|
| 1 | +--- |
| 2 | +id: searching |
| 3 | +title: Linear Search and Binary Search Algorithms |
| 4 | +sidebar_label: Linear Search and Binary Search |
| 5 | +tags: [python, java, c++, javascript, algorithms, search-algorithms, tutorial, in-depth] |
| 6 | +description: In this tutorial, we will explore linear search and binary search algorithms and their implementations in Python, Java, C++, and JavaScript with detailed explanations and examples. |
| 7 | +--- |
| 8 | + |
| 9 | +# Linear Search and Binary Search Algorithms |
| 10 | + |
| 11 | +In this tutorial, we will delve into two fundamental search algorithms: linear search and binary search. We'll discuss their concepts, implementations, time complexities, and applications in different programming languages including Python, Java, C++, and JavaScript. |
| 12 | + |
| 13 | +## 1. Linear Search |
| 14 | + |
| 15 | +Linear search, also known as sequential search, is a simple search algorithm that checks every element in a list or array until the target element is found or the end of the list is reached. It is straightforward but may be inefficient for large datasets. |
| 16 | + |
| 17 | + |
| 18 | + |
| 19 | +### Python Implementation |
| 20 | + |
| 21 | +```python |
| 22 | +def linear_search(arr, target): |
| 23 | + for i in range(len(arr)): |
| 24 | + if arr[i] == target: |
| 25 | + return i |
| 26 | + return -1 |
| 27 | + |
| 28 | +arr = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50] |
| 29 | +target = 30 |
| 30 | +print(linear_search(arr, target)) # Output: 2 |
| 31 | +``` |
| 32 | + |
| 33 | +### Java Implementation |
| 34 | + |
| 35 | +```java |
| 36 | +public class LinearSearch { |
| 37 | + |
| 38 | + public static int linearSearch(int[] arr, int target) { |
| 39 | + for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { |
| 40 | + if (arr[i] == target) { |
| 41 | + return i; |
| 42 | + } |
| 43 | + } |
| 44 | + return -1; |
| 45 | + } |
| 46 | + |
| 47 | + public static void main(String[] args) { |
| 48 | + int[] arr = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50}; |
| 49 | + int target = 30; |
| 50 | + System.out.println(linearSearch(arr, target)); // Output: 2 |
| 51 | + } |
| 52 | +} |
| 53 | +``` |
| 54 | + |
| 55 | +### C++ Implementation |
| 56 | + |
| 57 | +```cpp |
| 58 | +#include <iostream> |
| 59 | +#include <vector> |
| 60 | + |
| 61 | +int linearSearch(const std::vector<int>& arr, int target) { |
| 62 | + for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) { |
| 63 | + if (arr[i] == target) { |
| 64 | + return i; |
| 65 | + } |
| 66 | + } |
| 67 | + return -1; |
| 68 | +} |
| 69 | + |
| 70 | +int main() { |
| 71 | + std::vector<int> arr = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50}; |
| 72 | + int target = 30; |
| 73 | + std::cout << linearSearch(arr, target) << std::endl; // Output: 2 |
| 74 | + return 0; |
| 75 | +} |
| 76 | +``` |
| 77 | +
|
| 78 | +### JavaScript Implementation |
| 79 | +
|
| 80 | +```javascript |
| 81 | +function linearSearch(arr, target) { |
| 82 | + for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { |
| 83 | + if (arr[i] === target) { |
| 84 | + return i; |
| 85 | + } |
| 86 | + } |
| 87 | + return -1; |
| 88 | +} |
| 89 | +
|
| 90 | +let arr = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]; |
| 91 | +let target = 30; |
| 92 | +console.log(linearSearch(arr, target)); // Output: 2 |
| 93 | +``` |
| 94 | + |
| 95 | +## 2. Binary Search |
| 96 | + |
| 97 | +Binary search is a more efficient search algorithm for sorted arrays. It works by repeatedly dividing the search interval in half until the target element is found or the interval is empty. |
| 98 | + |
| 99 | +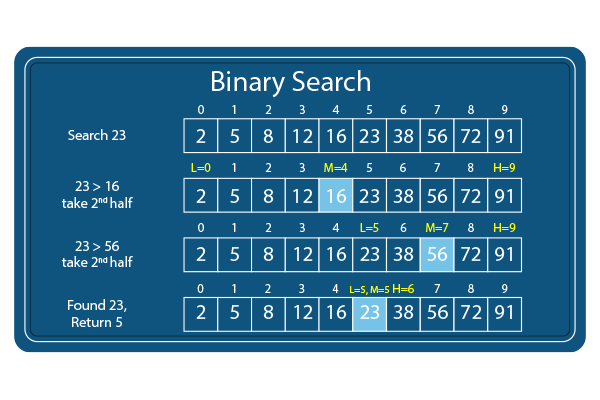 |
| 100 | + |
| 101 | +### Python Implementation |
| 102 | + |
| 103 | +```python |
| 104 | +def binary_search(arr, target): |
| 105 | + low = 0 |
| 106 | + high = len(arr) - 1 |
| 107 | + |
| 108 | + while low <= high: |
| 109 | + mid = (low + high) // 2 |
| 110 | + if arr[mid] == target: |
| 111 | + return mid |
| 112 | + elif arr[mid] < target: |
| 113 | + low = mid + 1 |
| 114 | + else: |
| 115 | + high = mid - 1 |
| 116 | + return -1 |
| 117 | + |
| 118 | +arr = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50] |
| 119 | +target = 30 |
| 120 | +print(binary_search(arr, target)) # Output: 2 |
| 121 | +``` |
| 122 | + |
| 123 | +### Java Implementation |
| 124 | + |
| 125 | +```java |
| 126 | +public class BinarySearch { |
| 127 | + |
| 128 | + public static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int target) { |
| 129 | + int low = 0; |
| 130 | + int high = arr.length - 1; |
| 131 | + |
| 132 | + while (low <= high) { |
| 133 | + int mid = (low + high) / 2; |
| 134 | + if (arr[mid] == target) { |
| 135 | + return mid; |
| 136 | + } else if (arr[mid] < target) { |
| 137 | + low = mid + 1; |
| 138 | + } else { |
| 139 | + high = mid - 1; |
| 140 | + } |
| 141 | + } |
| 142 | + return -1; |
| 143 | + } |
| 144 | + |
| 145 | + public static void main(String[] args) { |
| 146 | + int[] arr = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50}; |
| 147 | + int target = 30; |
| 148 | + System.out.println(binarySearch(arr, target)); // Output: 2 |
| 149 | + } |
| 150 | +} |
| 151 | +``` |
| 152 | + |
| 153 | +### C++ Implementation |
| 154 | + |
| 155 | +```cpp |
| 156 | +#include <iostream> |
| 157 | +#include <vector> |
| 158 | + |
| 159 | +int binarySearch(const std::vector<int>& arr, int target) { |
| 160 | + int low = 0; |
| 161 | + int high = arr.size() - 1; |
| 162 | + |
| 163 | + while (low <= high) { |
| 164 | + int mid = (low + high) / 2; |
| 165 | + if (arr[mid] == target) { |
| 166 | + return mid; |
| 167 | + } else if (arr[mid] < target) { |
| 168 | + low = mid + 1; |
| 169 | + } else { |
| 170 | + high = mid - 1; |
| 171 | + } |
| 172 | + } |
| 173 | + return -1; |
| 174 | +} |
| 175 | + |
| 176 | +int main() { |
| 177 | + std::vector<int> arr = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50}; |
| 178 | + int target = 30; |
| 179 | + std::cout << binarySearch(arr, target) << std::endl; // Output: 2 |
| 180 | + return 0; |
| 181 | +} |
| 182 | +``` |
| 183 | +
|
| 184 | +### JavaScript Implementation |
| 185 | +
|
| 186 | +```javascript |
| 187 | +function binarySearch(arr, target) { |
| 188 | + let low = 0; |
| 189 | + let high = arr.length - 1; |
| 190 | +
|
| 191 | + while (low <= high) { |
| 192 | + let mid = Math.floor((low + high) / 2); |
| 193 | + if (arr[mid] === target) { |
| 194 | + return mid; |
| 195 | + } else if (arr[mid] < target) { |
| 196 | + low = mid + 1; |
| 197 | + } else { |
| 198 | + high = mid - 1; |
| 199 | + } |
| 200 | + } |
| 201 | + return -1; |
| 202 | +} |
| 203 | +
|
| 204 | +let arr = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]; |
| 205 | +let target = 30; |
| 206 | +console.log(binarySearch(arr, target)); // Output: 2 |
| 207 | +``` |
| 208 | + |
| 209 | +## Time Complexity Analysis |
| 210 | + |
| 211 | +- **Linear Search**: |
| 212 | + - Best Case: $O(1)$ (when the target is found at the first position) |
| 213 | + - Worst Case: $O(n)$ (when the target is not present in the array or at the last position) |
| 214 | +- **Binary Search**: |
| 215 | + - Best Case: $O(1)$ (when the target is found at the middle position) |
| 216 | + - Worst Case: $O(log n)$ (when the target is not present in the array or at the last position) |
| 217 | + |
| 218 | +## Applications of Linear Search and Binary Search |
| 219 | + |
| 220 | +- **Linear Search**: Used in scenarios where the data is unsorted or small in size. |
| 221 | +- **Binary Search**: Ideal for searching in large sorted datasets, such as searching in databases or sorted arrays. |
| 222 | + |
| 223 | +## Conclusion |
| 224 | + |
| 225 | +In this tutorial, we explored linear search and binary search algorithms along with their implementations in Python, Java, C++, and JavaScript. Understanding these fundamental search algorithms is essential for solving various problems efficiently. |
0 commit comments