|
| 1 | +--- |
| 2 | +id: balanced-binary-tree |
| 3 | +title: Balanced Binary Tree Solution |
| 4 | +sidebar_label: 0110 Balanced Binary Tree |
| 5 | +tags: |
| 6 | + - Binary Tree |
| 7 | + - Depth-First Search |
| 8 | + - Recursion |
| 9 | + - LeetCode |
| 10 | + - C++ |
| 11 | + - Java |
| 12 | + - Python |
| 13 | +description: "This is a solution to the Balanced Binary Tree problem on LeetCode." |
| 14 | +--- |
| 15 | + |
| 16 | +## Problem Description |
| 17 | + |
| 18 | +Given a binary tree, determine if it is height-balanced. |
| 19 | + |
| 20 | +A height-balanced binary tree is defined as: |
| 21 | + |
| 22 | +- A binary tree in which the left and right subtrees of every node differ in height by no more than 1. |
| 23 | + |
| 24 | +### Examples |
| 25 | + |
| 26 | +**Example 1:** |
| 27 | + |
| 28 | +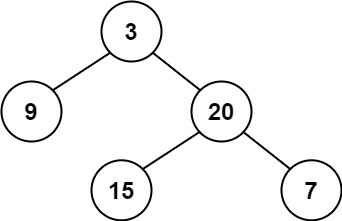 |
| 29 | + |
| 30 | +``` |
| 31 | +Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] |
| 32 | +Output: true |
| 33 | +``` |
| 34 | + |
| 35 | +**Example 2:** |
| 36 | + |
| 37 | +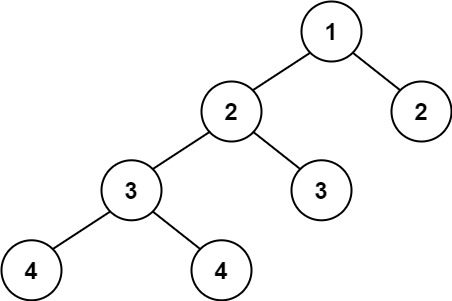 |
| 38 | +``` |
| 39 | +Input: root = [1,2,2,3,3,null,null,4,4] |
| 40 | +Output: false |
| 41 | +``` |
| 42 | + |
| 43 | +**Example 3:** |
| 44 | + |
| 45 | +``` |
| 46 | +Input: root = [] |
| 47 | +Output: true |
| 48 | +``` |
| 49 | + |
| 50 | +### Constraints |
| 51 | + |
| 52 | +- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range `[0, 5000]`. |
| 53 | +- $ -10^4 <=$ Node.val $<= 10^4 $ |
| 54 | + |
| 55 | +--- |
| 56 | + |
| 57 | +## Solution for Balanced Binary Tree Problem |
| 58 | + |
| 59 | +<Tabs> |
| 60 | + <tabItem value="Recursive" label="Recursive"> |
| 61 | + |
| 62 | +### Approach 1: Top-Down |
| 63 | + |
| 64 | +#### Intuition |
| 65 | + |
| 66 | +This method checks whether the tree is balanced strictly according to the definition of a balanced binary tree: the difference between the heights of the two subtrees is not greater than 1, and both the left and right subtrees are also balanced. With the helper function depth(), we can easily write the code. |
| 67 | + |
| 68 | +#### Implementation |
| 69 | + |
| 70 | +Implement a helper function `depth(root)` that returns the depth of the tree rooted at root. |
| 71 | +Check if the absolute difference between the depths of the left and right subtrees is not greater than 1. |
| 72 | +Recursively check if both the left and right subtrees are balanced. |
| 73 | +Return true if the tree is balanced, otherwise return false. |
| 74 | + |
| 75 | +#### Code in Different Languages |
| 76 | + |
| 77 | +<Tabs> |
| 78 | + <TabItem value="Java" label="Java" default> |
| 79 | + <SolutionAuthor name="@Vipullakum007"/> |
| 80 | + ```java |
| 81 | + class Solution { |
| 82 | + public int depth(TreeNode root) { |
| 83 | + if (root == null) return 0; |
| 84 | + return Math.max(depth(root.left), depth(root.right)) + 1; |
| 85 | + } |
| 86 | + |
| 87 | + public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) { |
| 88 | + if (root == null) return true; |
| 89 | + |
| 90 | + int left = depth(root.left); |
| 91 | + int right = depth(root.right); |
| 92 | + |
| 93 | + return Math.abs(left - right) <= 1 && isBalanced(root.left) && isBalanced(root.right); |
| 94 | + } |
| 95 | + } |
| 96 | + ``` |
| 97 | + |
| 98 | + </TabItem> |
| 99 | + <TabItem value="Python" label="Python"> |
| 100 | + <SolutionAuthor name="@Vipullakum007"/> |
| 101 | + ```python |
| 102 | + class Solution: |
| 103 | + def depth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int: |
| 104 | + if root is None: |
| 105 | + return 0 |
| 106 | + return max(self.depth(root.left), self.depth(root.right)) + 1 |
| 107 | + |
| 108 | + def isBalanced(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool: |
| 109 | + if root is None: |
| 110 | + return True |
| 111 | + |
| 112 | + left = self.depth(root.left) |
| 113 | + right = self.depth(root.right) |
| 114 | + |
| 115 | + return abs(left - right) <= 1 and self.isBalanced(root.left) and self.isBalanced(root.right) |
| 116 | + ``` |
| 117 | + |
| 118 | + </TabItem> |
| 119 | + <TabItem value="C++" label="C++"> |
| 120 | + <SolutionAuthor name="@Vipullakum007"/> |
| 121 | + ```cpp |
| 122 | + class Solution { |
| 123 | + public: |
| 124 | + int depth(TreeNode* root) { |
| 125 | + if (root == nullptr) return 0; |
| 126 | + return max(depth(root->left), depth(root->right)) + 1; |
| 127 | + } |
| 128 | + |
| 129 | + bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) { |
| 130 | + if (root == nullptr) return true; |
| 131 | + |
| 132 | + int left = depth(root->left); |
| 133 | + int right = depth(root->right); |
| 134 | + |
| 135 | + return abs(left - right) <= 1 && isBalanced(root->left) && isBalanced(root->right); |
| 136 | + } |
| 137 | + }; |
| 138 | + ``` |
| 139 | + |
| 140 | + </TabItem> |
| 141 | +</Tabs> |
| 142 | + |
| 143 | +#### Complexity Analysis |
| 144 | + |
| 145 | +- **Time Complexity**: O(n log n) in the worst case where n is the number of nodes in the tree. We visit each node once, and for each node, we calculate its depth. Since the depth calculation involves traversing the subtree, the overall time complexity is O(n log n). |
| 146 | +- **Space Complexity**: O(n) for the recursive call stack. |
| 147 | + |
| 148 | +</tabItem> |
| 149 | +<tabItem value="bottomup" label="Bottom-Up"> |
| 150 | + |
| 151 | +### Approach 2: Bottom-Up |
| 152 | + |
| 153 | +#### Intuition |
| 154 | + |
| 155 | +The second method is based on DFS. Instead of calling depth() explicitly for each child node, we return the height of the current node in DFS recursion. When the subtree of the current node (inclusive) is balanced, the function dfsHeight() returns a non-negative value as the height. Otherwise, -1 is returned. According to the left height and right height of the two children, the parent node could check if the subtree is balanced and decide its return value. |
| 156 | + |
| 157 | +#### Implementation |
| 158 | + |
| 159 | +Implement a helper function dfsHeight(root) that returns the height of the tree rooted at root. |
| 160 | +If the subtree rooted at root is balanced, return its height. Otherwise, return -1. |
| 161 | +Check if the returned height is -1 to determine if the tree is balanced. |
| 162 | + |
| 163 | +#### Code in Different Languages |
| 164 | + |
| 165 | +<Tabs> |
| 166 | + <TabItem value="Java" label="Java"> |
| 167 | + <SolutionAuthor name="@Vipullakum007"/> |
| 168 | + ```java |
| 169 | + class Solution { |
| 170 | + public int dfsHeight(TreeNode root) { |
| 171 | + if (root == null) return 0; |
| 172 | + |
| 173 | + int leftHeight = dfsHeight(root.left); |
| 174 | + if (leftHeight == -1) return -1; |
| 175 | + int rightHeight = dfsHeight(root.right); |
| 176 | + if (rightHeight == -1) return -1; |
| 177 | + |
| 178 | + if (Math.abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1) return -1; |
| 179 | + return Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1; |
| 180 | + } |
| 181 | + |
| 182 | + public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) { |
| 183 | + return dfsHeight(root) != -1; |
| 184 | + } |
| 185 | + } |
| 186 | + ``` |
| 187 | + |
| 188 | + </TabItem> |
| 189 | + <TabItem value="Python" label="Python"> |
| 190 | + <SolutionAuthor name="@Vipullakum007"/> |
| 191 | + ```python |
| 192 | + class Solution: |
| 193 | + def dfsHeight(self, root: TreeNode) -> int: |
| 194 | + if root is None: |
| 195 | + return 0 |
| 196 | + |
| 197 | + leftHeight = self.dfsHeight(root.left) |
| 198 | + if leftHeight == -1: |
| 199 | + return -1 |
| 200 | + right |
| 201 | + |
| 202 | + Height = self.dfsHeight(root.right) |
| 203 | + if rightHeight == -1: |
| 204 | + return -1 |
| 205 | + |
| 206 | + if abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1: |
| 207 | + return -1 |
| 208 | + return max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1 |
| 209 | + |
| 210 | + def isBalanced(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool: |
| 211 | + return self.dfsHeight(root) != -1 |
| 212 | + ``` |
| 213 | + |
| 214 | + </TabItem> |
| 215 | + <TabItem value="C++" label="C++"> |
| 216 | + <SolutionAuthor name="@Vipullakum007"/> |
| 217 | + ```cpp |
| 218 | + class Solution { |
| 219 | + public: |
| 220 | + int dfsHeight(TreeNode* root) { |
| 221 | + if (root == nullptr) return 0; |
| 222 | + |
| 223 | + int leftHeight = dfsHeight(root->left); |
| 224 | + if (leftHeight == -1) return -1; |
| 225 | + int rightHeight = dfsHeight(root->right); |
| 226 | + if (rightHeight == -1) return -1; |
| 227 | + |
| 228 | + if (abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1) return -1; |
| 229 | + return max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1; |
| 230 | + } |
| 231 | + |
| 232 | + bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) { |
| 233 | + return dfsHeight(root) != -1; |
| 234 | + } |
| 235 | + }; |
| 236 | + ``` |
| 237 | + |
| 238 | + </TabItem> |
| 239 | +</Tabs> |
| 240 | + |
| 241 | +#### Complexity Analysis |
| 242 | + |
| 243 | +- **Time Complexity**: O(n) in the worst case where n is the number of nodes in the tree. Each node is visited once. |
| 244 | +- **Space Complexity**: O(n) for the recursive call stack. |
| 245 | + |
| 246 | +</tabItem> |
| 247 | +</Tabs> |
| 248 | + |
| 249 | +## References |
| 250 | + |
| 251 | +- **LeetCode Problem**: [Balanced Binary Tree](https://leetcode.com/problems/balanced-binary-tree/) |
| 252 | +- **Solution Link**: [LeetCode Solution](https://leetcode.com/problems/balanced-binary-tree/solution/) |
| 253 | +- **Authors GeeksforGeeks Profile:** [Vipul lakum](https://leetcode.com/u/vipul_lakum_02/) |
| 254 | + |
| 255 | + |
| 256 | +--- |
0 commit comments