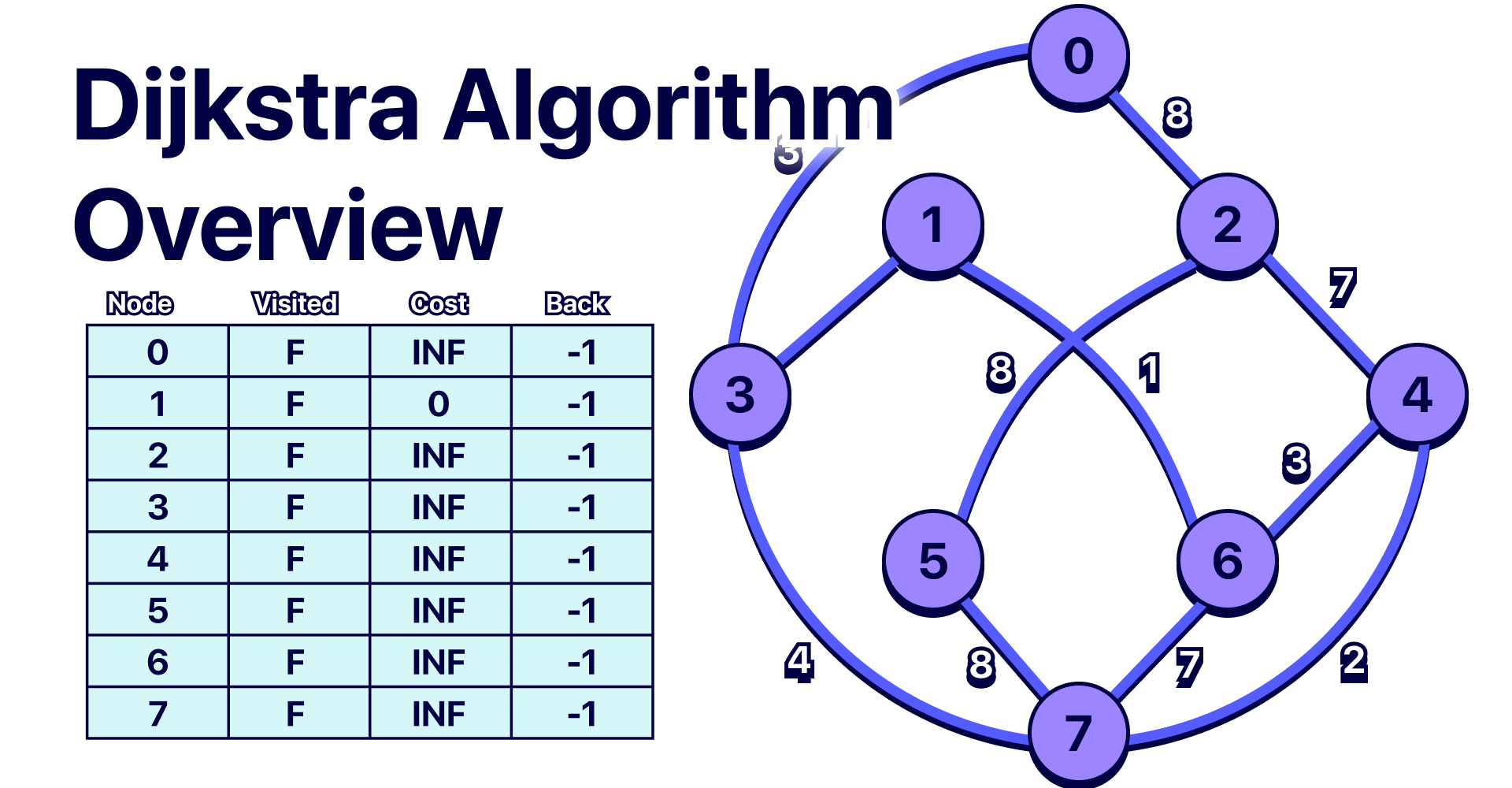 |
| 26 | + |
| 27 | +## Pseudocode for Dijkstra's Algorithm |
| 28 | + |
| 29 | +Here is the pseudocode for Dijkstra's Algorithm: |
| 30 | + |
| 31 | +``` |
| 32 | +function Dijkstra(Graph, source): |
| 33 | + create vertex set Q |
| 34 | +
|
| 35 | + for each vertex v in Graph: |
| 36 | + dist[v] ← INFINITY |
| 37 | + prev[v] ← UNDEFINED |
| 38 | + add v to Q |
| 39 | + dist[source] ← 0 |
| 40 | + |
| 41 | + while Q is not empty: |
| 42 | + u ← vertex in Q with min dist[u] |
| 43 | + remove u from Q |
| 44 | +
|
| 45 | + for each neighbor v of u: |
| 46 | + alt ← dist[u] + length(u, v) |
| 47 | + if alt < dist[v]: |
| 48 | + dist[v] ← alt |
| 49 | + prev[v] ← u |
| 50 | +
|
| 51 | + return dist[], prev[] |
| 52 | +``` |
| 53 | + |
| 54 | +## Implementing Dijkstra's Algorithm |
| 55 | + |
| 56 | +### Python Implementation |
| 57 | + |
| 58 | +```python |
| 59 | +import heapq |
| 60 | + |
| 61 | +def dijkstra(graph, start): |
| 62 | + priority_queue = [(0, start)] |
| 63 | + distances = {vertex: float('infinity') for vertex in graph} |
| 64 | + distances[start] = 0 |
| 65 | + previous_nodes = {vertex: None for vertex in graph} |
| 66 | + |
| 67 | + while priority_queue: |
| 68 | + current_distance, current_vertex = heapq.heappop(priority_queue) |
| 69 | + |
| 70 | + if current_distance > distances[current_vertex]: |
| 71 | + continue |
| 72 | + |
| 73 | + for neighbor, weight in graph[current_vertex].items(): |
| 74 | + distance = current_distance + weight |
| 75 | + |
| 76 | + if distance < distances[neighbor]: |
| 77 | + distances[neighbor] = distance |
| 78 | + previous_nodes[neighbor] = current_vertex |
| 79 | + heapq.heappush(priority_queue, (distance, neighbor)) |
| 80 | + |
| 81 | + return distances, previous_nodes |
| 82 | + |
| 83 | +def shortest_path(graph, start, goal): |
| 84 | + distances, previous_nodes = dijkstra(graph, start) |
| 85 | + path = [] |
| 86 | + while goal: |
| 87 | + path.append(goal) |
| 88 | + goal = previous_nodes[goal] |
| 89 | + return path[::-1] |
| 90 | + |
| 91 | +graph = { |
| 92 | + 'A': {'B': 1, 'C': 4}, |
| 93 | + 'B': {'A': 1, 'C': 2, 'D': 5}, |
| 94 | + 'C': {'A': 4, 'B': 2, 'D': 1}, |
| 95 | + 'D': {'B': 5, 'C': 1} |
| 96 | +} |
| 97 | + |
| 98 | +print(shortest_path(graph, 'A', 'D')) |
| 99 | +``` |
| 100 | + |
| 101 | +### Java Implementation |
| 102 | + |
| 103 | +```java |
| 104 | +import java.util.*; |
| 105 | + |
| 106 | +public class Dijkstra { |
| 107 | + |
| 108 | + public static void dijkstra(Map<String, Map<String, Integer>> graph, String start) { |
| 109 | + PriorityQueue<Node> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(node -> node.distance)); |
| 110 | + Map<String, Integer> distances = new HashMap<>(); |
| 111 | + Map<String, String> previousNodes = new HashMap<>(); |
| 112 | + |
| 113 | + for (String vertex : graph.keySet()) { |
| 114 | + distances.put(vertex, Integer.MAX_VALUE); |
| 115 | + previousNodes.put(vertex, null); |
| 116 | + } |
| 117 | + distances.put(start, 0); |
| 118 | + priorityQueue.add(new Node(start, 0)); |
| 119 | + |
| 120 | + while (!priorityQueue.isEmpty()) { |
| 121 | + Node current = priorityQueue.poll(); |
| 122 | + |
| 123 | + if (current.distance > distances.get(current.name)) { |
| 124 | + continue; |
| 125 | + } |
| 126 | + |
| 127 | + for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> neighbor : graph.get(current.name).entrySet()) { |
| 128 | + int distance = current.distance + neighbor.getValue(); |
| 129 | + |
| 130 | + if (distance < distances.get(neighbor.getKey())) { |
| 131 | + distances.put(neighbor.getKey(), distance); |
| 132 | + previousNodes.put(neighbor.getKey(), current.name); |
| 133 | + priorityQueue.add(new Node(neighbor.getKey(), distance)); |
| 134 | + } |
| 135 | + } |
| 136 | + } |
| 137 | + |
| 138 | + for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : distances.entrySet()) { |
| 139 | + System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " : " + entry.getValue()); |
| 140 | + } |
| 141 | + } |
| 142 | + |
| 143 | + public static List<String> shortestPath(Map<String, Map<String, Integer>> graph, String start, String goal) { |
| 144 | + dijkstra(graph, start); |
| 145 | + List<String> path = new ArrayList<>(); |
| 146 | + for (String at = goal; at != null; at = previousNodes.get(at)) { |
| 147 | + path.add(at); |
| 148 | + } |
| 149 | + Collections.reverse(path); |
| 150 | + return path; |
| 151 | + } |
| 152 | + |
| 153 | + public static void main(String[] args) { |
| 154 | + Map<String, Map<String, Integer>> graph = new HashMap<>(); |
| 155 | + graph.put("A", Map.of("B", 1, "C", 4)); |
| 156 | + graph.put("B", Map.of("A", 1, "C", 2, "D", 5)); |
| 157 | + graph.put("C", Map.of("A", 4, "B", 2, "D", 1)); |
| 158 | + graph.put("D", Map.of("B", 5, "C", 1)); |
| 159 | + |
| 160 | + System.out.println(shortestPath(graph, "A", "D")); |
| 161 | + } |
| 162 | + |
| 163 | + static class Node { |
| 164 | + String name; |
| 165 | + int distance; |
| 166 | + |
| 167 | + Node(String name, int distance) { |
| 168 | + this.name = name; |
| 169 | + this.distance = distance; |
| 170 | + } |
| 171 | + } |
| 172 | +} |
| 173 | +``` |
| 174 | + |
| 175 | +### C++ Implementation |
| 176 | + |
| 177 | +```cpp |
| 178 | +#include <iostream> |
| 179 | +#include <vector> |
| 180 | +#include <unordered_map> |
| 181 | +#include <queue> |
| 182 | +#include <stack> |
| 183 | +#include <limits> |
| 184 | +#include <algorithm> |
| 185 | + |
| 186 | +using namespace std; |
| 187 | + |
| 188 | +typedef pair<int, int> Node; |
| 189 | +typedef unordered_map<string, unordered_map<string, int>> Graph; |
| 190 | + |
| 191 | +unordered_map<string, int> dijkstra(const Graph& graph, const string& start, unordered_map<string, string>& previousNodes) { |
| 192 | + unordered_map<string, int> distances; |
| 193 | + for (const auto& node : graph) { |
| 194 | + distances[node.first] = numeric_limits<int>::max(); |
| 195 | + } |
| 196 | + distances[start] = 0; |
| 197 | + |
| 198 | + auto cmp = [](Node left, Node right) { return left.second > right.second; }; |
| 199 | + priority_queue<Node, vector<Node>, decltype(cmp)> priorityQueue(cmp); |
| 200 | + priorityQueue.push({start, 0}); |
| 201 | + |
| 202 | + while (!priorityQueue.empty()) { |
| 203 | + string current = priorityQueue.top().first; |
| 204 | + int currentDistance = priorityQueue.top().second; |
| 205 | + priorityQueue.pop(); |
| 206 | + |
| 207 | + if (currentDistance > distances[current]) { |
| 208 | + continue; |
| 209 | + } |
| 210 | + |
| 211 | + for (const auto& neighbor : graph.at(current)) { |
| 212 | + int distance = currentDistance + neighbor.second; |
| 213 | + if (distance < distances[neighbor.first]) { |
| 214 | + distances[neighbor.first] = distance; |
| 215 | + previousNodes[neighbor.first] = current; |
| 216 | + priorityQueue.push({neighbor.first, distance}); |
| 217 | + } |
| 218 | + } |
| 219 | + } |
| 220 | + |
| 221 | + return distances; |
| 222 | +} |
| 223 | + |
| 224 | +vector<string> shortestPath(const Graph& graph, const string& start, const string& goal) { |
| 225 | + unordered_map<string, string> previousNodes; |
| 226 | + dijkstra(graph, start, previousNodes); |
| 227 | + |
| 228 | + vector<string> path; |
| 229 | + for (string at = goal; !at.empty(); at = previousNodes[at]) { |
| 230 | + path.push_back(at); |
| 231 | + } |
| 232 | + reverse(path.begin(), path.end()); |
| 233 | + return path; |
| 234 | +} |
| 235 | + |
| 236 | +int main() { |
| 237 | + Graph graph = { |
| 238 | + {"A", {{"B", 1}, {"C", 4}}}, |
| 239 | + {"B", {{"A", 1}, {"C", 2}, {"D", 5}}}, |
| 240 | + {"C", {{"A", 4}, {"B", 2}, {"D", 1}}}, |
| 241 | + {"D", {{"B", 5}, {"C", 1}}} |
| 242 | + }; |
| 243 | + |
| 244 | + vector<string> path = shortestPath(graph, "A", "D"); |
| 245 | + for (const string& node : path) { |
| 246 | + cout << node << " "; |
| 247 | + } |
| 248 | + cout << endl; |
| 249 | + return 0; |
| 250 | +} |
| 251 | +``` |
| 252 | +
|
| 253 | +### JavaScript Implementation |
| 254 | +
|
| 255 | +```javascript |
| 256 | +function dijkstra(graph, start) { |
| 257 | + let distances = {}; |
| 258 | + let previousNodes = {}; |
| 259 | + let priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue(); |
| 260 | +
|
| 261 | + for (let vertex in graph) { |
| 262 | + if (vertex === start) { |
| 263 | + distances[vertex] = 0; |
| 264 | + priorityQueue.enqueue(vertex, 0); |
| 265 | + } else { |
| 266 | + |
| 267 | +
|
| 268 | + distances[vertex] = Infinity; |
| 269 | + priorityQueue.enqueue(vertex, Infinity); |
| 270 | + } |
| 271 | + previousNodes[vertex] = null; |
| 272 | + } |
| 273 | +
|
| 274 | + while (!priorityQueue.isEmpty()) { |
| 275 | + let currentVertex = priorityQueue.dequeue().element; |
| 276 | +
|
| 277 | + for (let neighbor in graph[currentVertex]) { |
| 278 | + let distance = distances[currentVertex] + graph[currentVertex][neighbor]; |
| 279 | + if (distance < distances[neighbor]) { |
| 280 | + distances[neighbor] = distance; |
| 281 | + previousNodes[neighbor] = currentVertex; |
| 282 | + priorityQueue.enqueue(neighbor, distance); |
| 283 | + } |
| 284 | + } |
| 285 | + } |
| 286 | +
|
| 287 | + return { distances, previousNodes }; |
| 288 | +} |
| 289 | +
|
| 290 | +function shortestPath(graph, start, goal) { |
| 291 | + let { distances, previousNodes } = dijkstra(graph, start); |
| 292 | + let path = []; |
| 293 | + while (goal) { |
| 294 | + path.push(goal); |
| 295 | + goal = previousNodes[goal]; |
| 296 | + } |
| 297 | + return path.reverse(); |
| 298 | +} |
| 299 | +
|
| 300 | +class PriorityQueue { |
| 301 | + constructor() { |
| 302 | + this.values = []; |
| 303 | + } |
| 304 | +
|
| 305 | + enqueue(element, priority) { |
| 306 | + this.values.push({ element, priority }); |
| 307 | + this.sort(); |
| 308 | + } |
| 309 | +
|
| 310 | + dequeue() { |
| 311 | + return this.values.shift(); |
| 312 | + } |
| 313 | +
|
| 314 | + isEmpty() { |
| 315 | + return this.values.length === 0; |
| 316 | + } |
| 317 | +
|
| 318 | + sort() { |
| 319 | + this.values.sort((a, b) => a.priority - b.priority); |
| 320 | + } |
| 321 | +} |
| 322 | +
|
| 323 | +let graph = { |
| 324 | + 'A': { 'B': 1, 'C': 4 }, |
| 325 | + 'B': { 'A': 1, 'C': 2, 'D': 5 }, |
| 326 | + 'C': { 'A': 4, 'B': 2, 'D': 1 }, |
| 327 | + 'D': { 'B': 5, 'C': 1 } |
| 328 | +}; |
| 329 | +
|
| 330 | +console.log(shortestPath(graph, 'A', 'D')); |
| 331 | +``` |
| 332 | + |
| 333 | +## Applications of Dijkstra's Algorithm |
| 334 | + |
| 335 | +- **Network Routing**: Finding the shortest path in network routing protocols such as OSPF. |
| 336 | +- **Map Services**: Computing the shortest routes in map services like Google Maps. |
| 337 | +- **Robotics**: Pathfinding in autonomous robots to navigate through environments. |
| 338 | +- **Game Development**: Pathfinding for game AI to navigate through game worlds. |
| 339 | + |
| 340 | +## Advanced Topics and Optimizations |
| 341 | + |
| 342 | +### Bidirectional Dijkstra |
| 343 | + |
| 344 | +Bidirectional Dijkstra runs two simultaneous searches: one forward from the source and one backward from the target. This can significantly speed up the search in large graphs. |
| 345 | + |
| 346 | +### Time Complexity |
| 347 | + |
| 348 | +The time complexity of Dijkstra's Algorithm depends on the data structures used: |
| 349 | +- Using a simple list: O(V^2) |
| 350 | +- Using a binary heap (priority queue): O((V + E) log V) |
| 351 | +- Using a Fibonacci heap: O(V log V + E) |
| 352 | + |
| 353 | +### Handling Negative Weights |
| 354 | + |
| 355 | +Dijkstra's Algorithm does not work with graphs that have negative weights. For such graphs, the Bellman-Ford Algorithm or Johnson's Algorithm can be used. |
| 356 | + |
| 357 | +### Path Reconstruction |
| 358 | + |
| 359 | +To reconstruct the shortest path from the source to a target node, we can backtrack from the target node using the `previous_nodes` dictionary. |
| 360 | + |
| 361 | +## Conclusion |
| 362 | + |
| 363 | +In this tutorial, we covered the fundamentals of Dijkstra's Algorithm, its implementation in Python, Java, C++, and JavaScript, and various optimizations and applications. Dijkstra's Algorithm is a powerful tool for finding the shortest path in graphs and is widely used in numerous domains. By mastering this algorithm, you can effectively solve a variety of shortest path problems in your projects. |
| 364 | + |
| 365 | +Happy coding! |
0 commit comments