|
| 1 | +--- |
| 2 | +id: kadane-algorithm |
| 3 | +title: Kadane’s Algorithm |
| 4 | +sidebar_label: Kadane’s Algorithm |
| 5 | +tags: [python, java, c++, javascript, programming, algorithms, subarray, array, tutorial, in-depth] |
| 6 | +description: In this tutorial, we will learn about Kadane’s Algorithm and its implementation in Python, Java, C++, and JavaScript with detailed explanations and examples. |
| 7 | +--- |
| 8 | + |
| 9 | +# Kadane’s Algorithm |
| 10 | +Kadane's algorithm is a greedy/dynamic programming algorithm that can be used on array problems to bring the time complexity down to |
| 11 | +O(n). It is used to calculate the maximum sum subarray ending at a particular position. |
| 12 | + |
| 13 | +## Problem Statement |
| 14 | +Given an integer array arr, find the contiguous subarray (containing at least one number) which has the largest sum and returns its sum. |
| 15 | + |
| 16 | +### Intuition |
| 17 | +The question above is asking us to find a group of contiguous values in an array that give the largest sum. We are then asked to return that sum. |
| 18 | +If we forget about Kadane's algorithm for a second, the brute force way to approach this would be to go through every single subarray and calculate the sum, while keeping track of a maximum sum. This will work but there is a lot of repeated work. For every iteration of our outer for loop, our inner loop does linear work. This makes the complexity |
| 19 | +𝑂(𝑛^2). |
| 20 | + |
| 21 | +## Brute Force Approach |
| 22 | + ```python |
| 23 | + def bruteForce(nums): |
| 24 | + maxSum = nums[0] |
| 25 | + for i in range(len(nums)): |
| 26 | + curSum = 0 |
| 27 | + for j in range(i, len(nums)): |
| 28 | + curSum += nums[j] |
| 29 | + maxSum = max(maxSum, curSum) |
| 30 | + return maxSum |
| 31 | +``` |
| 32 | +
|
| 33 | +## Optimized Approach - Kadane’s Algorithm |
| 34 | +The intuition of the algorithm is not to consider the subarray as a part of the answer if its sum is less than 0. A subarray with a sum less than 0 will always reduce our answer and so this type of subarray cannot be a part of the subarray with maximum sum. |
| 35 | +
|
| 36 | +Here, we will iterate the given array with a single loop and while iterating we will add the elements in a sum variable. Now, if at any point the sum becomes less than 0, we will set the sum as 0 as we are not going to consider any subarray with a negative sum. Among all the sums calculated, we will consider the maximum one. |
| 37 | +
|
| 38 | +Thus we can solve this problem with a single loop. |
| 39 | +
|
| 40 | +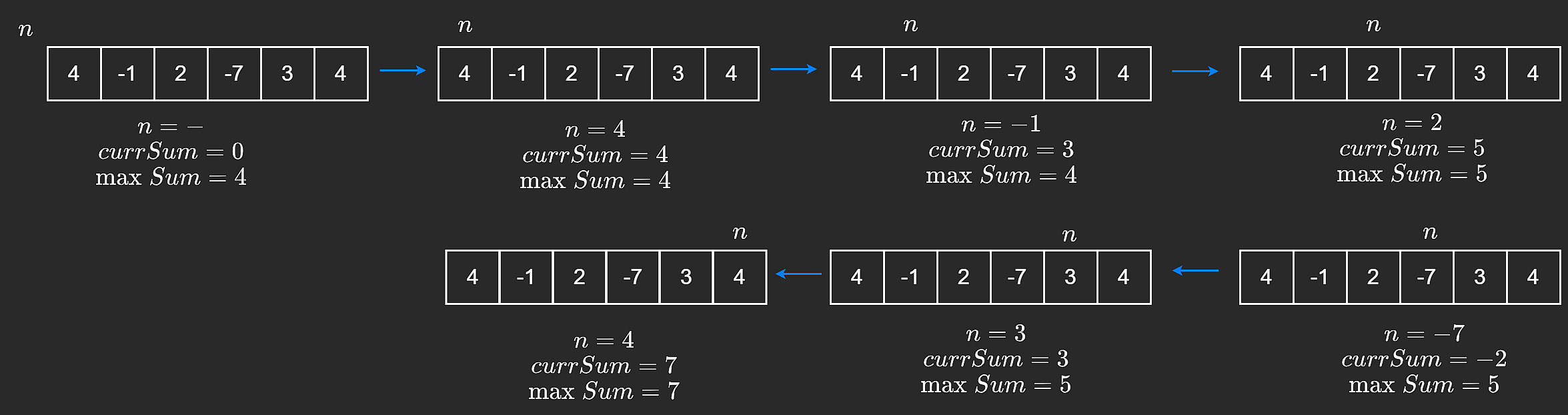 |
| 41 | +
|
| 42 | +## Pseudocode for Kadane’s Algorithm |
| 43 | +##### Initialize: |
| 44 | + - max_so_far = INT_MIN |
| 45 | + - max_ending_here = 0 |
| 46 | +
|
| 47 | + ##### Loop for each element of the array |
| 48 | +
|
| 49 | + - (a) max_ending_here = max_ending_here + a[i] |
| 50 | + - (b) if(max_so_far < max_ending_here) |
| 51 | + max_so_far = max_ending_here |
| 52 | + - (c) if(max_ending_here < 0) |
| 53 | + max_ending_here = 0 |
| 54 | +return max_so_far |
| 55 | +
|
| 56 | +
|
| 57 | +## Implementing Kadane’s Algorithm |
| 58 | +
|
| 59 | +### Python Implementation |
| 60 | +
|
| 61 | +```python |
| 62 | +import sys |
| 63 | +
|
| 64 | +def maxSubarraySum(arr, n): |
| 65 | + maxi = -sys.maxsize-1 # maximum sum |
| 66 | + sum = 0 |
| 67 | +
|
| 68 | + for i in range(n): |
| 69 | + sum += arr[i] |
| 70 | +
|
| 71 | + if sum > maxi: |
| 72 | + maxi = sum |
| 73 | +
|
| 74 | + # If sum < 0: discard the sum calculated |
| 75 | + if sum < 0: |
| 76 | + sum = 0 |
| 77 | +
|
| 78 | + # To consider the sum of the empty subarray |
| 79 | + # uncomment the following check: |
| 80 | +
|
| 81 | + #if maxi < 0: maxi = 0 |
| 82 | +
|
| 83 | + return maxi |
| 84 | +
|
| 85 | +``` |
| 86 | + |
| 87 | +### Java Implementation |
| 88 | + |
| 89 | +```java |
| 90 | + |
| 91 | +import java.util.*; |
| 92 | + |
| 93 | +public class Main { |
| 94 | + public static long maxSubarraySum(int[] arr, int n) { |
| 95 | + long maxi = Long.MIN_VALUE; // maximum sum |
| 96 | + long sum = 0; |
| 97 | + |
| 98 | + for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { |
| 99 | + |
| 100 | + sum += arr[i]; |
| 101 | + |
| 102 | + if (sum > maxi) { |
| 103 | + maxi = sum; |
| 104 | + } |
| 105 | + |
| 106 | + // If sum < 0: discard the sum calculated |
| 107 | + if (sum < 0) { |
| 108 | + sum = 0; |
| 109 | + } |
| 110 | + } |
| 111 | + |
| 112 | + // To consider the sum of the empty subarray |
| 113 | + // uncomment the following check: |
| 114 | + |
| 115 | + //if (maxi < 0) maxi = 0; |
| 116 | + |
| 117 | + return maxi; |
| 118 | + } |
| 119 | + |
| 120 | + public static void main(String args[]) { |
| 121 | + int[] arr = { -2, 1, -3, 4, -1, 2, 1, -5, 4}; |
| 122 | + int n = arr.length; |
| 123 | + long maxSum = maxSubarraySum(arr, n); |
| 124 | + System.out.println("The maximum subarray sum is: " + maxSum); |
| 125 | + |
| 126 | + } |
| 127 | + |
| 128 | +} |
| 129 | +``` |
| 130 | + |
| 131 | +### C++ Implementation |
| 132 | + |
| 133 | +```cpp |
| 134 | +long long maxSubarraySum(int arr[], int n) { |
| 135 | + long long maxi = LONG_MIN; // maximum sum |
| 136 | + long long sum = 0; |
| 137 | + |
| 138 | + for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { |
| 139 | + |
| 140 | + sum += arr[i]; |
| 141 | + |
| 142 | + if (sum > maxi) { |
| 143 | + maxi = sum; |
| 144 | + } |
| 145 | + |
| 146 | + // If sum < 0: discard the sum calculated |
| 147 | + if (sum < 0) { |
| 148 | + sum = 0; |
| 149 | + } |
| 150 | + } |
| 151 | + |
| 152 | + // To consider the sum of the empty subarray |
| 153 | + // uncomment the following check: |
| 154 | + |
| 155 | + //if (maxi < 0) maxi = 0; |
| 156 | + |
| 157 | + return maxi; |
| 158 | +} |
| 159 | + |
| 160 | +``` |
| 161 | +
|
| 162 | +### JavaScript Implementation |
| 163 | +
|
| 164 | +```javascript |
| 165 | +function maxSubarraySum(arr, n) { |
| 166 | + let maxi = Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER; // maximum sum |
| 167 | + let sum = 0; |
| 168 | +
|
| 169 | + for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) { |
| 170 | + sum += arr[i]; |
| 171 | +
|
| 172 | + if (sum > maxi) { |
| 173 | + maxi = sum; |
| 174 | + } |
| 175 | +
|
| 176 | + // If sum < 0: discard the sum calculated |
| 177 | + if (sum < 0) { |
| 178 | + sum = 0; |
| 179 | + } |
| 180 | + } |
| 181 | +
|
| 182 | + // To consider the sum of the empty subarray |
| 183 | + // uncomment the following check: |
| 184 | +
|
| 185 | + //if (maxi < 0) maxi = 0; |
| 186 | +
|
| 187 | + return maxi; |
| 188 | +} |
| 189 | +``` |
| 190 | + |
| 191 | +## Complexity Analysis |
| 192 | + #### Time Complexity : |
| 193 | + - $O(n)$ , We are using a single loop running N times. |
| 194 | + |
| 195 | + #### Space Complexity |
| 196 | + - $O(1)$ , as Only Variables are used. |
| 197 | +## Conclusion |
| 198 | +- Kadane's algorithm offers a straightforward and efficient approach to solving the maximum sum subarray problem, making it a fundamental technique in algorithmic problem-solving and data analysis. |
| 199 | + |
| 200 | + |
0 commit comments