|
| 1 | +--- |
| 2 | +id: flatten-a-multilevel-doubly-linked-list |
| 3 | +title: Flatten a Multilevel Doubly Linked List |
| 4 | +sidebar_label: 0430 - Flatten a Multilevel Doubly Linked List |
| 5 | +tags: |
| 6 | +- Linked List |
| 7 | +- Depth-First Search |
| 8 | +- Doubly-Linked List |
| 9 | +description: "This is a solution to the Flatten a Multilevel Doubly Linked List problem on LeetCode." |
| 10 | +--- |
| 11 | + |
| 12 | +## Problem Description |
| 13 | +You are given a doubly linked list, which contains nodes that have a next pointer, a previous pointer, and an additional child pointer. This child pointer may or may not point to a separate doubly linked list, also containing these special nodes. These child lists may have one or more children of their own, and so on, to produce a multilevel data structure as shown in the example below. |
| 14 | + |
| 15 | +Given the head of the first level of the list, flatten the list so that all the nodes appear in a single-level, doubly linked list. Let curr be a node with a child list. The nodes in the child list should appear after curr and before curr.next in the flattened list. |
| 16 | + |
| 17 | +Return the head of the flattened list. The nodes in the list must have all of their child pointers set to null. |
| 18 | +### Examples |
| 19 | + |
| 20 | +**Example 1:** |
| 21 | +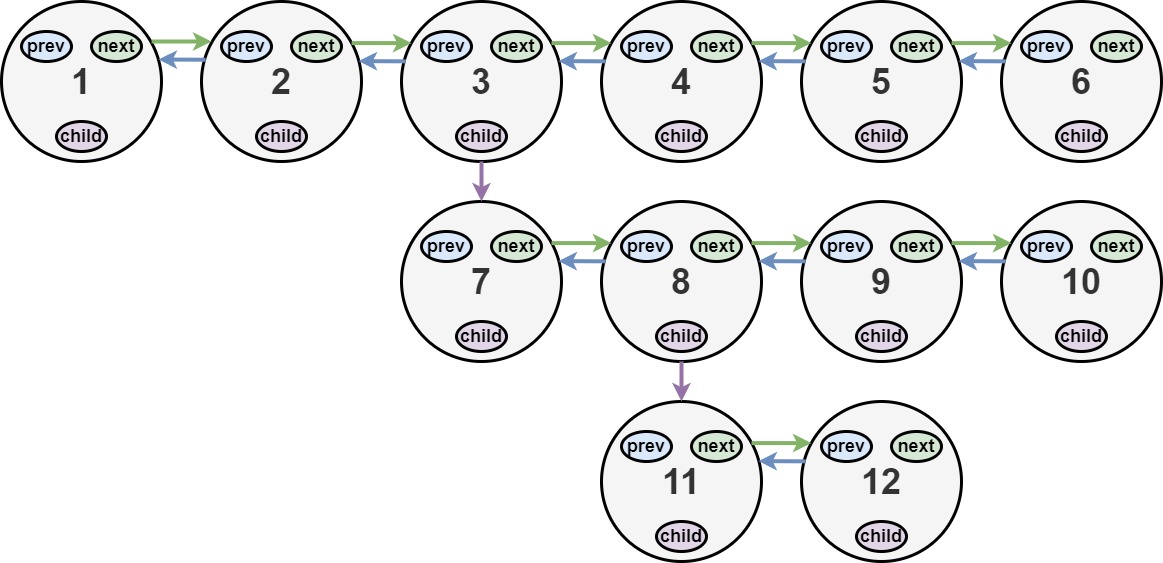 |
| 22 | +``` |
| 23 | +Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5,6,null,null,null,7,8,9,10,null,null,11,12] |
| 24 | +Output: [1,2,3,7,8,11,12,9,10,4,5,6] |
| 25 | +Explanation: The multilevel linked list in the input is shown. |
| 26 | +``` |
| 27 | +###### After flattening the multilevel linked list it becomes: |
| 28 | + |
| 29 | + |
| 30 | +**Example 2:** |
| 31 | + |
| 32 | +``` |
| 33 | +Input: head = [1,2,null,3] |
| 34 | +Output: [1,3,2] |
| 35 | +Explanation: The multilevel linked list in the input is shown. |
| 36 | +``` |
| 37 | +**Example 3:** |
| 38 | +``` |
| 39 | +Input: head = [] |
| 40 | +Output: [] |
| 41 | +Explanation: There could be empty list in the input. |
| 42 | +``` |
| 43 | + |
| 44 | +### Constraints |
| 45 | +- The number of Nodes will not exceed 1000. |
| 46 | +- `1 <= Node.val <= 10^5` |
| 47 | + |
| 48 | +## Solution for Flatten a Multilevel Doubly Linked List |
| 49 | + |
| 50 | +### Approach |
| 51 | +- Recursively traverse the original linked list, pushing nodes into a vector in the order they are visited, considering child nodes first. |
| 52 | +- Construct a flattened linked list from this vector, ensuring proper connections between nodes. |
| 53 | + |
| 54 | +<Tabs> |
| 55 | + <TabItem value="Solution" label="Solution"> |
| 56 | + |
| 57 | +#### Implementation |
| 58 | + |
| 59 | +```jsx live |
| 60 | +function Node(val, prev = null, next = null, child = null) { |
| 61 | + return { |
| 62 | + val: val, |
| 63 | + prev: prev, |
| 64 | + next: next, |
| 65 | + child: child |
| 66 | + }; |
| 67 | +} |
| 68 | + |
| 69 | +function flatten(head) { |
| 70 | + if (!head) return null; |
| 71 | + |
| 72 | + let stack = [head]; |
| 73 | + let dummy = new Node(0); |
| 74 | + let prev = dummy; |
| 75 | + |
| 76 | + while (stack.length > 0) { |
| 77 | + let current = stack.pop(); |
| 78 | + |
| 79 | + if (current.next) stack.push(current.next); |
| 80 | + if (current.child) { |
| 81 | + stack.push(current.child); |
| 82 | + current.child = null; |
| 83 | + } |
| 84 | + |
| 85 | + prev.next = current; |
| 86 | + current.prev = prev; |
| 87 | + prev = current; |
| 88 | + } |
| 89 | + |
| 90 | + dummy.next.prev = null; |
| 91 | + return dummy.next; |
| 92 | +} |
| 93 | + |
| 94 | +const input = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, null, null, null, 7, 8, 9, 10, null, null, 11, 12]; |
| 95 | + |
| 96 | +// Construct the linked list from the input array |
| 97 | +let head = new Node(input[0]); |
| 98 | +let current = head; |
| 99 | +let stack = [head]; |
| 100 | +for (let i = 1; i < input.length; i++) { |
| 101 | + if (input[i] === null) continue; |
| 102 | + let newNode = new Node(input[i]); |
| 103 | + current.next = newNode; |
| 104 | + newNode.prev = current; |
| 105 | + current = newNode; |
| 106 | + if (input[i] !== null) { |
| 107 | + stack.push(current); |
| 108 | + } |
| 109 | +} |
| 110 | + |
| 111 | +// Link child nodes |
| 112 | +for (let i = 0; i < input.length; i++) { |
| 113 | + if (input[i] === null) { |
| 114 | + let parent = stack.pop(); |
| 115 | + parent.child = parent.next; |
| 116 | + parent.next = null; |
| 117 | + if (parent.child) parent.child.prev = null; |
| 118 | + } |
| 119 | +} |
| 120 | + |
| 121 | +// Flatten the linked list |
| 122 | +let output = flatten(head); |
| 123 | + |
| 124 | +return ( |
| 125 | + <div> |
| 126 | + <p> |
| 127 | + <b>Input: </b>{JSON.stringify(input)} |
| 128 | + </p> |
| 129 | + <p> |
| 130 | + <b>Output:</b> {output ? output.toString() : 'null'} |
| 131 | + </p> |
| 132 | + </div> |
| 133 | +); |
| 134 | +``` |
| 135 | + |
| 136 | +### Code in Different Languages |
| 137 | + |
| 138 | +<Tabs> |
| 139 | + <TabItem value="JavaScript" label="JavaScript"> |
| 140 | + <SolutionAuthor name="@hiteshgahanolia"/> |
| 141 | + ```javascript |
| 142 | +var flatten = function(head) { |
| 143 | + const arr = []; |
| 144 | + const helper = (node) => { |
| 145 | + if(!node) return; |
| 146 | + arr.push(node); |
| 147 | + helper(node.child); |
| 148 | + helper(node.next); |
| 149 | + }; |
| 150 | + helper(head); |
| 151 | + for(let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { |
| 152 | + arr[i].prev = arr[i-1] || null; |
| 153 | + arr[i].next = arr[i+1] || null; |
| 154 | + arr[i].child = null; |
| 155 | + } |
| 156 | + return arr[0] || null; |
| 157 | +}; |
| 158 | + ``` |
| 159 | + </TabItem> |
| 160 | + <TabItem value="TypeScript" label="TypeScript"> |
| 161 | + <SolutionAuthor name="@hiteshgahanolia"/> |
| 162 | + ```typescript |
| 163 | + function flatten(head: Node | null): Node | null { |
| 164 | + if (!head) return null; |
| 165 | +
|
| 166 | + let pseudoHead: Node = new Node(0); |
| 167 | +
|
| 168 | + flattenDFS(pseudoHead, head); |
| 169 | +
|
| 170 | + pseudoHead.next.prev = null; |
| 171 | + return pseudoHead.next; |
| 172 | +}; |
| 173 | +
|
| 174 | +function flattenDFS(prev: Node, curr: Node | null): Node | null { |
| 175 | + if (!curr) return prev; |
| 176 | +
|
| 177 | + // Connect nodes |
| 178 | + curr.prev = prev; |
| 179 | + prev.next = curr; |
| 180 | +
|
| 181 | + let tempNext: Node | null = curr.next; |
| 182 | + let tail = flattenDFS(curr, curr.child); |
| 183 | +
|
| 184 | + // Clean child |
| 185 | + curr.child = null; |
| 186 | +
|
| 187 | + return flattenDFS(tail, tempNext); |
| 188 | +} |
| 189 | + ``` |
| 190 | + </TabItem> |
| 191 | + <TabItem value="Python" label="Python"> |
| 192 | + <SolutionAuthor name="@hiteshgahanolia"/> |
| 193 | + ```python |
| 194 | + class Solution: |
| 195 | + def flatten(self, head: 'Node') -> 'Node': |
| 196 | + def getTail(node): |
| 197 | + prev = None |
| 198 | + while node: |
| 199 | + _next = node.next |
| 200 | + if node.child: |
| 201 | + # ... <-> node <-> node.child <-> ... |
| 202 | + node.next = node.child |
| 203 | + node.child = None |
| 204 | + node.next.prev = node |
| 205 | + # get the end node of the node.child list |
| 206 | + prev = getTail(node.next) |
| 207 | + if _next: |
| 208 | + # ... <-> prev (end node) <-> _next (originally node.next) <-> ... |
| 209 | + _next.prev = prev |
| 210 | + prev.next = _next |
| 211 | + else: |
| 212 | + prev = node |
| 213 | + node = _next # loop through the list of nodes |
| 214 | + return prev # return end node |
| 215 | + |
| 216 | + getTail(head) |
| 217 | + return head |
| 218 | + ``` |
| 219 | + |
| 220 | + </TabItem> |
| 221 | + <TabItem value="Java" label="Java"> |
| 222 | + <SolutionAuthor name="@hiteshgahanolia"/> |
| 223 | +``` |
| 224 | +class Solution { |
| 225 | + |
| 226 | + Node prev = null; |
| 227 | + |
| 228 | + public Node flatten(Node head) { |
| 229 | + dfsHelper(head); |
| 230 | + return head; |
| 231 | + } |
| 232 | + |
| 233 | + public void dfsHelper(Node current) { |
| 234 | + if (current == null) return; |
| 235 | + // postorder traversal, going right first or next in this case |
| 236 | + dfsHelper(current.next); |
| 237 | + dfsHelper(current.child); |
| 238 | + // don't forget to set prev.prev pointer |
| 239 | + if (prev != null) prev.prev = current; |
| 240 | + // see explanation below |
| 241 | + current.next = prev; |
| 242 | + current.child = null; |
| 243 | + prev = current; |
| 244 | + } |
| 245 | +} |
| 246 | +``` |
| 247 | +</TabItem> |
| 248 | + <TabItem value="C++" label="C++"> |
| 249 | + <SolutionAuthor name="@hiteshgahanolia"/> |
| 250 | +
|
| 251 | +```cpp |
| 252 | +class Node { |
| 253 | +public: |
| 254 | + int val; |
| 255 | + Node* prev; |
| 256 | + Node* next; |
| 257 | + Node* child; |
| 258 | +}; |
| 259 | +
|
| 260 | + void solve(Node *head, vector<Node*>& ans, Node *curr) { |
| 261 | + if (curr == NULL) { |
| 262 | + return; |
| 263 | + } |
| 264 | + ans.push_back(curr); |
| 265 | + if (curr->child) { |
| 266 | + solve(head, ans, curr->child); |
| 267 | + } |
| 268 | + if (curr->next) { |
| 269 | + solve(head, ans, curr->next); |
| 270 | + } |
| 271 | + } |
| 272 | +
|
| 273 | + Node* flatten(Node* head) { |
| 274 | + if (!head) return nullptr; |
| 275 | + vector<Node*> ans; |
| 276 | + Node *curr = head; |
| 277 | + solve(head, ans, curr); |
| 278 | +
|
| 279 | + Node *newHead = NULL; |
| 280 | + curr = NULL; |
| 281 | +
|
| 282 | + for (int i = 0; i < ans.size(); i++) { |
| 283 | + if (curr == NULL) { |
| 284 | + curr = ans[i]; |
| 285 | + newHead = ans[i]; |
| 286 | + } else { |
| 287 | + curr->next = ans[i]; |
| 288 | + curr->next->prev = curr; |
| 289 | + curr->child = NULL; |
| 290 | + curr = curr->next; |
| 291 | + } |
| 292 | + } |
| 293 | + return newHead; |
| 294 | +} |
| 295 | + |
| 296 | +``` |
| 297 | + </TabItem> |
| 298 | + </Tabs> |
| 299 | + |
| 300 | +#### Complexity Analysis |
| 301 | +- Time Complexity: $ O(N)$ |
| 302 | + - Space Complexity: $ O(N)$ |
| 303 | +</TabItem> |
| 304 | +</Tabs> |
| 305 | + |
| 306 | +## References |
| 307 | + |
| 308 | +- **LeetCode Problem**: [Count Primes](https://leetcode.com/problems/count-primes/description/) |
| 309 | + |
| 310 | +- **Solution Link**: [LeetCode Solution](https://leetcode.com/problems/count-primes/solutions) |
| 311 | + |
0 commit comments